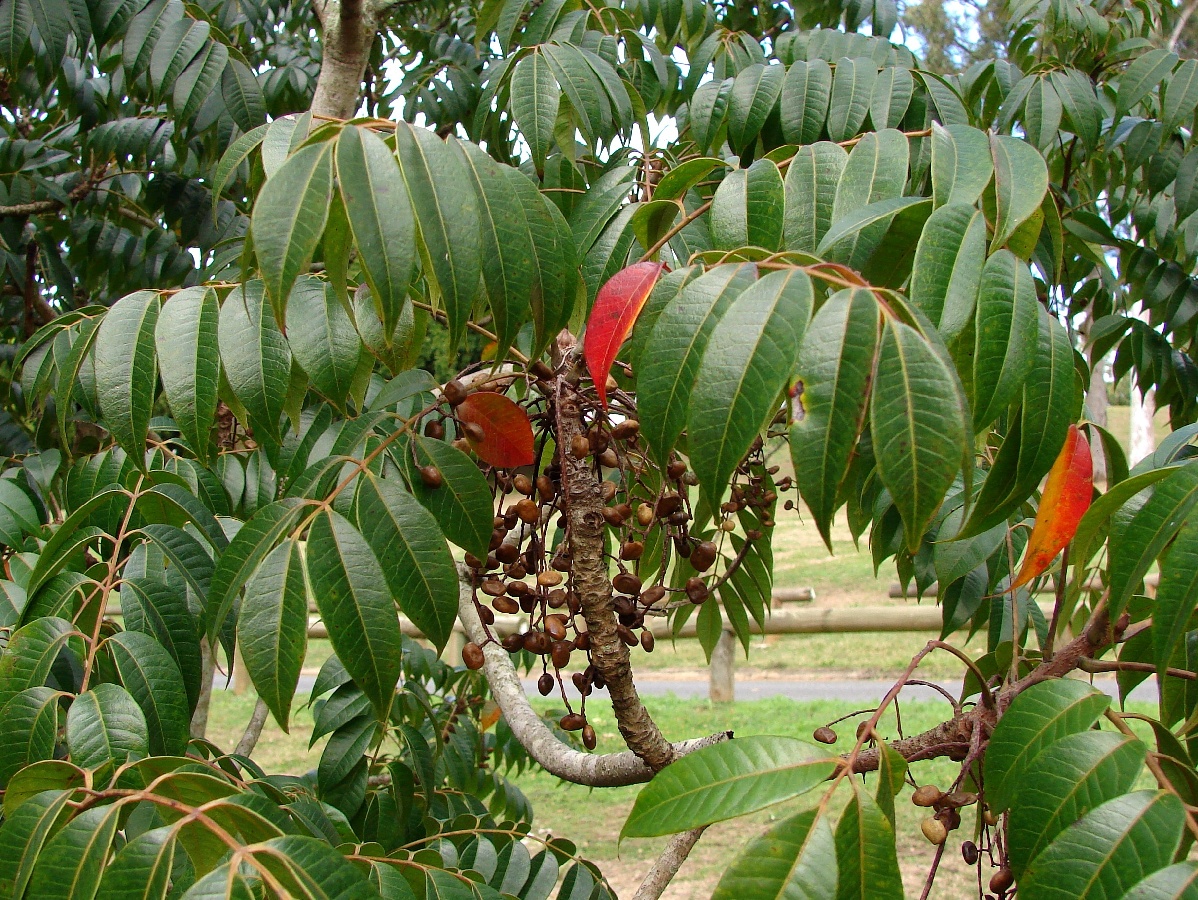
ໄມ້ເກັດລີນ
Wax Tree
Toxicodendron succedaneum (L.) Kuntze
ພືດ
ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ປາມ
Rhus succedanea var. japonica Engl.
Toxicodendron succedaneum var. succedaneum
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ສິ່ງປູກສ້າງ
ອາຫານ: ໝາກມີອາຊີດອ່ອນສາມາດກີນໄດ້. ແຕ່ມີການລາຍງານວ່າຄວນລະມັດລະວັງເນື່ອງຈາກຄວາມເປັນພິດໂດຍທົ່ວຂອງສາຍພັນ.
ຢາ: ເປັນຢາລ້າງສານພິດ, ຕ້ານເຊື້ອໄວຣັດ, ຮັກສານ້ຳບີ, ຮັກສາອາການໄຂ້ຂຶ້ນ, ພະຍາດຕາ. ໃຊ້ເປັນຢາລ້າງໜ້າທີ່ຖືກສານພິດ. ແຕ່ໃຊ້ດ້ວຍຄວາມລະມັດລະວັງເນື່ອງຈາກຕົ້ນໄມ້ນີ້ກໍ່ມີສານພິດຄືກັນ. ໝາກສາມາດໃຊ້ເພື່ອຮັກສາອາການເນົ່າເປື່ອຍຂອງຜິວໜັງ. ໄຂມັນຈະໝາກສາມາດໃຊ້ເພື່ອຮັກສາຜີວໜັງ ແລະ ຮົ່ມຢາ. ສານສະກັດຈາກໃບສາມາດຕ້ານເຊື້ອມະເຮັງ ແລະ ໄວຣັດໄດ້ດີ.
ການນຳໃຊ້ປະໂຫຍດອື່ນໆ: ໃບມີທາດປະສົມທານີນ 20%, ສາມາດເກັບໃນຊ່ວງລະດູໃບໄມ້ຫຼົ່ນເພື່ອໃຊ້ເປັນສີຍ້ອມຜ້າໄດ້ສີນ້ຳຕານ. ນ້ຳມັນສາມາດໃຊ້ເປັນສີເລັກເກີທາໄມ້. ຖືກໃຊ້ມາດົນໃນສີນລະປະຂອງຢີ່ປຸ່ນ ແລະ ເພື່ອແຕ້ມຮູບ ເຊີ່ງໄດ້ເກັບໄວ້ໃນບ່ອນຮົ່ມຈົນກວ່າເລັກເກີແຫ້ງ. ສີຍ້ອມຜ້າເປັນສີເຫຼືອງໄດ້ຈາກເນື້ອໄມ້. ໄຂມັນໄດ້ຈາກໝາກເພື່ອເຮັດໄທຂຽນໄດ້. ໝາກມີໄຂປະມານ 17%. ທາດອາຊິດໄຂມັນແມ່ນ 77%, ສະແຕຣິກອາຊິດ ແລະ ອາແຣກຊິດິກ 5%, ໄດອາຊິກ 6%, ໂອເຣອິກ ແລະ ໄລໂນເລອິກ 12%. ແກ່ນມີນ້ຳມັນໄກເຊີໄຣດ໌ 25%, ໂອເຣອິກ 47% ແລະ ໄລໂນເລອິກ 28%.
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ໂພຊະນາການ
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | N/A | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
Tanaka. T. & Nakao S. 1976. Tanaka's Cyclopedia of Edible Plants of the World. Keigaku Publishing; Tokyo
Gupta. B. L. 1945. Forest Flora of Chakrata, Dehra Dun and Saharanpur. Forest Research Institute Press
Manandhar. N. P. 2002. Plants and People of Nepal. Timber Press. Oregon.
Chopra. R. N., Nayar. S. L. and Chopra. I. C. 1986. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants (Including the Supplement). Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi.
Buchanan. R.. 1987. A Weavers Garden. McGraw-Hill Contemporary
