ເລກລຳດັບທີ: 51
ລະດັບການຮວບຮວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ຂໍ້ມູນລະອຽດ
ປັບປູງຄັ້ງລ່າສຸດ: N/A
ຂ່າຕາແດງ
Galanga
Alpinia galanga (L.) Willd.
ພືດ
ພືດລົ້ມລຸກ
ຜັກ ແລະ ພືດລົ້ມລຸກ
×
ຊື່ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ:
ຂ່າໃຫຍ່, ຂ່າບ້ານ ( Siamese-ginger, Greater galangal, Ggreater galanga and Languas.)
ຊື່ພ້ອງ
:
Alpinia alba (Retz.) Roscoe
Alpinia bifida Warb.
Alpinia carnea Griff.
Alpinia galanga subsp. pyramidata (Blume) K.Schum.
Alpinia galanga var. galanga
Alpinia galanga var. pyramidata (Blume) K.Schum.
Alpinia pyramidata Blume
Alpinia rheedei Wight
Alpinia viridiflora Griff.
Amomum galanga (L.) Lour.
Amomum medium Lour.
Galanga major Garsault
Galanga officinalis Salisb.
Hellenia alba (Retz.) Willd.
Heritiera alba Retz.
Languas galanga (L.) Stuntz
Languas pyramidata (Blume) Merr.
Languas vulgare J.Koenig
Maranta galanga L.
Zingiber galanga (L.) Stokes
Zingiber medium Stokes
Zingiber sylvestre Gaertn.
Alpinia bifida Warb.
Alpinia carnea Griff.
Alpinia galanga subsp. pyramidata (Blume) K.Schum.
Alpinia galanga var. galanga
Alpinia galanga var. pyramidata (Blume) K.Schum.
Alpinia pyramidata Blume
Alpinia rheedei Wight
Alpinia viridiflora Griff.
Amomum galanga (L.) Lour.
Amomum medium Lour.
Galanga major Garsault
Galanga officinalis Salisb.
Hellenia alba (Retz.) Willd.
Heritiera alba Retz.
Languas galanga (L.) Stuntz
Languas pyramidata (Blume) Merr.
Languas vulgare J.Koenig
Maranta galanga L.
Zingiber galanga (L.) Stokes
Zingiber medium Stokes
Zingiber sylvestre Gaertn.
ຊື່ສະກຸນ:
Zingiberaceae
ຊະນິດໃກ້ຄຽງ:
ຂ່າຫຼາວ/ Kha Rao
ຂ່ານ້ຳ/ False Cardamom Ginger
ຂ່າດົງ/ Oblong's Leaves Galanga
ຂ່າຊາຍເຫຼືອງ/ Yellow Galanga
ຕົ້ນຝາງ/ Barbados Pride
ຂ່າແດງ / Wild Smaller Ganglangal
ມານຂ່າ / Smaller Banana Flower Galangal
ຂ່າໂຄມ / Banana Flower Galangal
ຂ່ານ້ຳ/ False Cardamom Ginger
ຂ່າດົງ/ Oblong's Leaves Galanga
ຂ່າຊາຍເຫຼືອງ/ Yellow Galanga
ຕົ້ນຝາງ/ Barbados Pride
ຂ່າແດງ / Wild Smaller Ganglangal
ມານຂ່າ / Smaller Banana Flower Galangal
ຂ່າໂຄມ / Banana Flower Galangal
ບັນຍາຍລັກສະນະທາງພືດສາດ:
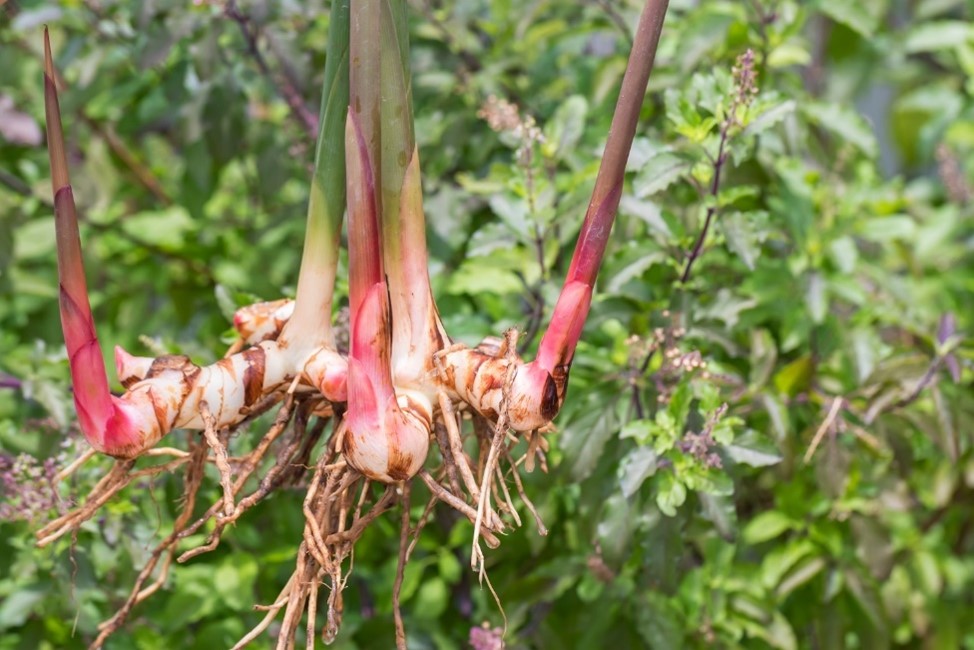
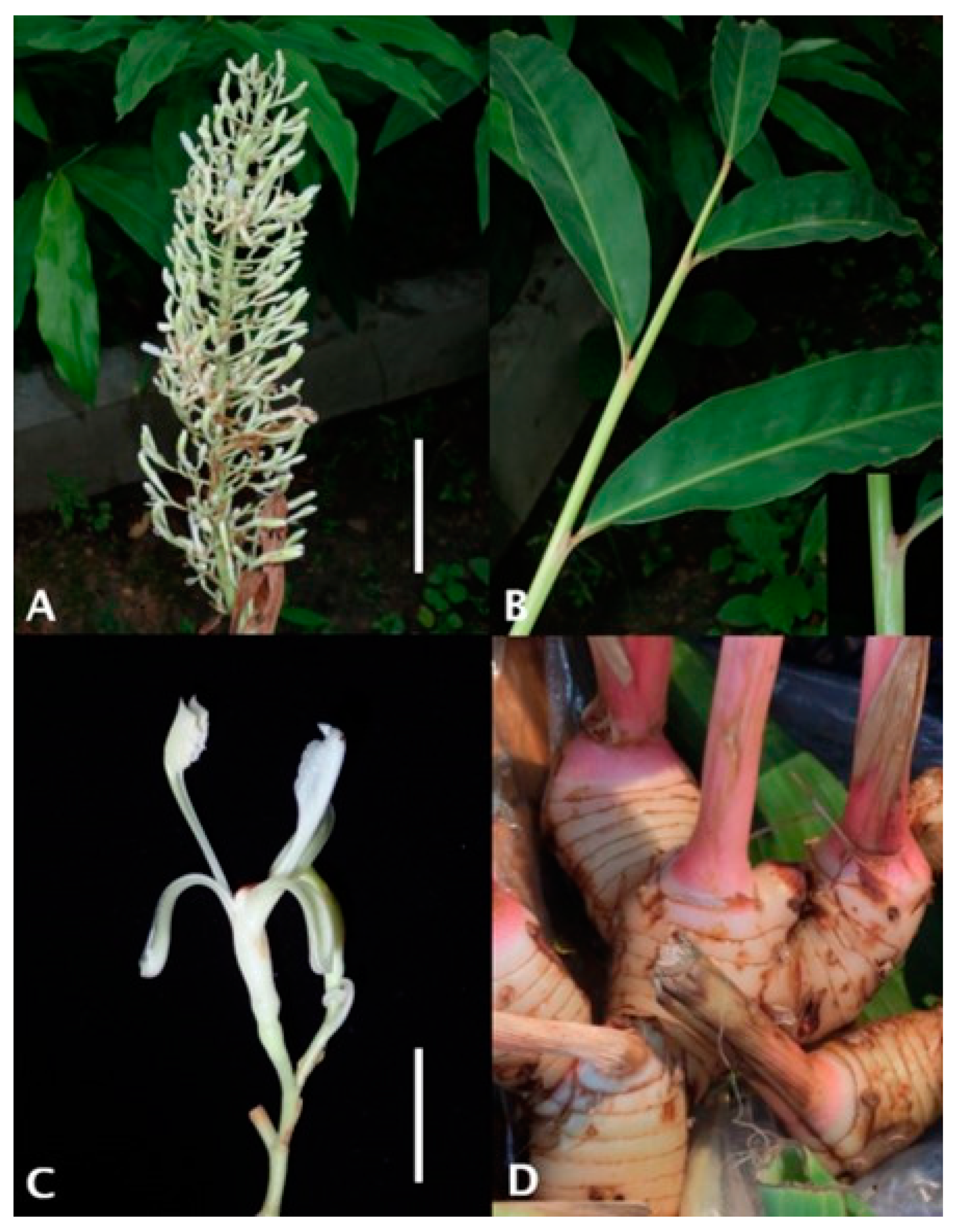
ພືດຊະນິດນີ້ມີເຫງົ້າໃຕ້ດິນທີ່ບວມຂື້ນເພື່ອເກັບສານອາຫານ ພືດຊະນິດນີ້ມີລຳຕົ້ນທຽມທີ່າມາດເຕບໂຕສູງຮອດ 2 ແມັດ, ລຳຕົ້ົນທຽມບໍ່ແມ່ນລຳຕົ້ນແທ້ ແຕ່ເກີດຈາກກາບໃບທີ່ຮຽງກັນແໜ້ນ, ບໍລິເວນໂຄນໃບມີຫູໃບ ຮູບກົມ ແລະ ຍາວປະມານ 5 ມມ. ກ້ານໃບ ຊິ່ງເປັນກ້ານທີ່ເຊື່ອມແຜ່ນໃບກັບລຳຕົ້ນທຽມ, ຍາວປະມານ 6 ມມ.
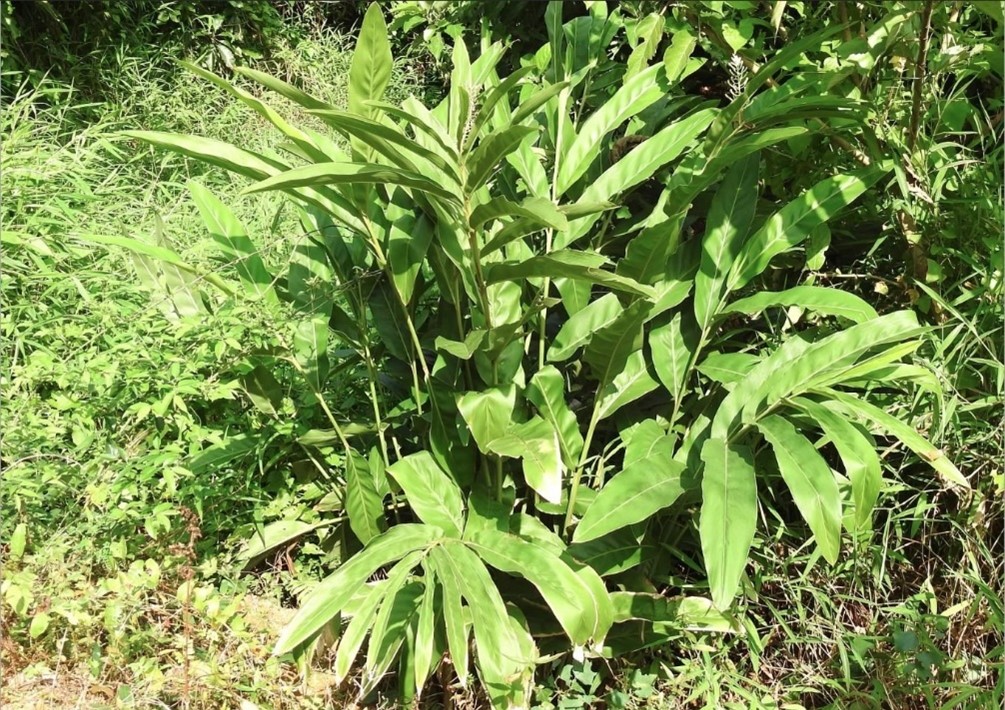
ແຜ່ນໃບຮູບຂອບຂະໜານ ຫຼື ຮູບຫອກ, ຍາວ 25 ຫາ 35 ຊມ. ແລະ ກວ້າງ 6 ຫາ 10 ຊມ., ໃບອາດຈະລຽບ (ບໍ່ມີຂົນ) ຫຼື ມີຂົນລະອຽດບໍລິເວນຜິວໃບດ້ານລຸຸ່ມ, ໂຄນໃບຮຽວແຫຼມ, ປາຍໃບແຫຼມ ຫຼື ຮຽວແຫຼມ.
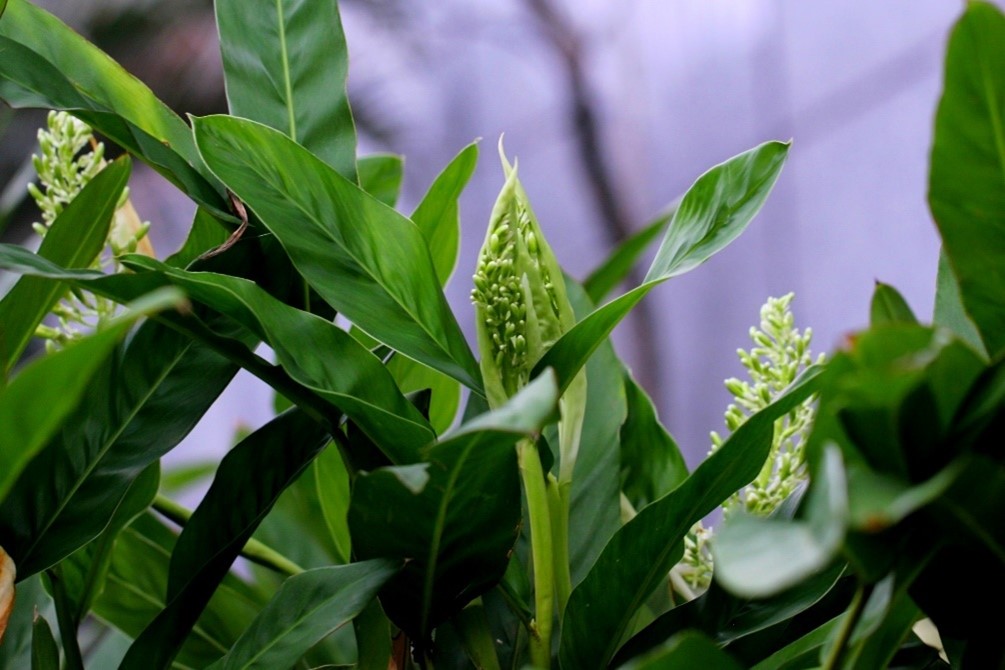
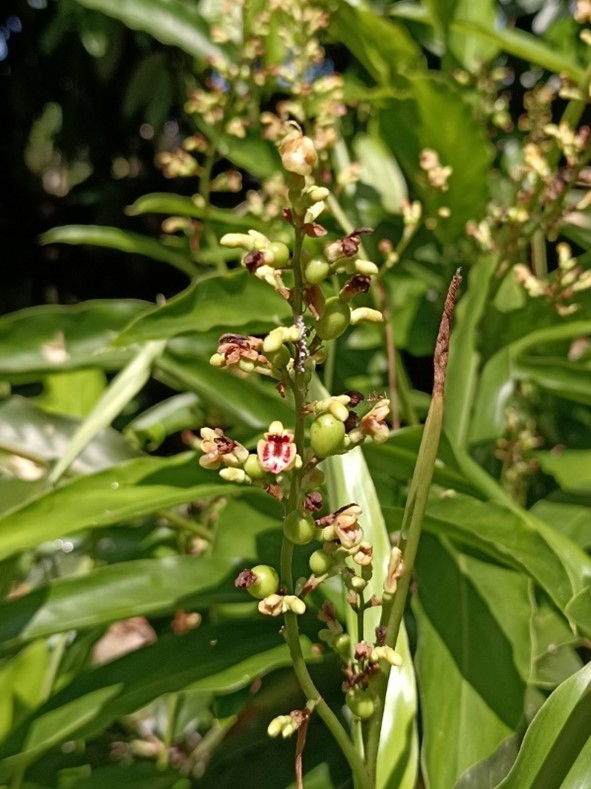
ຊໍ່ດອກເປັນແບບແຕກແໜ່ງ (panicle) ຂະໜາດປະມານ 20x30 ຊມ., ແກນກາງອາດລຽບ ຫຼື ມີຂົນລະອຽດ, ແຕກກິ່ງກ້ານຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ ໂດຍມີຄວາມຍາວ 2 ຫາ 4 ຊມ. ແຕ່ລະກິ່ງມັກມີດອກຍ່ອຍຢູ່ 2 ຫາ 6 ດອກ. ໃບປະດັບ ແລະ ໃບປະດັບຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຕິດທົນ ໝາຍຄວາມວ່າຕິດຢູ່ຕະຫຼອດໄລຍະທີ່ດອກຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ, ໃບປະດັບຮູບຫອກ ແຍາາວ 5 ຫາ 8 ມມ., ສີຂຽວ, ສີຂາວ ແລະ ມີກິ່ນຫອມ. ກາບດອກມີລັກສະນະເປັນຫຼອດ, ຍາວ 6 ຫາ 10 ມມ. ໂດຍມີກີບດອກຍາວເປັນຮູບໄຂ່,ຍາວ 1,6 ຫາ 1,8 ຊມ.
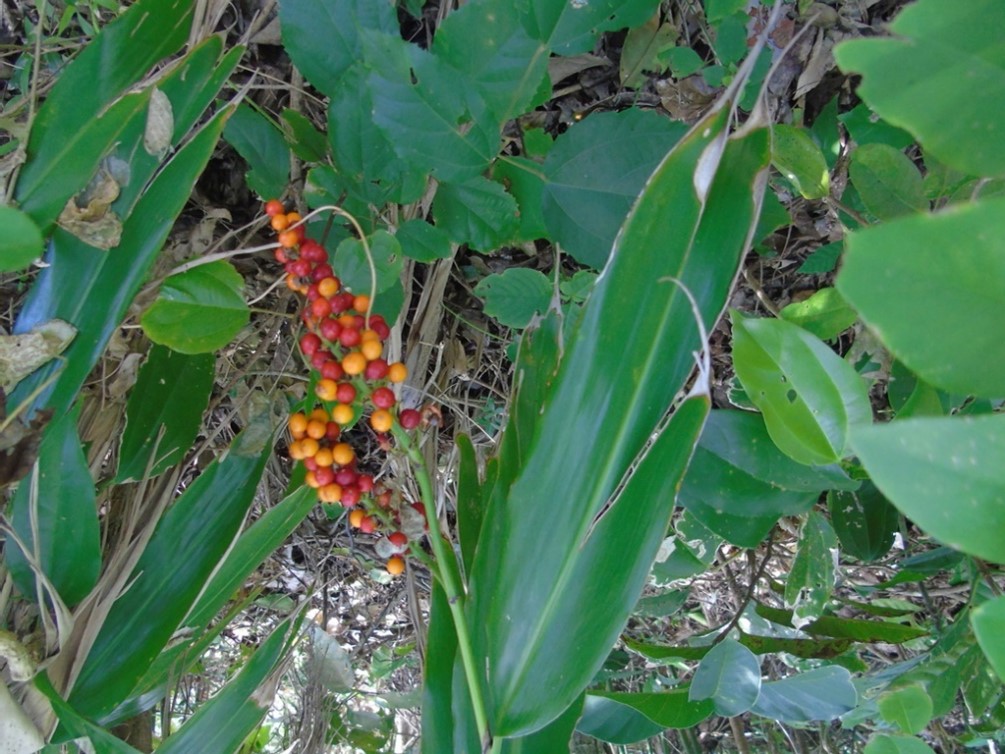
ໝາກມີລັກສະນະເປັນແຄັບຊູນ, ເມື່ອແຫ້ງຈະປ່ຽນເປັນສີນ້ຳຕານ ຫຼື ສີແດງ, ມີລັກສະນະເປັນຮູບຮີ, ບລເວນກາງຈະແຄບເລັກນ້ອຍ, ຍາວປະມານ 1 ຫາ 1,5 ຊມ., ກວ້າງປະມານ 7 ມມ. ແຄັບຊູນມີລັກສະນະບາງ ແລະ ລຽບ. ແກ່ນມີ 3 ຫາ 6 ແກ່ນ.
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1]
ແຜ່ນໃບຮູບຂອບຂະໜານ ຫຼື ຮູບຫອກ, ຍາວ 25 ຫາ 35 ຊມ. ແລະ ກວ້າງ 6 ຫາ 10 ຊມ., ໃບອາດຈະລຽບ (ບໍ່ມີຂົນ) ຫຼື ມີຂົນລະອຽດບໍລິເວນຜິວໃບດ້ານລຸຸ່ມ, ໂຄນໃບຮຽວແຫຼມ, ປາຍໃບແຫຼມ ຫຼື ຮຽວແຫຼມ.
ຊໍ່ດອກເປັນແບບແຕກແໜ່ງ (panicle) ຂະໜາດປະມານ 20x30 ຊມ., ແກນກາງອາດລຽບ ຫຼື ມີຂົນລະອຽດ, ແຕກກິ່ງກ້ານຈຳນວນຫຼາຍ ໂດຍມີຄວາມຍາວ 2 ຫາ 4 ຊມ. ແຕ່ລະກິ່ງມັກມີດອກຍ່ອຍຢູ່ 2 ຫາ 6 ດອກ. ໃບປະດັບ ແລະ ໃບປະດັບຂະໜາດນ້ອຍຕິດທົນ ໝາຍຄວາມວ່າຕິດຢູ່ຕະຫຼອດໄລຍະທີ່ດອກຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ, ໃບປະດັບຮູບຫອກ ແຍາາວ 5 ຫາ 8 ມມ., ສີຂຽວ, ສີຂາວ ແລະ ມີກິ່ນຫອມ. ກາບດອກມີລັກສະນະເປັນຫຼອດ, ຍາວ 6 ຫາ 10 ມມ. ໂດຍມີກີບດອກຍາວເປັນຮູບໄຂ່,ຍາວ 1,6 ຫາ 1,8 ຊມ.
ໝາກມີລັກສະນະເປັນແຄັບຊູນ, ເມື່ອແຫ້ງຈະປ່ຽນເປັນສີນ້ຳຕານ ຫຼື ສີແດງ, ມີລັກສະນະເປັນຮູບຮີ, ບລເວນກາງຈະແຄບເລັກນ້ອຍ, ຍາວປະມານ 1 ຫາ 1,5 ຊມ., ກວ້າງປະມານ 7 ມມ. ແຄັບຊູນມີລັກສະນະບາງ ແລະ ລຽບ. ແກ່ນມີ 3 ຫາ 6 ແກ່ນ.
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1]
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກ:
Native to Assam, Bangladesh, Borneo, Cambodia, China South-Central, China Southeast, Hainan, Jawa, Malaya, Myanmar, Philippines, Sumatera, Lao, Thailand, Vietnam. [2]
Global distribution of Alpinia galanga between 1900 to 2025. Source: [3]
Global distribution of Alpinia galanga between 1900 to 2025. Source: [3]
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນໃນລາວ
:
ເຂດພູສູງພາກເໜືອຂອງລາວ
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດພູສູງສາຍພູຫຼວງ ແລະ ເຂດພູພຽງແຂວງຊຽງຂວາງ
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງຕອນລຸ່ມ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກກາງ
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດພູສູງສາຍພູຫຼວງ ແລະ ເຂດພູພຽງແຂວງຊຽງຂວາງ
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງຕອນລຸ່ມ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກກາງ
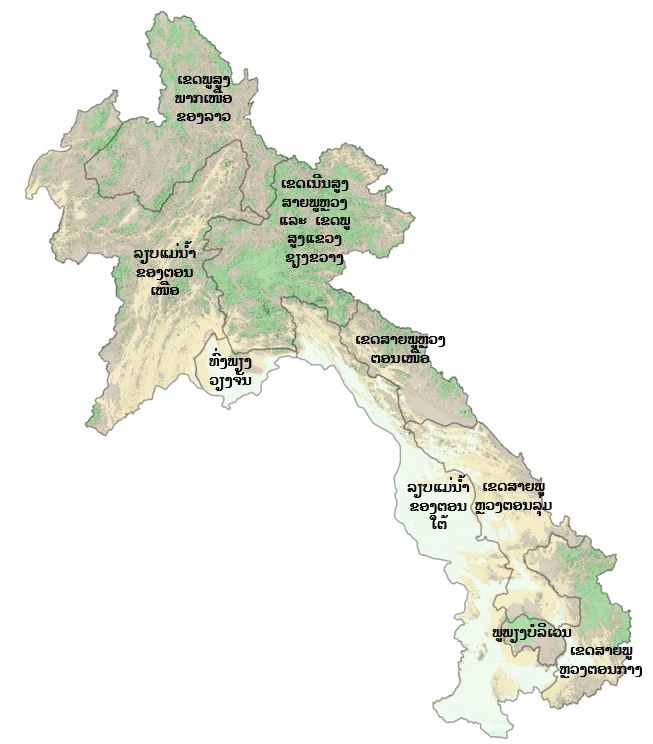
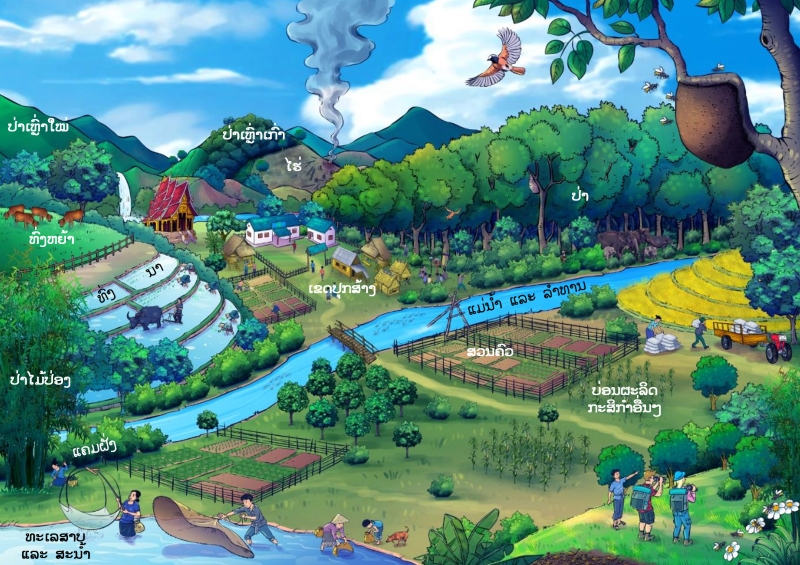
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນຕາມພູມສັນຖານ
:
ປ່າດົງດິບ
ປ່າປະສົມປ່ຽນໃບ
ແຄມຝັ່ງນໍ້າ
ເຂດຜະລິດພືດຜົນເນີນສູງ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າແກ່
ປ່າປະສົມປ່ຽນໃບ
ແຄມຝັ່ງນໍ້າ
ເຂດຜະລິດພືດຜົນເນີນສູງ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າແກ່

ສະເພາະຖິ່ນໃນລາວ:
ພື້ນເມືອງ
ຮຸກຮານ
:
ບໍ່ຮຸກຮານ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນູຮັກ IUCN
:
ບໍ່ມີຄວາມສ່ຽງ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນຸຮັກແຫ່ງຊາດລາວ
:
ບໍ່ຖືກລະບຸໃນບັນຊີປະເພດໃດ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ປະເພດການນຳໃຊ້:
ການຍ້ອມສີ
ກິດຈະກໍາເພື່ອຄວາມລື່ນເລີງ
ອາຫານ
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ກິດຈະກໍາເພື່ອຄວາມລື່ນເລີງ
ອາຫານ
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ບັນຍາຍການນຳໃຊ້:
ອາຫານ: ໝາກ ແລະ ສ່ວນອື່ນໆຂອງຂ່າ ມີກິ່ນຫອມ ແລິະ ມີຣົດຊາດຫວານໃຊ້ສຳຫຼັບປຸ່ງອາຫານຕ່າງໆ, ໜໍ່ອ່ອນ ແລະ ຊໍ່ດອກອ່ອນໃຊ້ຮັບປະທານເປັນຜັກ. ໃນລາວ ແລະ ໄທ ເຫງົ້າມັກໃຊ້ເປັນເຄື່ອງປຸ່ງໃນແກງສົ້ມ ເຊັ່ນ ຕົ້ມຍຳ [5]. ຂ່າເປັນພືດທີ່ໃຊ້ປະກອບອາາຫານໄດ້ຫຼາຍປະເພດ. [6]
ສະມຸນໄພ: ນອກຈາກໃຊ້ເປັນອາຫານແລ້ວ ຂ່າຍັງຖືວ່າເປັນສະມຸນໄພທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນຍາແຜນບູຮານອີກດ້ວຍ [6]. ເຊິ່ງຊາວບ້ານມັກເກັບໝາກຂ່າມາຂາຍໃນຕະຫຼາດສະມຸນໄພຈີນອີກດ້ວຍ ເຊິ່ງສາມາດນຳມາໃຊ້ຮັກສາອາຫານບໍ່ຍ່ອຍ, ເຈັບທ້ອງ, ຖອກທ້ອງ, ແລະ ຮາກ. ນ້ຳມັນລະເຫີຍທີ່ສະກດັຈາກຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໃບຍັງໃຊ້ຮັກສາອາການເຊື່ອມສະມັດຕະພາບທາງເພດ ແລະ ບັນເທົາອາການກະວົນກະວາຍ ລວມທັງຮັກສາພະຍາດທາງຜິວໜັງໄດ້ອີກດ້ວຍ. ນອກຈາກນີ້ ຫົວຂ່າ ແລະ ແກ່ນຍັງໃຊ້ເປັນນ້ຳມັນຫອມໃນຢາຮັກສາພະຍາດອີກດ້ວຍ. [5]
ໃຊ້ເພື່ອການຜ່ອນຄາຍ: ເຫງົ້າໃຊ້ເປັນເຄື່ອງເທດ ແຫຼ່ງຂອງນ້ຳມັນຫອມລະເຫີຍ ຫຼື ໃຊ້ໃນການແຕ່ງກິ່ນແອວກໍຮໍ. [5]
ການຍ້ອມສີ: ເຫງົ້າຂ່າຍັງນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຍ້ອມສີຜາໃຫ້ເປັນສີເຫຼືອງ ແລະ ສີຂຽວອົມເຫຼືອງອີກດ້ວຍ. [5]
ສະມຸນໄພ: ນອກຈາກໃຊ້ເປັນອາຫານແລ້ວ ຂ່າຍັງຖືວ່າເປັນສະມຸນໄພທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນຍາແຜນບູຮານອີກດ້ວຍ [6]. ເຊິ່ງຊາວບ້ານມັກເກັບໝາກຂ່າມາຂາຍໃນຕະຫຼາດສະມຸນໄພຈີນອີກດ້ວຍ ເຊິ່ງສາມາດນຳມາໃຊ້ຮັກສາອາຫານບໍ່ຍ່ອຍ, ເຈັບທ້ອງ, ຖອກທ້ອງ, ແລະ ຮາກ. ນ້ຳມັນລະເຫີຍທີ່ສະກດັຈາກຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໃບຍັງໃຊ້ຮັກສາອາການເຊື່ອມສະມັດຕະພາບທາງເພດ ແລະ ບັນເທົາອາການກະວົນກະວາຍ ລວມທັງຮັກສາພະຍາດທາງຜິວໜັງໄດ້ອີກດ້ວຍ. ນອກຈາກນີ້ ຫົວຂ່າ ແລະ ແກ່ນຍັງໃຊ້ເປັນນ້ຳມັນຫອມໃນຢາຮັກສາພະຍາດອີກດ້ວຍ. [5]
ໃຊ້ເພື່ອການຜ່ອນຄາຍ: ເຫງົ້າໃຊ້ເປັນເຄື່ອງເທດ ແຫຼ່ງຂອງນ້ຳມັນຫອມລະເຫີຍ ຫຼື ໃຊ້ໃນການແຕ່ງກິ່ນແອວກໍຮໍ. [5]
ການຍ້ອມສີ: ເຫງົ້າຂ່າຍັງນຳໃຊ້ເຂົ້າໃນການຍ້ອມສີຜາໃຫ້ເປັນສີເຫຼືອງ ແລະ ສີຂຽວອົມເຫຼືອງອີກດ້ວຍ. [5]
ການປູກ ການລ້ຽງ:
ປູກ ແລະ ທຳມະຊາດ
ລະດູການເກັບກູ້:
ມັງກອນ
ກຸມພາ
ມີນາ
ເມສາ
ພຶກສະພາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ກຸມພາ
ມີນາ
ເມສາ
ພຶກສະພາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຕ່ອງໂສ້ມູນຄ່າ:
ເນື່ອງຈາກຂ່າສາມາດກິນໄດ້ທັງເງົ້າ, ໜໍ່ ແລະ ໝາກ ເພາະສະນັ້ນຈຶ່ງສາມາດເກັບຂາຍໄດ້ທັງເຫງົ້າ, ໜໍ່ ແລະ ໝາກ [6]. ລາຄາຂາຍເຫງົ້າ 80,000 ກີບຕໍ່ກິໂລ, ສ່ວນໜໍ່ຂາຍໃນລາຄາ 25,000 ກີບຕໍ່ກິໂລ. [5]
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ສະພາບໂດຍລວມ:
ພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ເໝາະສົມໃນການປູກຂ່າ: ພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ເໝາະສົມທີ່ສຸດ ໃນການປູກຂ່າຄວນມີລະດັບຄວາມສູງເໜືອໜ້ານ້ຳທະເລຢູ່ທີ່ 500 ຫາ 1,500 ມ. ຂ່າຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕໄດ້ດີທັງພື້ນທີ່ທົ່ງພຽງ ແລະ ຄ້ອຍຊັນ, ແຕ່ຄວາມຊັນທີ່ເໝາະສົມແມ່ນຢູ່ລະຫວ່າງ 15 ຫາ 25 ອົງສາ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ມີການຖ່າຍເທອາກາດດີຂື້ນ. ແຕ່ຖ້າປູກຂ່າເພື່ອເກັບໝາກ ສິ່ງສຳຄັນຄືບໍຄວນຕັດຕົ້ນໄມ້ໃຫຍ່ທີ່ບັງແສງແດດອອກ ເນື່ອງຈາກຕົ້ນຂ່າຄວນໄດ້ຮັບແສງປະມານຮ້ອຍ 70%
ການຄັດເລືອກສາຍພັນ: ເຫງົ້າຂ່າທີ່ຈະນຳມາຂະຫຍາຍພັນຄວນມີອາຍຸບໍ່ເກີນ 2 ຫາ 3 ປີ. [6]
ການກຽມພື້ນທີ່:
ການແກມແນວພັນ: ຄວນແຍກເຫງົ້າແກ່ ແລະ ເຫງົ້າອ່ອນອອກຈາກກັນ ໂດຍໃຫ້ມີໜໍ່ປະມານ 2 ຫາ 3 ໜໍ່ຕໍ່ເງົ້າ, ຈາກນັ້ນຕັດຮາກ, ໃບ ແລະ ລຳຕົ້ນອອກ ໂດຍຈົ່ງໄວ້ປະມານ 30 ຊມ. ເພື່ອກຽມປູກ. [6]
ເທັກນິກການປູກ: ການປູກແມ່ນຈະນຳເຫງົ້າທີ່ກຽມໄວ້ລົງໃນຂຸມປະມານ 2 ຫາ 3 ເຫງົ້າຕໍ່ຂຸມ, ໂດຍເວັ້ນໄລຍະຫ່າງລະຫວ່າງຂຸ່ມຢູ່ທີ່ 20x20 ຊມ. ຈາກນັ້ນນຳແກບປະສົມກັບດິນທີ່ຂຸດອອກມາ ແລ້ວທົມໃຫ້ແໜ້ນ. [6]
ການເບິ່ງແຍງ ແລະ ບຳລຸງຮັກສາ:
ການກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດ: ໃນໄລຍະທຳອິດຫຼັງຈາກປູກຈະກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດ 3 ຄັ້ງຕໍ່ປີ, ເມື່ອຮອດປີທີ່ 4 ຄວນກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດ 2 ຄັ້ງຕໍ່ປີ ແລະ ເມື່ອຕົ້ນກ້າອາຍຸ 7 ປີຂື້ນໄປ ຈະກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດປີລະຄັ້ງ. [6]
ການຫົດນ້ຳ: ການໃຫ້ນ້ຳຄວນໃຫ້ເດືອນ 2 ຄັ້ງ ຄື ວັນທີ່ 1 ແລະ ວັນທີ່ 16 ໂດຍຈະເປີດນ້ຳເຂົ້າປະມານເຄິ່ງມື້ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ນ້ຳຄ່ອຍໆຊມເຂົ້າໄປໃນດິນ ເມື່ອຮອດວັນທີ່ 16 ໃຫ້ໃຊ້ວິທີດຽວກັນນີ້, ແຕຖ້າຮາກສັງເກດເຫັນວ່າດິນຍັງມີຄວາມຊຸ່ມ ກໍ່ບໍ່ຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງໃຫ້ນ້ຳອີກ. [6]
ການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ: ຝຸ່ນທີ່ແນະນຳສຳຫຼັບຕົ້ນຂ່າຄື ຂີ້ໄກ່ໃຊ້ຄູ່ກັບຝຸ່ນເຄມີໃນປະລິມານເລັກນ້ອ ຕະຫຼອດໄລຍະການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ 8 ເດືອນ ແມ່ນໃນໄລຍະເດືອນທີ່ 1 ຫາ ເດືອນທີ່ 4 ໃຫ້ໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນສູດ 6-0-0, ແລະ ເດືອນທີ່ 5 ຫາ 7 ໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນສູດ 0-0-60 ໂດຍຈະໂຮຍຝຸ່ນບໍລິເວນຮອບໆຕົ້ນຂ່າ ໂດຍເວັ້ນໄລຍະຫ່າງປະມານ 10 ຊມ. ເພາະເປັນຊ່ວງທີ່ຮາກຝອຍຈະງອກອອກມາເພື່ອດູດຊັບສານອາຫານ. [6]
ການເກັບກ່ຽວ:
ການເກັບກ່ຽວເຫງົ້າ: ການຂຸດຂ່າເປັນເລື່ອງງ່າຍໂດຍສະເພາະ ເມື່ອດິນມີແກບປົນຢູ່, ທຸກຄັ້ງທີ່ຂຸດຂ່າຄວນທົມດ້ວຍແກບດຳທຸກຄັ້ງ ວິທີນີ້ບໍພຽງແຕ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ຂ່າງາມເທົ່ານັ້ນ ແຕ່ຍັງເຮັດໃຫ້ການຂຸດຂ່າໃນປີຕໍ່ໄປງ່າຍຂື້ນ. ຫຼັງຈາກໄດ້ຂ່າອອກມາແລ້ວໃຫ້ຕັດກ້ານອອກເຫຼືອໄວ້ປະມານໜຶ່ງກຳມື ແລ້ວໃຊ້ສາຍຢາງສີດລ້າງດິນອອກໃຫ້ໝົດ ຂາກນັ້ນແຊ່ຂ່າໄວ້ໃນນ້ຳສະອາດກ່ອນຈະບັນຈຸລົງໃນຖົງ ວິທີ່ນີ້ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ຂ່າສົດຢູ່ໄດ້ຫຼາຍວັນ. [6]
ການເກັບກ່ຽວໝາກ: ທຸກຄັ້ງທີເຮົາເກັບໝາຂ່າເຮາຈະເລືອກໝາກທີ່ສຸກ ແລະ ແກ່ເຕັມທີ່ແລ້ວ. [6]
ການຈັດການຫຼັງການເກັບກ່ຽວ: ນຳໝາກຂ່າເຂົ້າໃນເຕົາອົບເປັນເວລາປະມານ 12 ຫາ 24 ຊົ່ວໂມງ ໂດຍໃຫ້ແນ່ໃຈວ່າອຸ່ນຫະພູມຄົງທີ່, ຄວນພິກ ຫຼື ຄົນໝາກຂ່າທຸກໆ 30 ນາທີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແຫ້ງສະໝໍ່າສະເໝີ. ວິທີນີ້ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ສາມາດເກັບໝາກຂ່າໄວ້ໄດ້ດົນຂື້ນ, ເປັນການເພີ່ມມູນຄ່າ ແລະ ຫຼຸດຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນການເກີດເຊື້ອຣາ. [6]
ພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ເໝາະສົມໃນການປູກຂ່າ: ພື້ນທີ່ທີ່ເໝາະສົມທີ່ສຸດ ໃນການປູກຂ່າຄວນມີລະດັບຄວາມສູງເໜືອໜ້ານ້ຳທະເລຢູ່ທີ່ 500 ຫາ 1,500 ມ. ຂ່າຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕໄດ້ດີທັງພື້ນທີ່ທົ່ງພຽງ ແລະ ຄ້ອຍຊັນ, ແຕ່ຄວາມຊັນທີ່ເໝາະສົມແມ່ນຢູ່ລະຫວ່າງ 15 ຫາ 25 ອົງສາ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ມີການຖ່າຍເທອາກາດດີຂື້ນ. ແຕ່ຖ້າປູກຂ່າເພື່ອເກັບໝາກ ສິ່ງສຳຄັນຄືບໍຄວນຕັດຕົ້ນໄມ້ໃຫຍ່ທີ່ບັງແສງແດດອອກ ເນື່ອງຈາກຕົ້ນຂ່າຄວນໄດ້ຮັບແສງປະມານຮ້ອຍ 70%
ການຄັດເລືອກສາຍພັນ: ເຫງົ້າຂ່າທີ່ຈະນຳມາຂະຫຍາຍພັນຄວນມີອາຍຸບໍ່ເກີນ 2 ຫາ 3 ປີ. [6]
ການກຽມພື້ນທີ່:
ການແກມແນວພັນ: ຄວນແຍກເຫງົ້າແກ່ ແລະ ເຫງົ້າອ່ອນອອກຈາກກັນ ໂດຍໃຫ້ມີໜໍ່ປະມານ 2 ຫາ 3 ໜໍ່ຕໍ່ເງົ້າ, ຈາກນັ້ນຕັດຮາກ, ໃບ ແລະ ລຳຕົ້ນອອກ ໂດຍຈົ່ງໄວ້ປະມານ 30 ຊມ. ເພື່ອກຽມປູກ. [6]
ເທັກນິກການປູກ: ການປູກແມ່ນຈະນຳເຫງົ້າທີ່ກຽມໄວ້ລົງໃນຂຸມປະມານ 2 ຫາ 3 ເຫງົ້າຕໍ່ຂຸມ, ໂດຍເວັ້ນໄລຍະຫ່າງລະຫວ່າງຂຸ່ມຢູ່ທີ່ 20x20 ຊມ. ຈາກນັ້ນນຳແກບປະສົມກັບດິນທີ່ຂຸດອອກມາ ແລ້ວທົມໃຫ້ແໜ້ນ. [6]
ການເບິ່ງແຍງ ແລະ ບຳລຸງຮັກສາ:
ການກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດ: ໃນໄລຍະທຳອິດຫຼັງຈາກປູກຈະກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດ 3 ຄັ້ງຕໍ່ປີ, ເມື່ອຮອດປີທີ່ 4 ຄວນກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດ 2 ຄັ້ງຕໍ່ປີ ແລະ ເມື່ອຕົ້ນກ້າອາຍຸ 7 ປີຂື້ນໄປ ຈະກຳຈັດວັດສະພືດປີລະຄັ້ງ. [6]
ການຫົດນ້ຳ: ການໃຫ້ນ້ຳຄວນໃຫ້ເດືອນ 2 ຄັ້ງ ຄື ວັນທີ່ 1 ແລະ ວັນທີ່ 16 ໂດຍຈະເປີດນ້ຳເຂົ້າປະມານເຄິ່ງມື້ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ນ້ຳຄ່ອຍໆຊມເຂົ້າໄປໃນດິນ ເມື່ອຮອດວັນທີ່ 16 ໃຫ້ໃຊ້ວິທີດຽວກັນນີ້, ແຕຖ້າຮາກສັງເກດເຫັນວ່າດິນຍັງມີຄວາມຊຸ່ມ ກໍ່ບໍ່ຈຳເປັນຕ້ອງໃຫ້ນ້ຳອີກ. [6]
ການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ: ຝຸ່ນທີ່ແນະນຳສຳຫຼັບຕົ້ນຂ່າຄື ຂີ້ໄກ່ໃຊ້ຄູ່ກັບຝຸ່ນເຄມີໃນປະລິມານເລັກນ້ອ ຕະຫຼອດໄລຍະການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ 8 ເດືອນ ແມ່ນໃນໄລຍະເດືອນທີ່ 1 ຫາ ເດືອນທີ່ 4 ໃຫ້ໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນສູດ 6-0-0, ແລະ ເດືອນທີ່ 5 ຫາ 7 ໃຊ້ຝຸ່ນສູດ 0-0-60 ໂດຍຈະໂຮຍຝຸ່ນບໍລິເວນຮອບໆຕົ້ນຂ່າ ໂດຍເວັ້ນໄລຍະຫ່າງປະມານ 10 ຊມ. ເພາະເປັນຊ່ວງທີ່ຮາກຝອຍຈະງອກອອກມາເພື່ອດູດຊັບສານອາຫານ. [6]
ການເກັບກ່ຽວ:
ການເກັບກ່ຽວເຫງົ້າ: ການຂຸດຂ່າເປັນເລື່ອງງ່າຍໂດຍສະເພາະ ເມື່ອດິນມີແກບປົນຢູ່, ທຸກຄັ້ງທີ່ຂຸດຂ່າຄວນທົມດ້ວຍແກບດຳທຸກຄັ້ງ ວິທີນີ້ບໍພຽງແຕ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ຂ່າງາມເທົ່ານັ້ນ ແຕ່ຍັງເຮັດໃຫ້ການຂຸດຂ່າໃນປີຕໍ່ໄປງ່າຍຂື້ນ. ຫຼັງຈາກໄດ້ຂ່າອອກມາແລ້ວໃຫ້ຕັດກ້ານອອກເຫຼືອໄວ້ປະມານໜຶ່ງກຳມື ແລ້ວໃຊ້ສາຍຢາງສີດລ້າງດິນອອກໃຫ້ໝົດ ຂາກນັ້ນແຊ່ຂ່າໄວ້ໃນນ້ຳສະອາດກ່ອນຈະບັນຈຸລົງໃນຖົງ ວິທີ່ນີ້ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ຂ່າສົດຢູ່ໄດ້ຫຼາຍວັນ. [6]
ການເກັບກ່ຽວໝາກ: ທຸກຄັ້ງທີເຮົາເກັບໝາຂ່າເຮາຈະເລືອກໝາກທີ່ສຸກ ແລະ ແກ່ເຕັມທີ່ແລ້ວ. [6]
ການຈັດການຫຼັງການເກັບກ່ຽວ: ນຳໝາກຂ່າເຂົ້າໃນເຕົາອົບເປັນເວລາປະມານ 12 ຫາ 24 ຊົ່ວໂມງ ໂດຍໃຫ້ແນ່ໃຈວ່າອຸ່ນຫະພູມຄົງທີ່, ຄວນພິກ ຫຼື ຄົນໝາກຂ່າທຸກໆ 30 ນາທີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແຫ້ງສະໝໍ່າສະເໝີ. ວິທີນີ້ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ສາມາດເກັບໝາກຂ່າໄວ້ໄດ້ດົນຂື້ນ, ເປັນການເພີ່ມມູນຄ່າ ແລະ ຫຼຸດຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນການເກີດເຊື້ອຣາ. [6]
ໂພຊະນາການ
ຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ບັນຍາຍຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
N/A
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | 0.85 | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | Potassium 589 mg |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | 3.58 | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
ເຄດິດຮູບພາບ:
Rhizome and Shoot of Alpinia galanga. [1] Plantura [Online]. Uploaded by: Regina. Available: https://plantura.garden/uk/vegetables/galangal/galangal-overview. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
Stem and leaves of Alpinia galanga. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 28 June 2019 by: Alan Kwok and Ada Tai. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/27792066. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
Inflorescence of Alpinia galanga. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 24 May 2020 by: Agnes Trekker. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/47060957. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
Flower and young fruit of Alpinia galanga. [4] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 10 July 2024 by: Nieda. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/221735622. [Accessed: 13 August 2024].
Ripe fruit of Alpinia galanga. [5] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 25 April 2019 by: Liselle Santos. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/23040421. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
Stem and leaves of Alpinia galanga. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 28 June 2019 by: Alan Kwok and Ada Tai. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/27792066. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
Inflorescence of Alpinia galanga. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 24 May 2020 by: Agnes Trekker. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/47060957. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
Flower and young fruit of Alpinia galanga. [4] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 10 July 2024 by: Nieda. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/221735622. [Accessed: 13 August 2024].
Ripe fruit of Alpinia galanga. [5] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded 25 April 2019 by: Liselle Santos. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/23040421. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
ອ້າງອິງ:
[1] "Flora of China," eFloras, 2024. [Online]. Available: http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200028269. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
[2] "Taxon: Mitragyna speciosa," Plants of the World Online, Kew Sci-ence, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:795279-1. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
[3] "Species Page," Global Biodiversity Information Facility, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/5302225. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
[4] "Checklist of Plants in Laos," Pha Khao Lao, 2024. [Online]. Avail-able: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Checklist-plant-of-Laos-read-only-1.pdf. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
[5] "100 Non-Timber Forest Products," Pha Khao Lao, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/100_NTFPs.pdf. [Accessed: 15 May 2025].
[6]. ບຸນຈັນ ເມກອາລຸນ ແລະ ອຸລາທຳ ລາຊະສິມມາ, 2025. ເຕັກນິກການປູກຂ່າ. ສະຖາບັນຄົ້ນຄວ້າກະຊິກຳ, ປ່າໄມ້ ແລະ ພັດທະນາຊົນນະບົດ, ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າປ່າໄມ້, ໂຄງການກະສິກຳເພື່ອໂພຊະນາການ ໄລຍະ II. ໜ້າ: 1-13.
[7] "Nutritional Compositions and Phytochemical Properties of the Edible Flowers from Selected Zingiberaceae Found in Thailand," PubMed Central, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5799243/pdf/fnut-05-00003.pdf. [Accessed: May. 16, 2025].
[2] "Taxon: Mitragyna speciosa," Plants of the World Online, Kew Sci-ence, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:795279-1. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
[3] "Species Page," Global Biodiversity Information Facility, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/5302225. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
[4] "Checklist of Plants in Laos," Pha Khao Lao, 2024. [Online]. Avail-able: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Checklist-plant-of-Laos-read-only-1.pdf. [Accessed: 14 May 2025].
[5] "100 Non-Timber Forest Products," Pha Khao Lao, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://phakhaolao.la/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/100_NTFPs.pdf. [Accessed: 15 May 2025].
[6]. ບຸນຈັນ ເມກອາລຸນ ແລະ ອຸລາທຳ ລາຊະສິມມາ, 2025. ເຕັກນິກການປູກຂ່າ. ສະຖາບັນຄົ້ນຄວ້າກະຊິກຳ, ປ່າໄມ້ ແລະ ພັດທະນາຊົນນະບົດ, ສູນຄົ້ນຄວ້າປ່າໄມ້, ໂຄງການກະສິກຳເພື່ອໂພຊະນາການ ໄລຍະ II. ໜ້າ: 1-13.
[7] "Nutritional Compositions and Phytochemical Properties of the Edible Flowers from Selected Zingiberaceae Found in Thailand," PubMed Central, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5799243/pdf/fnut-05-00003.pdf. [Accessed: May. 16, 2025].
ຜູ້ສ້າງ Factsheet:
Manoluck Bounsihalath
ຜູ້ກວດສອບ Factsheet:
,





