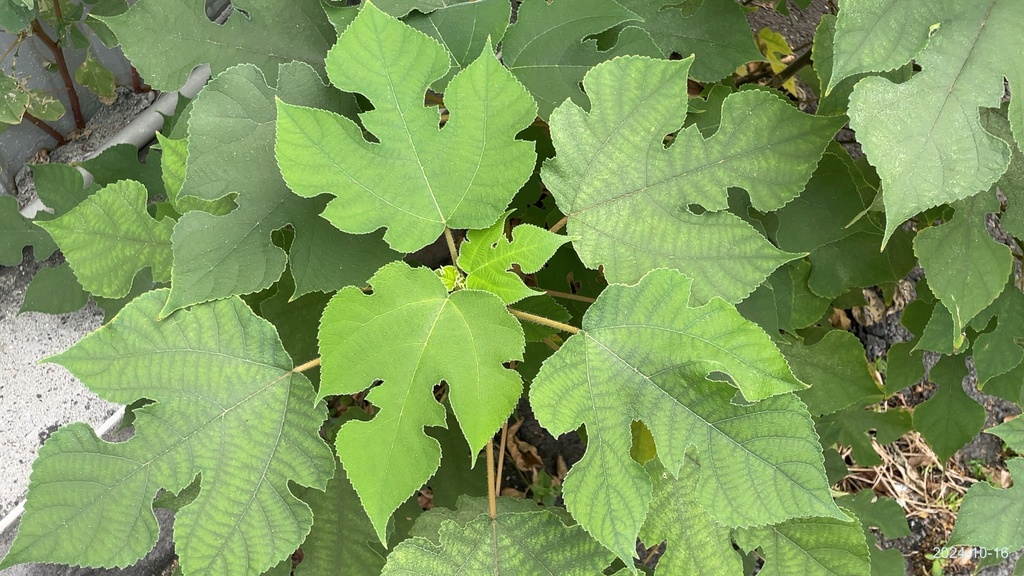
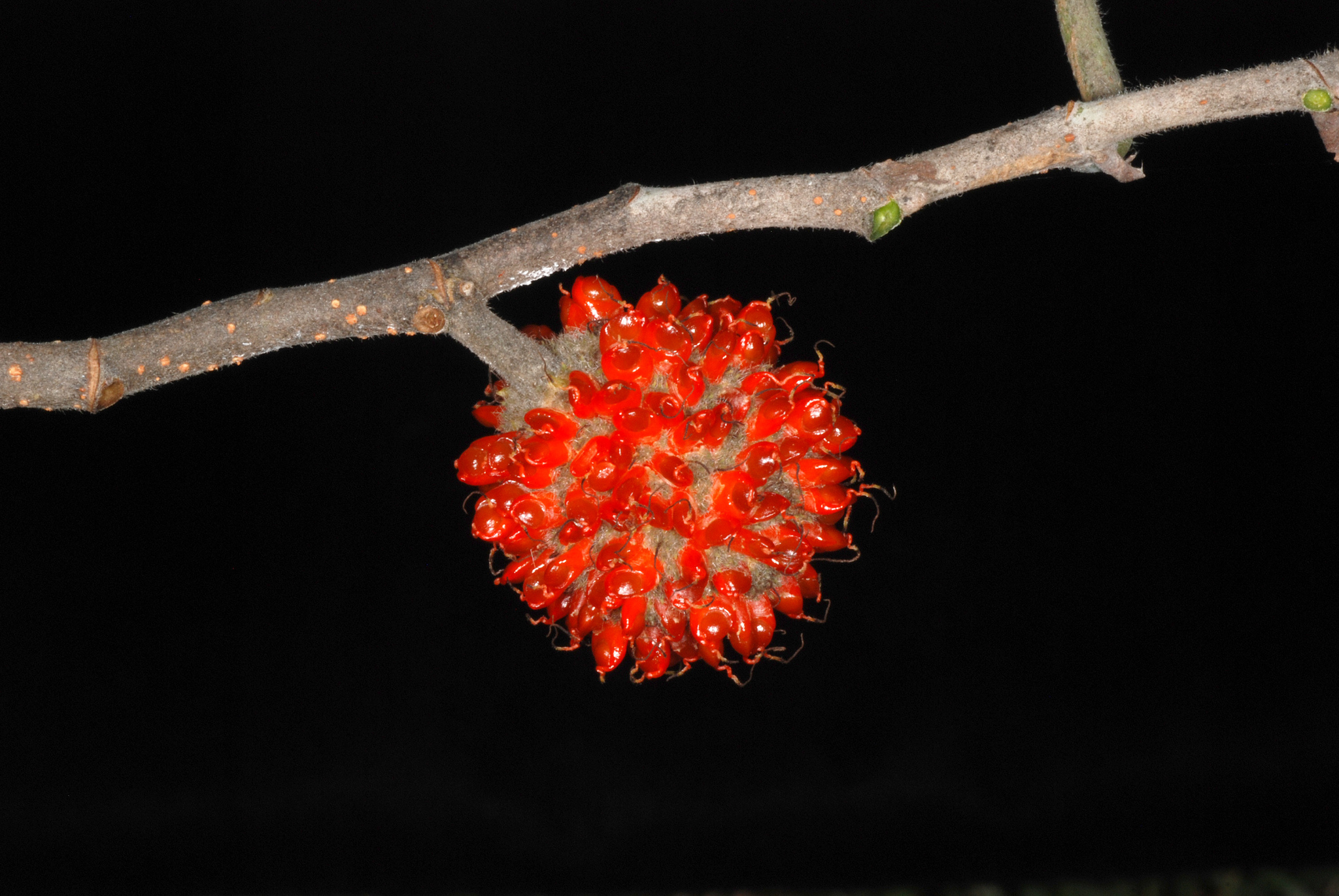
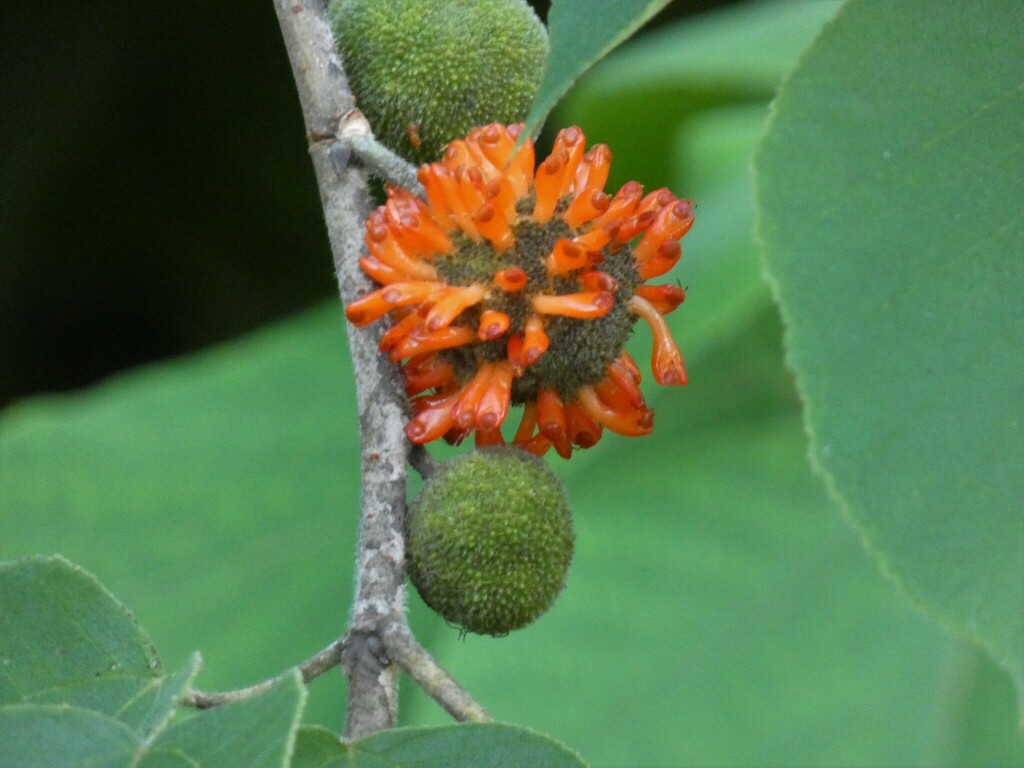
ປໍສາ
Paper Mulberry
Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) L'Hér. ex Vent.
ພືດ
ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ
ຕົ້ນໄມ້ ແລະ ປາມ
Broussonetia kazi Siebold ex Blume
Broussonetia maculata Steud.
Broussonetia nana Bureau
Broussonetia navicularis Lodd. ex Bureau
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
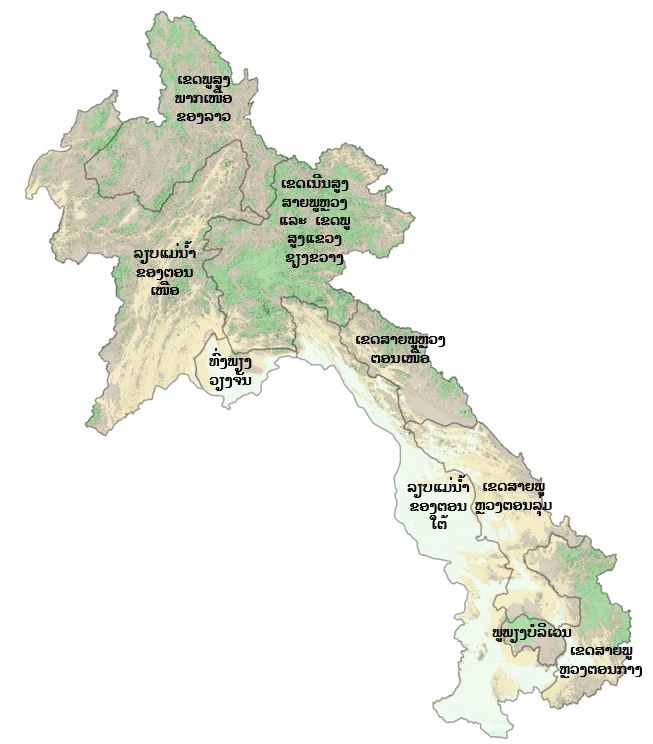
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດພູສູງສາຍພູຫຼວງ ແລະ ເຂດພູພຽງແຂວງຊຽງຂວາງ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ອຸປະກອນ ແລະ ເຄື່ອງມື
ກິດຈະກຳການກະເສດ
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ເປືອກປໍສາ ໄດ້ນຳໃຊ້ກັນໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນຕ່າງໆ ຫຼາຍສັດຕະວັດມາແລ້ວ ຄືນຳມາເຮັດເຈ້ຍ ແລະ ເຄື່ອງນຸ່ງຫົ່ມ. ຄົນຍີ່ປຸ່ນ ກໍໄດ້ນຳເອົາພືດໃນສະກຸນດຽວກັນນີ້ ມາເຮັດເຈ້ຍ “ວາຊີ” ແລະ ເຄື່ອງນຸ່ງສຳລັບເຂົ້າພິທີແຕ່ງງານ. ໃນປະເທດລາວເຮົາ ກໍໄດ້ນຳເອົາປໍສາມາເຮັດເປັນຂອງທີ່ລະນຶກຫຼາຍປະເພດຂາຍໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນ ໃນຂະນະທີ່ສົ່ງອອກເປືອກ ແລະ ເສັ້ນໃຍ. ຢູ່ແຂວງ ຊຽງຂວາງ ເພິ່ນໄດ້ນຳເອົາເປືອກປໍສາມາເຮັດເປັນເຈ້ຍສຳລັບພິທີທາງສາດສະໜາ ແລະ ເຮັດແຜ່ນຄັນຮົ່ມ. ຢູ່ແຂວງຫຼວງພະບາງ ໄດ້ນຳເອົາຂີ້ເທົ່າຈາກການເຜົາລຳຕົ້ນປໍສາ ມາຟອກເຈ້ຍທີ່ຜະລິດຈາກເປືອກປໍສາໃຫ້ຂາວ ແລະ ນຳທີ່ໃຊ້ຟອກເຈ້ຍນັ້ນ ຍັງເອົາໄປນຳໃຊ້ເປັນປຸຍສຳລັບຕົ້ນໄມ້ອີກດ້ວຍ. ນອກຈາກນນັ້ນໃບປໍສາຍັງນຳມາເປັນ ອາຫານໝູ, ງົວ, ຄວາຍ. ແກ່ນປໍສາບັນຈຸມີນ້ຳມັນ ຊຶ່ງຢູ່ຫວຽດນາມ ເພິ່ນໃຊ້ເຮັດສະບູ, ສານຂີ້ເຜິ້ງ ແລະ ຜະລິດເປັນນ້ຳມັນເຄືອບເງົາທາໄມ້. ປະຊາຊົນຢູ່ໃນຫຼາຍທ້ອງຖິ່ນໄດ້ນຳເອົາໝາກ, ໃບ, ເປືອກ ແລະ ຮາກມາໃຊ້ເປັນຢາປົວທອ້ງບິດ. ບັນຫາກ່ຽວກັບໝາກໄຂ່ຫຼັງ ກໍສາມາດປົວໄດ້ ໂດຍເອົາຮາກປໍສາ, ເມັດເຂົ້າ ແລະ ອ້ອຍດຳ ຕົ້ມປະສົມກັນແລ້ວດື່ມ. ໄມ້ປໍສາໃຊ້ສຳລັບເຮັດຟືນ ແລະ ໃຊ້ປູກເຫັດໄດ້ (ເຫັດຫູໜູ).
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ໂພຊະນາການ
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | N/A | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
Hussain, K., Shahazad, A. and Hussnain, S. 2008. An Ethnobotanical Survey of Important Wild Medicinal Plants of Hattar District Haripur, Pakistan. Ethnobotanical Leaflets 12: 29-35.
Eric C. Morgan and William A. Overholt. 2004. Wild land Weeds: Paper Mulberry, Broussonetia papyrifera. ENY-702. Entomology and Nematology. Florida Cooperative Extension Service. University of Florida IFAS.


