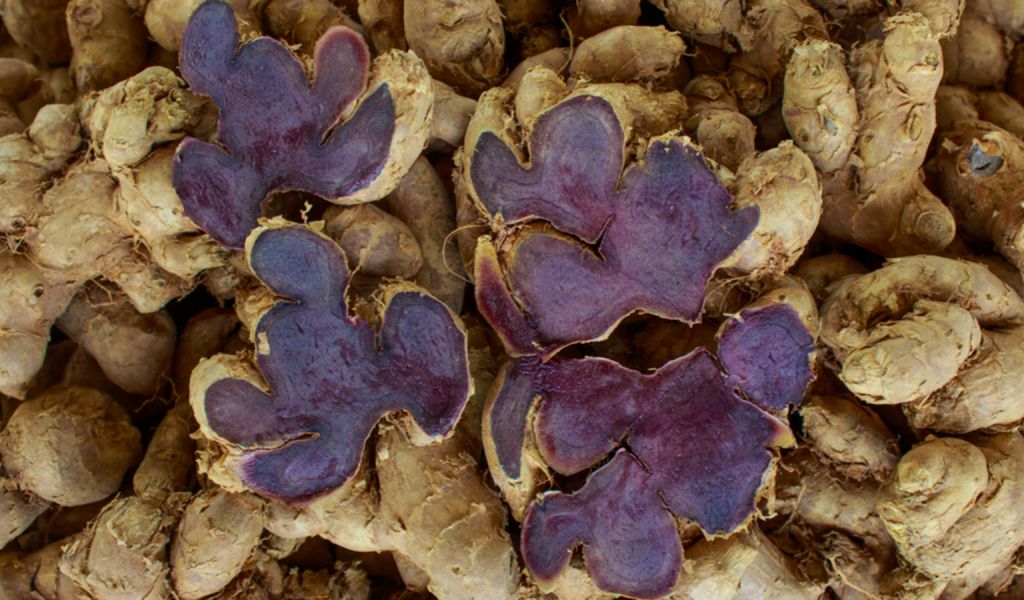
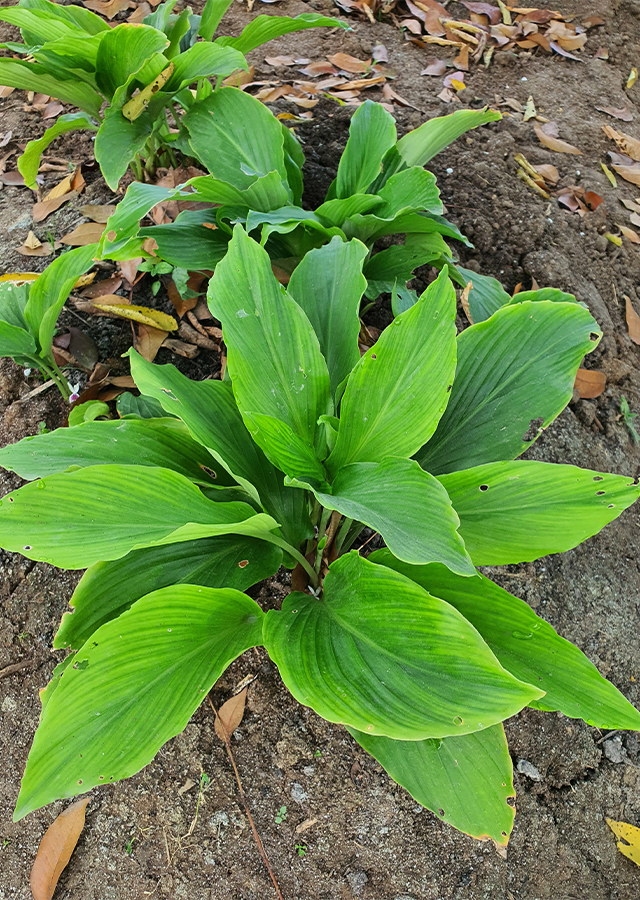
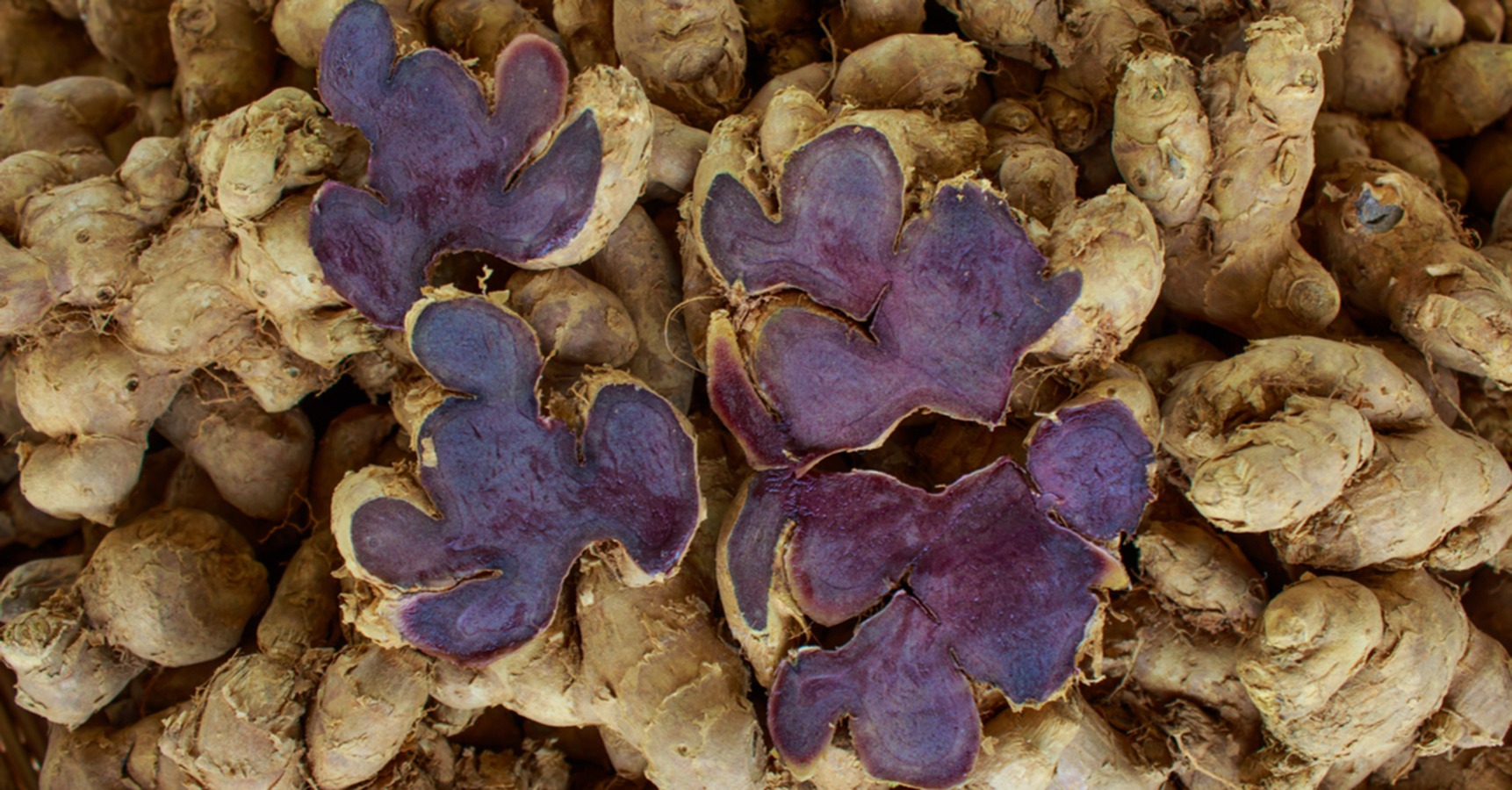
ຂີງດຳ
Black Ginger
Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker
ພືດ
ພືດລົ້ມລຸກ
ດອກໄມ້
Stahlianthus rubromarginatus S.Q.Tong
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ເປັນພືດທີ່ມີສັບພະຄູນເປັນຢາສະໝູນໄພ ສານສະກັດຈາກຂີງດຳມີປະສິດທີພາບໃນການຕ້ານເຊື້ອມາເລເຣຍ, ເຊື້ອຣາ ແລະ ໄມໂຄແບັກເທີເຣຍ, ຕ້ານການເກີດພະຍາດພູມແທ້ ແລະ ກ້ານການເກີດບາດແຜໃນກະເພາະອາຫານ. ເອົາຫົວມາຜະລິດເປັນຢາຮັກສາພະຍາດ ແລະ ບຳລູງຮ່າງກາຍ ແລະ ເຄື່ອງດືມ ໂດຍສະເພາະໃນກຸ່ມຜະລິດຕະພັນໂອທອບ ເປັນພືດທີ່ນິຍົມນຳມາປູກຕາມຄວາມເຊື້ອຂອງຊາວບ້ານເຜົ້າມົ້ງຖືວ່າຂີງດຳເປັນສະໝູນໄພປະຈຳເຜົ່າ ເຂົາເຈົ້ານຳໃຫ້ຖົງຕິດຕົວຕະຫຼອດເວລາເມື່ອມີການເດີ່ນທາງໄປໄກບ້ານ. ເມື່ອດ້ານທາງຂື້ນພູ ຫຼື ໄປເຮັດວຽກເມື່ອຍເພື່ອເພີ່ມພະລັງງານ, ຂັບນ້ຳປັດສະວະ, ແກ້ພະຍາດກະເພາະ ແລະ ປວດທ້ອງ.
ສັບພະຄູນໃນການຮັກສາພະຍາດມີດັ່ງນີ້: 1. ຊ່ວຍບຳລຸງຮ່າງກາຍຕົ້ມໃສ່ໄກ່, 2. ແກ້ປວດເມື່ອຍ ແລະ ຮັກສາອາການເໜືອຍລ້າ, 3. ຊ່ວຍກະຕຸ້ນສະມັດຕະພາບທາງເພດ, 4. ຊ່ວຍຂັບລົມໃນກະເພາະອາຫານ, 5. ແກ້ຈຸກສຽກປວດທ້ອງ, 6. ຂັບນ້ຳປັດສະວະ, 7. ບ໋ອງເຫຼົ້າເພື່ອດື່ມແກ້ມົດລູກພີການ ຫຼື ມົດລູກຢ້ອນ, 8. ຕົ້ມດື່ມແກ້ພະຍາດຕາແດງ, 9. ກະຕຸ້ນລະບົບປະສາດ, 10. ຮັກສາສົມດຸນຄວາມດັນເລືອດ, 11. ຊ່ວຍຂະຫຍາຍຫຼອດເລືອດຫົວໃຈ, 12. ພະຍາດເກົ້າ, 13. ຊ່ວຍຮັກສາພະຍາດກະເພາະອາຫານ, 14. ຊ່ວຍຮັກສາລະບົບການຍ່ອຍອາຫານໃຫ້ເກີດສົມດູນ, 15. ຮັກສາຜູ້ເປັນພະຍາດເບົາຫວານ ລົດລະດັບນ້ຳຕານໃນເລືອດ.
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ໂພຊະນາການ
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | N/A | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
Saensouk, S., Saensouk, P and Chanshotikul, N. 2017. Diversity and traditional uses of Zingiberaceae in Nong Khai Province, Thailand. KKU Sci. J. 45(3) 574-594.
Paiwan Sudwan, Kanokporn Saenphet, Supap Saenphet and Songkiet Suwansirikul. 2006. Effect of Kaempferia parviflora Wall. Ex. Baker on
Sexual Activity of Male Rats and its Toxicity. SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH Vol 37 (suppl 3)
Pitakpawasutthi, Y., Palanuvej, C., Ruangrungsi, N. 2018. Quality evaluation of Kaempferia parviflora rhizome with reference to 5,7-dimethoxyflavone. Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research 9(1):26-3.



