ເລກລຳດັບທີ: 494
ລະດັບການຮວບຮວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ຂໍ້ມູນພື້ນຖານ
ປັບປູງຄັ້ງລ່າສຸດ: N/A
ໝາກຕຸມກາ
Strychnine
Strychnos nux-vomica L.
ພືດ
ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ປາມ
×
ຊື່ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ:
ໄທ: ກຣະຊີ, ໂກດກາກລີງ, ກາ ກລີງ,ຕູມກາແດງ, ຊະແລງໃຈ, ຊແລງທົມ, ຊແລງເບື່ອ, ແສງບອງ, ບົງບວຍຊີ
ກຳປູເຈຍ: ຊແລງ ຕຸດ, ຊແລງ ທົມ
ວຽດນາມ: ໂກຈີ, ກູຈີ. ມາຕຽນ
ອັງກິດ: Strychnine, Snake Wood ( Thai: krachi, kot ka kling, ka kling, tumka deng, saleng chai, saleng thom, saleng beau, seng beau, hong-buai-chee
Cambodian: slaeng touch, slaeng thom
Vietnamese: co chi, cu chi, ma tien
Chinese: ma qian zi
English: strychnine, snake woo)
ຊື່ພ້ອງ
:
Strychnos ligustrina Blume
Strychnos nux-vomica var. oligosperma Dop
Strychnos spireana Dop
Strychnos vomica St.-Lag.
Strychnos nux-vomica var. oligosperma Dop
Strychnos spireana Dop
Strychnos vomica St.-Lag.
ຊື່ສະກຸນ:
Loganiaceae
ຊະນິດໃກ້ຄຽງ:
ບັນຍາຍລັກສະນະທາງພືດສາດ:
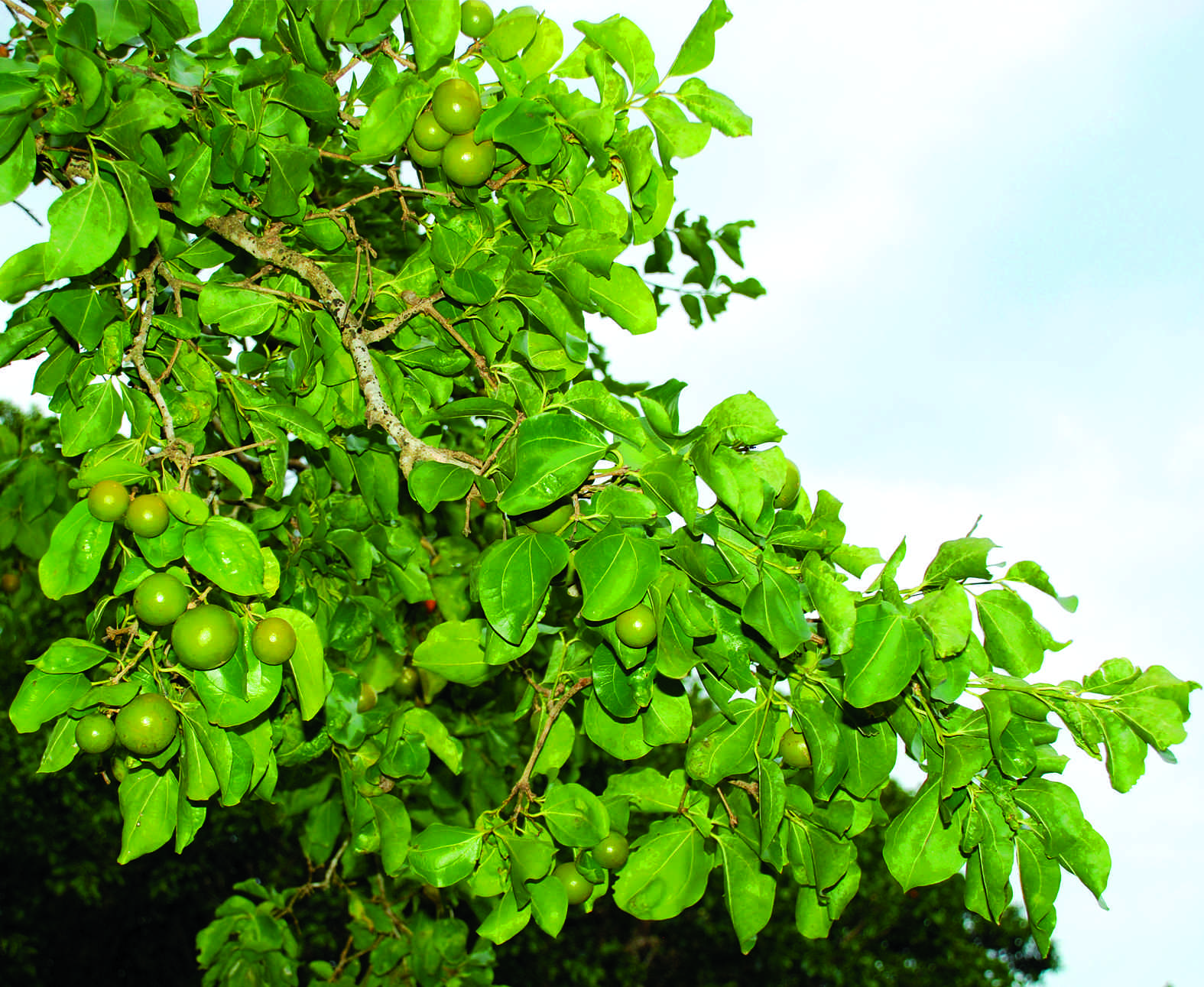
ຕົ້ນແສງເບື່ອ ເປັນຕົ້ນໄມ້ຫຼົ່ນໃບ, ສູງປະມານ 5-25 ມ, ມີເຮືອນຍອດແບນ ແລະ ມີໜ້າຕ້າງ ພຽງເອິກ 15 ຊມ. ເປືອກສີເທົ່າ, ມີກາບເປັນວົງແຫວນອ້ອມຕົ້ນ. ກິ່ງມີສີເທົ່າແກມເຫຼືອງ, ບາງຄັ້ງກໍມີໜາມ. ໃບກວ້າງ ມົນຮູບໄຂ່, ຂະໜາດ 4-10.5 x 3-8.6 ຊມ, ມີກ້ານ 5-11 ມມ, ບາງ, ຜ່ອຍ ແລະ ເຫຼື້ອມ. ກ້ານຊໍ່ດອກ ສີນ້ຳຕານຈືດ ແລະ ມີຂົນ, ຍາວ 2.5-5.5 ຊມ ແລະ ມີຫຼາຍດອກສີຂຽວປົນເຫຼືອງ ຂະໜາດ 8-13 ມມ. ໝາກ ເມື່ອສຸກ ຈະປ່ຽນຈາກສີຂຽວເຫຼືອງເຫຼື້ອມ ເປັນ ສີແດງ, ແຂງ ມີເປືອກໝາກໜາ. ໝາກມີເສັ້ນຜ່າສູນກາງ 2.5 -4 ຊມ, ທາງໃນເປັນສີຂາວ, ມີ 1 ແກ່ນ - 4 ແກ່ນ, ແຕ່ລະແກ່ນ ຍາວ 2.1-2.2 ມ. ແກ່ນຂອງມັນແປມົນ ຄ້າຍຄືແຜ່ນດິສ, ໜາ ປະມານ 6 ມມ, ມີຂົນດົກເຮັດໃຫ້ເບິ່ງຄືເຫຼື້ອມ, ບໍ່ມີກິນ ແຕ່ມີລົດຊາດຂົມຫຼາຍ. ແສງເບື່ອຊະນິດນີ້ແມ່ນຫຼົງກັນງາຍ ກັບຊະນິດ Strychnos nux-blanda ທີ່ມີໝາກໃຫຍ່ຂະໜາດ ປະມານ 5-8 ຊມ
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກ:
N/A
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນໃນລາວ
:
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
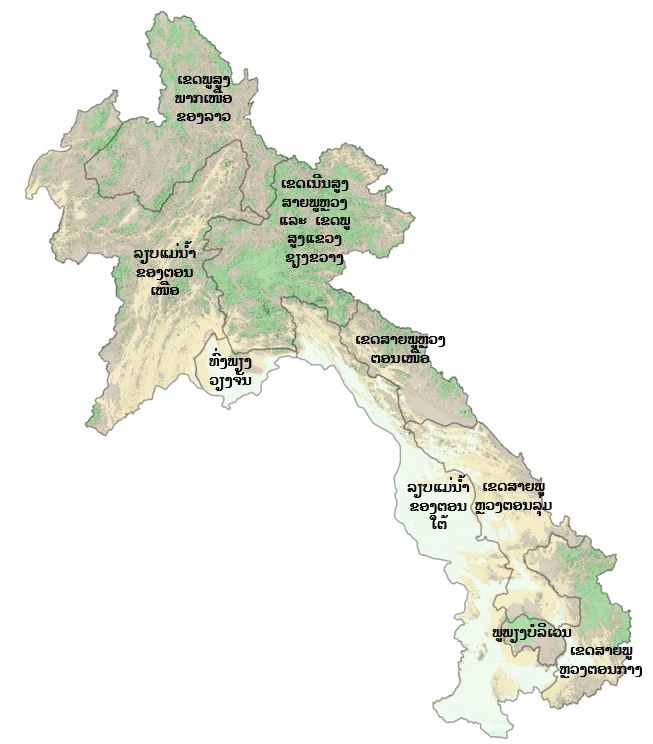
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນຕາມພູມສັນຖານ
:
ສະເພາະຖິ່ນໃນລາວ:
N/A
ຮຸກຮານ
:
N/A
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນູຮັກ IUCN
:
N/A
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນຸຮັກແຫ່ງຊາດລາວ
:
N/A
ການນຳໃຊ້
ປະເພດການນຳໃຊ້:
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ບັນຍາຍການນຳໃຊ້:
ແກ່ນໝາກແສງເບື່ອ ເປັນແຫຼ່ງຂອງທາດສະຕຣິກນີນ (strychnine) ແລະ ບຣູຊີນ (brucine) ທີ່ເປັນເສດຖະກິດ ຊຶ່ງນຳໃຊ້ເປັນທາດເບື່ອ ຫຼືເປັນຢາ. ແກ່ນຂອງມັນ ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໄປປຸງແຕ່ງ ເຮັດຢາເບື່ອ ເພື່ອໃຊ້ປະສົມໃຫ້ຢາມີລົດຂົມ ແລະ ໃຊ້ເປັນວັດຖຸດິບສຳລັບໄປຜະລິດ ຢາຜ່ອນຄາຍ ກ້າມຊີ້ນ ຫຼື ຢາປົວປະດົງຂໍ່, ປົວອາການປວດຂໍ່ກະດູກ ແລະ ອາການລ່ອຍ ມຶນຊາ. ສານສະກັດ ນັກສະໂວມີກາ (nux vomica) ມັນຖືກໃຊ້ຮ່ວມ ກັບສານສະກັດຈາກພືດອື່ນ ໃນການຜະລຶດຢາເມັດ. ນອກຈາກເນື້ອເຍື່ອຂອງເປືອກໄມ້ສົດ ແມ່ນໃຊ້ເພື່ອຕ້ານພະຍາດຂີ້ຮາກ ແລະ ທ້ອງບິດ. ໃບໃຊ້ຍ່ອງແປະປົວຝີໜອງ ແລະ ແກ່ນໃຊ້ຕົ້ມໃສ່ນໍ້ານົມ ແລ້ວຕຳໃຫ້ແຫຼກເປັນກ້ອນໜຽວ ເພື່ອແກ້ການຕິດຝິ່ນ. ແກ່ນສາມາດນຳມາກິນໄດ້ ໃນເວລາທີ່ມັນຍັງອ່ອນ ແຕ່ບໍ່ແນະນຳໃຫ້ກິນ ເພາະຖ້າກິນຫຼາຍອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ເສຍຊີວິດໄດ້.
ການປູກ ການລ້ຽງ:
N/A
ລະດູການເກັບກູ້:
ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຕ່ອງໂສ້ມູນຄ່າ:
N/A
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
N/A
ໂພຊະນາການ
ຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ບັນຍາຍຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
N/A
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | N/A | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
ເຄດິດຮູບພາບ:
ອ້າງອິງ:
NAFRI, NUoL, SNV.2007. Non - Timber forest products in the Lao PDR. A Manmual of 100 Commercial and Traditional products. The National Agriculture and Forestry Research Insititute.
Saydara, K. and Lamxay, V. 1999. Non-Timber Forest Products with commercial Potential in Lao PDR.
Smitinand, T. & Larsen, K., eds. (1993) Flora of Thailand, Vol. 6, part 3. (Royal Forest Department: Bangkok). Department of Chemistry, Capital Normal University, Beijing 100037, P.R. China.
Saydara, K. and Lamxay, V. 1999. Non-Timber Forest Products with commercial Potential in Lao PDR.
Smitinand, T. & Larsen, K., eds. (1993) Flora of Thailand, Vol. 6, part 3. (Royal Forest Department: Bangkok). Department of Chemistry, Capital Normal University, Beijing 100037, P.R. China.
ຜູ້ສ້າງ Factsheet:
ຜູ້ກວດສອບ Factsheet:
,
