ເລກລຳດັບທີ: 56
ລະດັບການຮວບຮວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ຂໍ້ມູນລະອຽດ
ປັບປູງຄັ້ງລ່າສຸດ: 2026-02-11
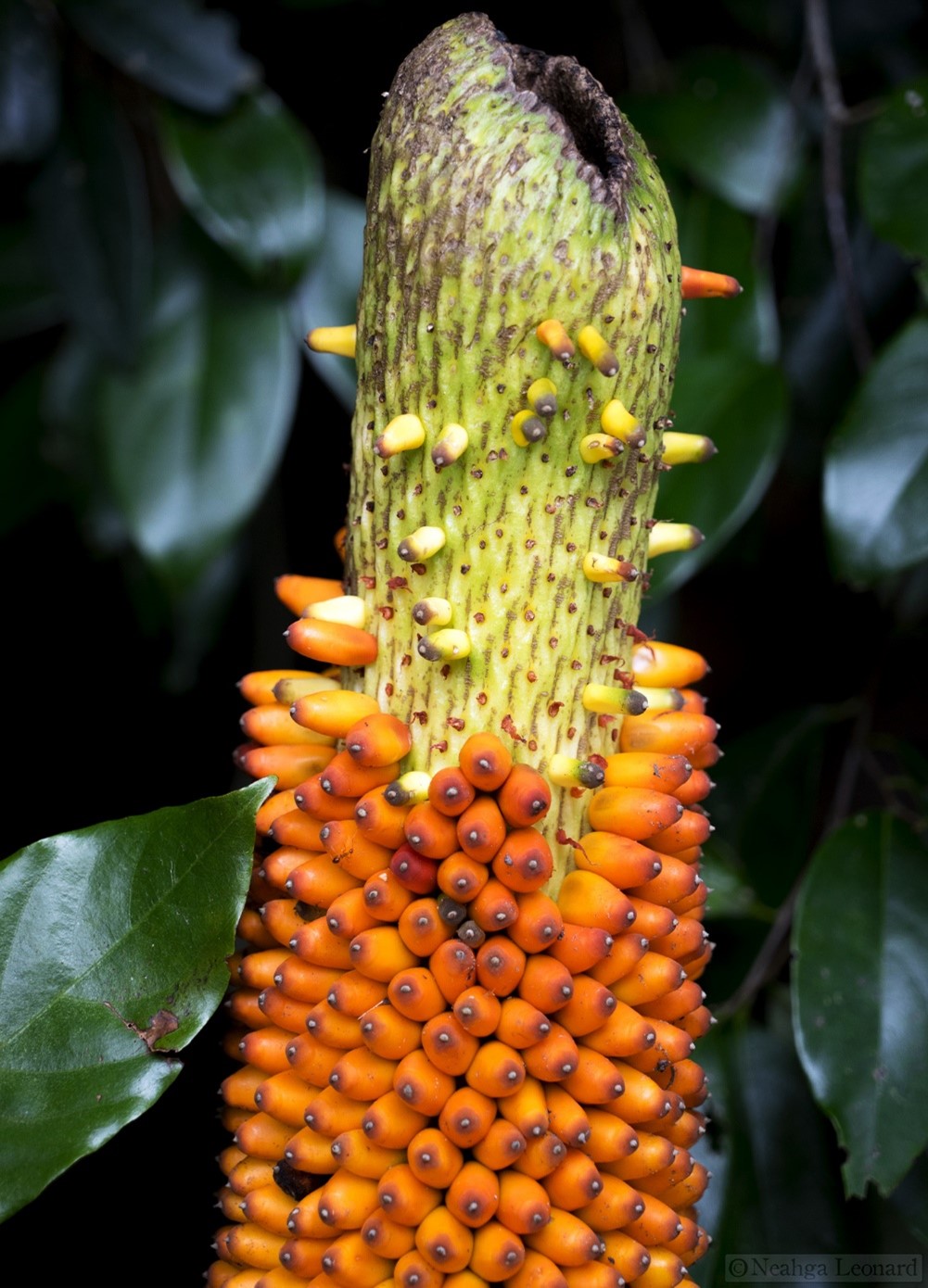
ຫົວກະບຸກ
Elephant Foot Yam
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson
ພືດ
ພືດລົ້ມລຸກ
ຜັກ ແລະ ພືດລົ້ມລຸກ
×
ຊື່ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ:
ຫົວດຸກເດືອ, ອີລອກໃຫຍ່, ອີລອກຄາງກົບ. ( Whitespot Giant Arum, Pungapung, Sweet-yam, Telinga-potato, Telingo-potato.)
ຊື່ພ້ອງ
:
Amorphophallus campanulatus Decne.
Amorphophallus campanulatus f. darnleyensis F.M.Bailey
Amorphophallus campanulatus subsp. blumei Prain
Amorphophallus campanulatus subsp. darnleyensis F.M.Bailey
Amorphophallus campanulatus var. blumei Prain
Amorphophallus chatty Andrews
Amorphophallus decurrens (Blanco) Kunth
Amorphophallus dixenii K.Larsen & S.S.Larsen
Amorphophallus dubius Blume
Amorphophallus giganteus Blume
Amorphophallus gigantiflorus Hayata
Amorphophallus malaccensis Ridl.
Amorphophallus microappendiculatus Engl.
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius subsp. campanulatus (Decne.) Sivad.
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius var. campanulatus Sivad.
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius var. paeoniifolius
Amorphophallus rex Prain
Amorphophallus rex Prain ex Hook.f.
Amorphophallus sativus Blume
Amorphophallus virosus N.E.Br.
Arum campanulatum Roxb.
Arum decurrens Blanco
Arum phalliferum Oken
Arum rumphii Gaudich.
Arum rumphii Oken
Candarum hookeri Schott
Candarum roxburghii Schott
Candarum rumphii Schott
Conophallus giganteus Schott
Conophallus giganteus Schott ex Miq.
Conophallus sativus (Blume) Schott
Dracontium paeoniifolium Dennst.
Dracontium polyphyllum Dennst.
Dracontium polyphyllum G.Forst.
Dunalia artensis Montrouz.
Hydrosme gigantiflora (Hayata) S.S.Ying
Kunda verrucosa Raf.
Plesmonium nobile Schott
Pythion campanulatum Mart.
Amorphophallus campanulatus f. darnleyensis F.M.Bailey
Amorphophallus campanulatus subsp. blumei Prain
Amorphophallus campanulatus subsp. darnleyensis F.M.Bailey
Amorphophallus campanulatus var. blumei Prain
Amorphophallus chatty Andrews
Amorphophallus decurrens (Blanco) Kunth
Amorphophallus dixenii K.Larsen & S.S.Larsen
Amorphophallus dubius Blume
Amorphophallus giganteus Blume
Amorphophallus gigantiflorus Hayata
Amorphophallus malaccensis Ridl.
Amorphophallus microappendiculatus Engl.
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius subsp. campanulatus (Decne.) Sivad.
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius var. campanulatus Sivad.
Amorphophallus paeoniifolius var. paeoniifolius
Amorphophallus rex Prain
Amorphophallus rex Prain ex Hook.f.
Amorphophallus sativus Blume
Amorphophallus virosus N.E.Br.
Arum campanulatum Roxb.
Arum decurrens Blanco
Arum phalliferum Oken
Arum rumphii Gaudich.
Arum rumphii Oken
Candarum hookeri Schott
Candarum roxburghii Schott
Candarum rumphii Schott
Conophallus giganteus Schott
Conophallus giganteus Schott ex Miq.
Conophallus sativus (Blume) Schott
Dracontium paeoniifolium Dennst.
Dracontium polyphyllum Dennst.
Dracontium polyphyllum G.Forst.
Dunalia artensis Montrouz.
Hydrosme gigantiflora (Hayata) S.S.Ying
Kunda verrucosa Raf.
Plesmonium nobile Schott
Pythion campanulatum Mart.
ຊື່ສະກຸນ:
Araceae
ຊະນິດໃກ້ຄຽງ:
ຫົວດອກເດືອກາບໂຄ້ງ/ ຫົວດອກເດືອກາບໂຄ້ງ
ຫົວດູກເດືອນົກ/ Kraus's Voodoo Lily
ອີລອກພູ/ Mekong Aroids
ຫົວດູກເດືອນົກ/ Kraus's Voodoo Lily
ອີລອກພູ/ Mekong Aroids
ບັນຍາຍລັກສະນະທາງພືດສາດ:
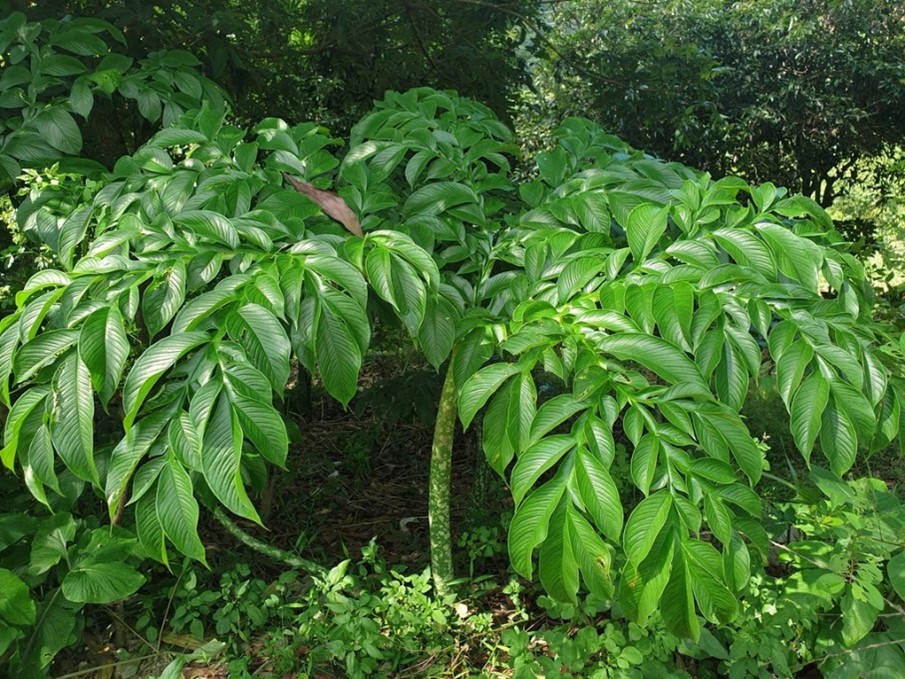
ພືດຊະນິດນີ້ມີຫົວສີນ້ຳຕານເຂັ້ມຮູບຄ້າຍຮູບກົງແປເລັກນ້ອຍ, ສູງປະມານ 20 ຊມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 30 ຊມ, ຫົວຈະມີຮອຍແຜອ້ອມເປັນວົງແຫວນ ເຊິ່ງເປັນຮອຍທີ່ເກີດຈາຫຮາກ. ໃນແຕ່ລະລະດູ ຫົວຈະແຕັກໜໍອອກມາຄ້າຍເຫງົ້າໜາ ຍາວປະມານ 10 ຊມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 4 ຊມ.
ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປພືດຊະນິດຈະມີໃບ 1 ຫາ 2 ໃບ. ກ້ານໃບ (petioles) ມີຜິວສີຂຽວອອ່ນໄປຈັນຮອດສີຂຽວເຂັ້ມ ຫຼື ສີຂຽວປົນດຳ, ມັກມີຈຸສີຂາວອ່ອນຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ ແລະ ນ້ອຍ ຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ, ຈຸດຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ມັກຈະຢູ່ລວມກັນຢູ ໂດຍສະເພາະບໍລິເວນໂຄນກ້ານໃ, ກ້ານໃບອາດຍາວຮອດ 2 ມ ແລະ ກວ້າງຮອດ 20 ຊມ, ໂດຍຜິວຈະມີລັກສະນະຍົ້້ນເລັກນ້ອຍ (ເປັນຮ່ອງຕື້ນ) ຫຼື ຄຸມດ້ວຍປຸ່ມແຫຼມນ້ອຍໆ.
ໃບມີລັກສະນະເປັນແສກຍາວ ແລະ ມີຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ຫຼາຍ, ກວ້າງປະມານ 3 ມ, ເສັ້ນກາງໃບຫຼັກມີລັກສະນະເປັນປີກ ອາດແຄບ ຫຼື ກວ້າງເກືແບຮອດໂຄນໃບ. ໃບຍ່ອຍຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ເທິງແຜ່ນໃບມີສີແຕກຕ່າງກັນ, ຜິວໃບດ້ານລຸ່ມມີສີຂຽວປານຫາງ ຫຼື ສີຂຽວອ່ອນ, ຜິວໃບດ້າເທິງມີສີຂຽວປານກາງ, ໃບຍ່ອຍມີຮູບຮ່າງທີ່ຫຼາກຫຼາຍແຕກຕ່າງກັນ ມີທັງຮູບກົມ, ຮູບໄຂ່, ຮູບໄຂ່ປີ້ນ, ຮູບຫອກ ຫຼື ຮູບຫອກປີ້ນ, ໃບຍ່ອຍຍາວ 3 ຫາ 35 ຊມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 2 ຫາ 12 ຊມ, ປາຍແຫຼມ.
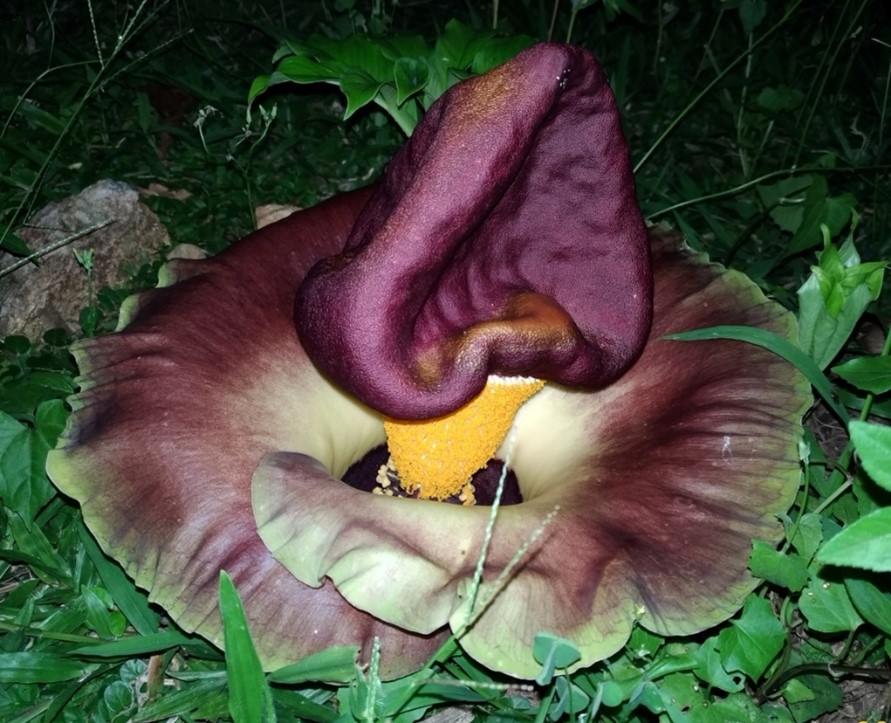
ຊໍ່ດອກມີກ້ານສັ້ນ ຍາວ 3 ຫາ 20 ຊມ ກວ້າງ 1 ຫາ 8 ຊມ, ໂດຍປົກກະຕິຈະມີສີອ່ອນ ແລະ ລຽບ (ບໍ່ມີຂົນ) ກ່ວາກ້ານໃບ. ໃບປະດັບຊໍ່ດອກຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ອ້ອມຫອບຊໍ່ດອກ ຮູບຄ້າຍລະຄັງ, ກວ້າງ ແລະ ຍາວ ໂດຍມີຄວາມຍາວ 10 ຫາ 45 ຊມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 15 ຫາ 60 ຊມ.
ດອກຈະຕິດກັບກ້ານຊໍ່ດອກໂດຍຕົງ ບໍ່ມີກ້ານດອກ. ດອກແມ່ມີລັກສະນະຮູບຊົງກະບອກ, ຍາວ 3 ຫາ 25 ມມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 1 ຫາ 12 ມມ, ດອກອອກຮຽງຕົວກັນແໜ້ນ ຫຼື ຫ່າງກັນເລັກນ້ອຍ. ເຕົ້າໄຂ່ມີສີຂຽວອ່ອນ ຫຼື ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ເປັນສີມ່ວງແດງ ຫຼື ມີໂຄນສີຂາວ, ແປ ແລະ ກົມ ເມື່ອເບິ່ງຈາກດ້ານຂ້າງ, ສູງ 1.5 ຫາ 2.5 ມມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 3 ຫາ 5 ມມ, ເຕົ້າໄຂ່ແບ່ງອອກເປັນ 2 ຫາ 3 ຫ້ອງ (locules). ດອກເພດຜູ້ ມີເກສອນເພດຜູ້ 4 ຫາ 6 ອັນ ແຕ່ລະອັນຍາວ 4 ຫາ 6 ມມ, ມີກ້ານເກສອນເພດຜູ້ສັ້ນປະມານ 0.5 ມມ, ເຊື່ອມຕິດກັນ, ຖົງລະອອກເກສອນສີຂາວນວນ ຮູບຊົງກະບອກ.
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1]
ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປພືດຊະນິດຈະມີໃບ 1 ຫາ 2 ໃບ. ກ້ານໃບ (petioles) ມີຜິວສີຂຽວອອ່ນໄປຈັນຮອດສີຂຽວເຂັ້ມ ຫຼື ສີຂຽວປົນດຳ, ມັກມີຈຸສີຂາວອ່ອນຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ ແລະ ນ້ອຍ ຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ, ຈຸດຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ມັກຈະຢູ່ລວມກັນຢູ ໂດຍສະເພາະບໍລິເວນໂຄນກ້ານໃ, ກ້ານໃບອາດຍາວຮອດ 2 ມ ແລະ ກວ້າງຮອດ 20 ຊມ, ໂດຍຜິວຈະມີລັກສະນະຍົ້້ນເລັກນ້ອຍ (ເປັນຮ່ອງຕື້ນ) ຫຼື ຄຸມດ້ວຍປຸ່ມແຫຼມນ້ອຍໆ.
ໃບມີລັກສະນະເປັນແສກຍາວ ແລະ ມີຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ຫຼາຍ, ກວ້າງປະມານ 3 ມ, ເສັ້ນກາງໃບຫຼັກມີລັກສະນະເປັນປີກ ອາດແຄບ ຫຼື ກວ້າງເກືແບຮອດໂຄນໃບ. ໃບຍ່ອຍຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ເທິງແຜ່ນໃບມີສີແຕກຕ່າງກັນ, ຜິວໃບດ້ານລຸ່ມມີສີຂຽວປານຫາງ ຫຼື ສີຂຽວອ່ອນ, ຜິວໃບດ້າເທິງມີສີຂຽວປານກາງ, ໃບຍ່ອຍມີຮູບຮ່າງທີ່ຫຼາກຫຼາຍແຕກຕ່າງກັນ ມີທັງຮູບກົມ, ຮູບໄຂ່, ຮູບໄຂ່ປີ້ນ, ຮູບຫອກ ຫຼື ຮູບຫອກປີ້ນ, ໃບຍ່ອຍຍາວ 3 ຫາ 35 ຊມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 2 ຫາ 12 ຊມ, ປາຍແຫຼມ.
ຊໍ່ດອກມີກ້ານສັ້ນ ຍາວ 3 ຫາ 20 ຊມ ກວ້າງ 1 ຫາ 8 ຊມ, ໂດຍປົກກະຕິຈະມີສີອ່ອນ ແລະ ລຽບ (ບໍ່ມີຂົນ) ກ່ວາກ້ານໃບ. ໃບປະດັບຊໍ່ດອກຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ອ້ອມຫອບຊໍ່ດອກ ຮູບຄ້າຍລະຄັງ, ກວ້າງ ແລະ ຍາວ ໂດຍມີຄວາມຍາວ 10 ຫາ 45 ຊມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 15 ຫາ 60 ຊມ.
ດອກຈະຕິດກັບກ້ານຊໍ່ດອກໂດຍຕົງ ບໍ່ມີກ້ານດອກ. ດອກແມ່ມີລັກສະນະຮູບຊົງກະບອກ, ຍາວ 3 ຫາ 25 ມມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 1 ຫາ 12 ມມ, ດອກອອກຮຽງຕົວກັນແໜ້ນ ຫຼື ຫ່າງກັນເລັກນ້ອຍ. ເຕົ້າໄຂ່ມີສີຂຽວອ່ອນ ຫຼື ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ເປັນສີມ່ວງແດງ ຫຼື ມີໂຄນສີຂາວ, ແປ ແລະ ກົມ ເມື່ອເບິ່ງຈາກດ້ານຂ້າງ, ສູງ 1.5 ຫາ 2.5 ມມ ແລະ ກວ້າງ 3 ຫາ 5 ມມ, ເຕົ້າໄຂ່ແບ່ງອອກເປັນ 2 ຫາ 3 ຫ້ອງ (locules). ດອກເພດຜູ້ ມີເກສອນເພດຜູ້ 4 ຫາ 6 ອັນ ແຕ່ລະອັນຍາວ 4 ຫາ 6 ມມ, ມີກ້ານເກສອນເພດຜູ້ສັ້ນປະມານ 0.5 ມມ, ເຊື່ອມຕິດກັນ, ຖົງລະອອກເກສອນສີຂາວນວນ ຮູບຊົງກະບອກ.
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1]
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກ:
Native to Andaman Is., Assam, Bangladesh, Borneo, Cambodia, China South-Central, China Southeast, East Himalaya, Hainan, India, Jawa, Laos, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Maluku, Myanmar, New Guinea, Northern Territory, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam. [2]
Global distribution of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius between 1894 to 2026. Source: [3]
Global distribution of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius between 1894 to 2026. Source: [3]
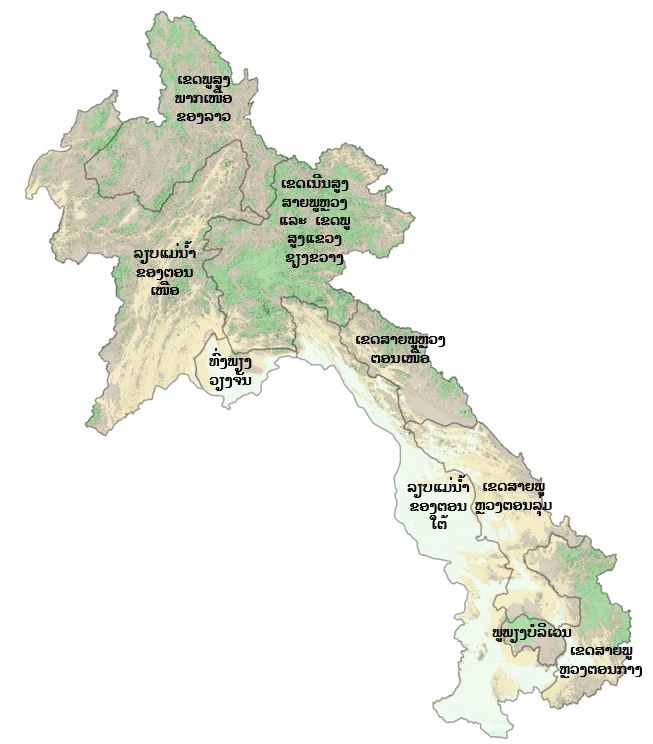
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນໃນລາວ
:
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນຕາມພູມສັນຖານ
:
ປ່າດົງດິບ
ແຄມຝັ່ງນໍ້າ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າອ່ອນ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າແກ່
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
ແຄມຝັ່ງນໍ້າ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າອ່ອນ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າແກ່
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ

ສະເພາະຖິ່ນໃນລາວ:
ພື້ນເມືອງ
ຮຸກຮານ
:
ບໍ່ຮຸກຮານ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນູຮັກ IUCN
:
ມີຄວາມສ່ຽງໜ້ອຍສຸດ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນຸຮັກແຫ່ງຊາດລາວ
:
ບໍ່ຖືກລະບຸໃນບັນຊີປະເພດໃດ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ປະເພດການນຳໃຊ້:
ກິດຈະກຳການກະເສດ
ວັດທະນະທຳ ແລະ ຮີດຄອງ
ອາຫານ
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ວັດທະນະທຳ ແລະ ຮີດຄອງ
ອາຫານ
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ບັນຍາຍການນຳໃຊ້:
ອາຫານ: ໃບ ແລະ ຮາກສາມາກກິນໄດ້ ແລະ ມັກຈະຖືກນຳມາປຸ່ງເປັນອາຫານ [7]. ແປ້ງທີ່ສະກັດຈາກຫົວຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ໃຊ້ເປັນອາຫານລົດນ້ຳໜັກໄດ້ [6]. ເຖິ່ງແມ່ນວ່າຫົວກະບຸກຈະເປັນພິດ ບາງຄັ້ງກໍ່ມີການນຳມາປຸ່ງສຸກກິນໃນລາວ ແລະ ພື້ນທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ, ເມື່ອນຳມາຂູດຕາກໃຫ້ແຫ້ງຈະໄດ້ແປ້ງທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການອົບເຂົ້າໜົມໄດ້ [8].
ສະໝຸນໄພ: ຮາກມີຄຸນສົມບັນທາງຢາຫຼາຍປະການ ໄດ້ແກ່ ຊ່ວຍຂັບລົມ, ບຳລຸງຮ່າງກາຍ, ບຳລຸງກະເພາະອາຫານ, ກະຕຸ້ນ ແລະ ຂັບເສມຫະ, ນອກຈາກນີ້ຍັງໃຊ້ຮັກສາພະຍາດໄຂຂໍ້ອັກເສບແບບເສບພັນ [7]. ຕາມການລາຍງານຂໍ້ມູນຈາກ IMT ຫົວມັກຖືກມານຳໃຊ້ຮັກສາໄຂ້ມາລາເຣຍ ແລະ ການສຶກສາລ້າສຸດຊີ້ໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ ຫົວກະບຸກອາດຈະຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຄໍເລສເຕຣໍ ແລະ ໃຫ້ປະໂຫຍດທາງໂພຊະນາການສຳຫຼັບຜູ້ປ່ວຍພະຍາດເບົາຫວານ [8]. ແກ່ນ ແລະ ຫົວໃຂຊ້ຫຼຸດຄໍເລສເຕີຣໍ, ແກ້ອາການໄອ, ຮັກສາມາລາເຣຍ ແລະ ໂຣກຕັບ ລວມທັງກຳຈັດສານພິດອອກຈາກຮ່າງກາຍ. [6]
ກິດຈະກຳທາງການກະເສດ: ໂຄນກ້ານໃບ ກົມໃຫຍ່ຄ້າຍຫົວກະບຸກ ນຳມາຕົ້ມໃຫ້ໝູກິນ, ໝາກສຸກນຳມາເປັນອາຫານນົກ. [6]
ສາສະໜາ ຫຼື ຄວາມເຊື່ອ: ໃນປະເທດລາວພືດເຫຼົ່ານີ້ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ ຖືວ່າເປັນພືດພິເສດ ເຊື່ອກັນວ່າຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ງູຍ້ານກົວ ຫຼື ຊ່ວຍເຮັດໃຫ້ຫາປາໄດ້. [8]
ໝາຍເຫດ: ຫົວກະບຸກມີແປ້ງ ແລະ ນ້ຳຕານ ນອກຈາກນີ້ຍັງມີຜຶກແຄວຊຽມອອັກຊາເລດຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຄ້າຍເຂັມຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ ເຊິ່ງອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດອາການຄັນ ແລະ ອັກເສບ, ການກິນຫົວກະບຸກດິບອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດອາການແສບຮ້ອນໃນປາກ ແລະ ຜື່ນຂື້ນ. [6]
ສະໝຸນໄພ: ຮາກມີຄຸນສົມບັນທາງຢາຫຼາຍປະການ ໄດ້ແກ່ ຊ່ວຍຂັບລົມ, ບຳລຸງຮ່າງກາຍ, ບຳລຸງກະເພາະອາຫານ, ກະຕຸ້ນ ແລະ ຂັບເສມຫະ, ນອກຈາກນີ້ຍັງໃຊ້ຮັກສາພະຍາດໄຂຂໍ້ອັກເສບແບບເສບພັນ [7]. ຕາມການລາຍງານຂໍ້ມູນຈາກ IMT ຫົວມັກຖືກມານຳໃຊ້ຮັກສາໄຂ້ມາລາເຣຍ ແລະ ການສຶກສາລ້າສຸດຊີ້ໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ ຫົວກະບຸກອາດຈະຊ່ວຍຫຼຸດຄໍເລສເຕຣໍ ແລະ ໃຫ້ປະໂຫຍດທາງໂພຊະນາການສຳຫຼັບຜູ້ປ່ວຍພະຍາດເບົາຫວານ [8]. ແກ່ນ ແລະ ຫົວໃຂຊ້ຫຼຸດຄໍເລສເຕີຣໍ, ແກ້ອາການໄອ, ຮັກສາມາລາເຣຍ ແລະ ໂຣກຕັບ ລວມທັງກຳຈັດສານພິດອອກຈາກຮ່າງກາຍ. [6]
ກິດຈະກຳທາງການກະເສດ: ໂຄນກ້ານໃບ ກົມໃຫຍ່ຄ້າຍຫົວກະບຸກ ນຳມາຕົ້ມໃຫ້ໝູກິນ, ໝາກສຸກນຳມາເປັນອາຫານນົກ. [6]
ສາສະໜາ ຫຼື ຄວາມເຊື່ອ: ໃນປະເທດລາວພືດເຫຼົ່ານີ້ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ ຖືວ່າເປັນພືດພິເສດ ເຊື່ອກັນວ່າຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ງູຍ້ານກົວ ຫຼື ຊ່ວຍເຮັດໃຫ້ຫາປາໄດ້. [8]
ໝາຍເຫດ: ຫົວກະບຸກມີແປ້ງ ແລະ ນ້ຳຕານ ນອກຈາກນີ້ຍັງມີຜຶກແຄວຊຽມອອັກຊາເລດຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຄ້າຍເຂັມຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ ເຊິ່ງອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດອາການຄັນ ແລະ ອັກເສບ, ການກິນຫົວກະບຸກດິບອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດອາການແສບຮ້ອນໃນປາກ ແລະ ຜື່ນຂື້ນ. [6]
ການປູກ ການລ້ຽງ:
ຊະນິດທຳມະຊາດ
ລະດູການເກັບກູ້:
ມັງກອນ
ກຸມພາ
ມີນາ
ເມສາ
ພຶກສະພາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ກຸມພາ
ມີນາ
ເມສາ
ພຶກສະພາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຕ່ອງໂສ້ມູນຄ່າ:
ໃນອາດີດຫົວກະບຸກສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ໃຊ້ສຳຫຼັບບໍລິໂພກພາຍໃນປະເທດ ແຕ່ປັດຈຸບັນມີການສົ່ງອອກຫົວກະບຸກແຫ້ງໄປຍັງປະເທດຈີນ ໃນລາຄາຕັ້ງແຕ່ 30.000 ຫາ 165.000 ກີບຕໍ່ກິໂລ, ສ່ວນລາຄາຫົວກະບຸກສົດຢູ່ທີປະມານ 18.000 ກີບຕໍ່ກິໂລ.
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ການເກັບກ່ຽວ:
ຫົວກະບຸກສາມາດເກັບກ່ຽວໄດ້ຕະຫຼອດປີ ແຕ່ຕ້ອງຂຸດຈາກດິນຢ່າງລະມັດລະວັງ ເພາະຖ້າເກີດຄວາມເສຍ ອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດການຕິດເຊື້ອຈາກພະຍາດ ແລະ ແມງໄມ້ສັດຕູພືດ, ຄວນລະມັດລະວັງບໍ່ໃຫ້ເກີດຄວາມເສຍຫາຍລະຫວ່າງການຂົນສົ່ງດ້ວຍ. [6]
ການຕິດຕາມປະຊາກອນ:
ເປັນພືດທີ່ພົບໄດ້ທົວໄປໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ, ມີຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ ແລະ ຂື້ນຕາມພື້ນທີ່ຮົກເຮື້ອ, ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ກຸ່ມປະຊາກອນໃນປັດຈຸບັນຍັງບໍ່ທັນຊັດເຈນ. [7]
ການເກັບກູ້ແບບຍືຍຍົງ:
ການແຂງຂັນກັນເກັບກ່ຽວຫົວຈາກໃຕ້ດິນອາດເປັນອົນຕະລາຍຕໍ່ພືດ, ແລະ ການເກັບກ່ຽວຄວນເຮັດຫຼັງຈາກພືດອອກແກ່ສຸກແລ້ວເທົ່ານັ້ນ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ໄດ້ຫົວທີ່ມີມາດຕະຖານ ພື້ຕ້ອງຂະຫຍາຍຕົວດົນກ່ວາ 1 ປີ. [6]
ຫົວກະບຸກສາມາດເກັບກ່ຽວໄດ້ຕະຫຼອດປີ ແຕ່ຕ້ອງຂຸດຈາກດິນຢ່າງລະມັດລະວັງ ເພາະຖ້າເກີດຄວາມເສຍ ອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດການຕິດເຊື້ອຈາກພະຍາດ ແລະ ແມງໄມ້ສັດຕູພືດ, ຄວນລະມັດລະວັງບໍ່ໃຫ້ເກີດຄວາມເສຍຫາຍລະຫວ່າງການຂົນສົ່ງດ້ວຍ. [6]
ການຕິດຕາມປະຊາກອນ:
ເປັນພືດທີ່ພົບໄດ້ທົວໄປໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ, ມີຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ ແລະ ຂື້ນຕາມພື້ນທີ່ຮົກເຮື້ອ, ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ກຸ່ມປະຊາກອນໃນປັດຈຸບັນຍັງບໍ່ທັນຊັດເຈນ. [7]
ການເກັບກູ້ແບບຍືຍຍົງ:
ການແຂງຂັນກັນເກັບກ່ຽວຫົວຈາກໃຕ້ດິນອາດເປັນອົນຕະລາຍຕໍ່ພືດ, ແລະ ການເກັບກ່ຽວຄວນເຮັດຫຼັງຈາກພືດອອກແກ່ສຸກແລ້ວເທົ່ານັ້ນ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ໄດ້ຫົວທີ່ມີມາດຕະຖານ ພື້ຕ້ອງຂະຫຍາຍຕົວດົນກ່ວາ 1 ປີ. [6]
ໂພຊະນາການ
ຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ບັນຍາຍຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
N/A
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | 1.2 | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | 18.4 | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | 0.1 | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | vitamin A 260 IU, thiamine (vitamin B1) 0.0006g, niacin (Vitamin B3) 0.07g, and riboflavin (vitamin B 2) 0.07g |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | calcium 0.05g, phosphorus 0.34g, iron 0.06 g |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
ເຄດິດຮູບພາບ:
[1] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 12 November 2012 by: Chief Re-dEarth. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/147190. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 21 June 2019 by: Tuyen Van Pham. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/27375341. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 23 January 2024 by: Michaela Blech. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/197354122. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[4] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 07 June 2021 by: abhi jith. Availa-ble: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/81992028. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[5] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 29 June 2023 by: Gordon Chen. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/17009272. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[6] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 18 January 2017 by: earthknight. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/4966405. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 21 June 2019 by: Tuyen Van Pham. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/27375341. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 23 January 2024 by: Michaela Blech. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/197354122. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[4] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 07 June 2021 by: abhi jith. Availa-ble: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/81992028. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[5] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 29 June 2023 by: Gordon Chen. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/17009272. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
[6] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 18 January 2017 by: earthknight. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/4966405. [Accessed 29 October 2024].
ອ້າງອິງ:
[1] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson," World Flora Online. [Online]. Available: https://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-0000965117#local. [Ac-cessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[2] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson," Plants of the World Online. [Online]. Available: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:60444138-2. [Accessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[3] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson," GBIF. [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/2871533. [Accessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[4] V. Lamxay, S. Lanorsavanh, K. Chanthavong, K. Souvannakhoummane, and S. Bounphanmy, A Checklist of the Vascular Plants of Lao PDR, version 1.0 [PDF]. Faculty of Natural Sciences, National University of Laos, Vienti-ane, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/A-Checklist-of-the-Vascular-Plants-of-Lao-PDR.pdf. [Accessed: 09-Feb-2026].
[5] V. Lamxay, S. Lanorsavanh, K. Chanthavong, K. Souvannakhoummane, and S. Bounphanmy, A Checklist of the Vascular Plants of Lao PDR, Ver-sion 1.0 [PDF]. Faculty of Natural Sciences, National University of Laos, Vientiane, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Checklist-plant-of-Laos-read-only-1.pdf. [Accessed: 09-Feb-2026].
[6] M. Greijmans, National University of the Lao PDR, National Agricul-ture and Forestry Research Institute, and SNV Netherlands Development Organisation, Non-Timber Forest Products in the Lao PDR: A Manual of 100 Commercial and Traditional Products [PDF]. Vientiane, Lao PDR: Na-tional University of the Lao PDR; National Agriculture and Forestry Re-search Institute; SNV Netherlands Development Organisation, 2007. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/100_NTFPs.pdf. [Accessed: 09-Feb-2026].
[7] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius," IUCN Red List. [Online]. Available: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/44393336/44531586#habitat-ecology. [Accessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[8] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius," Pha Tad Ke. [Online]. Available: https://www.pha-tad-ke.com/plant/amorphophallus-paeoniifolius/. [Ac-cessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[9] D. Shahbuddin, M. Reddy, R. Ridzuan, and R. Sjahril, “Botanical As-pects, Nutritional Benefits and Cultivation of Elephant Foot Yam (Amor-phophallus paeoniifolius),” Malaysian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 2423–2446, 2025, doi: 10.11113/mjfas.v21n4.3656. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/394984431_Botanical_Aspects_Nutritional_Benefits_and_Cultivation_of_Elephant_Foot_Yam_Amorphophallus_paeoniifolius. [Accessed: 10-Feb-2026].
[2] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson," Plants of the World Online. [Online]. Available: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:60444138-2. [Accessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[3] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson," GBIF. [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/2871533. [Accessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[4] V. Lamxay, S. Lanorsavanh, K. Chanthavong, K. Souvannakhoummane, and S. Bounphanmy, A Checklist of the Vascular Plants of Lao PDR, version 1.0 [PDF]. Faculty of Natural Sciences, National University of Laos, Vienti-ane, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/A-Checklist-of-the-Vascular-Plants-of-Lao-PDR.pdf. [Accessed: 09-Feb-2026].
[5] V. Lamxay, S. Lanorsavanh, K. Chanthavong, K. Souvannakhoummane, and S. Bounphanmy, A Checklist of the Vascular Plants of Lao PDR, Ver-sion 1.0 [PDF]. Faculty of Natural Sciences, National University of Laos, Vientiane, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Checklist-plant-of-Laos-read-only-1.pdf. [Accessed: 09-Feb-2026].
[6] M. Greijmans, National University of the Lao PDR, National Agricul-ture and Forestry Research Institute, and SNV Netherlands Development Organisation, Non-Timber Forest Products in the Lao PDR: A Manual of 100 Commercial and Traditional Products [PDF]. Vientiane, Lao PDR: Na-tional University of the Lao PDR; National Agriculture and Forestry Re-search Institute; SNV Netherlands Development Organisation, 2007. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/100_NTFPs.pdf. [Accessed: 09-Feb-2026].
[7] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius," IUCN Red List. [Online]. Available: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/44393336/44531586#habitat-ecology. [Accessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[8] "Amorphophallus paeoniifolius," Pha Tad Ke. [Online]. Available: https://www.pha-tad-ke.com/plant/amorphophallus-paeoniifolius/. [Ac-cessed: Oct. 28, 2024].
[9] D. Shahbuddin, M. Reddy, R. Ridzuan, and R. Sjahril, “Botanical As-pects, Nutritional Benefits and Cultivation of Elephant Foot Yam (Amor-phophallus paeoniifolius),” Malaysian Journal of Fundamental and Applied Sciences, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 2423–2446, 2025, doi: 10.11113/mjfas.v21n4.3656. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/394984431_Botanical_Aspects_Nutritional_Benefits_and_Cultivation_of_Elephant_Foot_Yam_Amorphophallus_paeoniifolius. [Accessed: 10-Feb-2026].
ຜູ້ສ້າງ Factsheet:
Komkeo and Manoluck bounsihalat
ຜູ້ກວດສອບ Factsheet:
,




