ເລກລຳດັບທີ: 3654
ລະດັບການຮວບຮວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ຂໍ້ມູນລະອຽດ
ປັບປູງຄັ້ງລ່າສຸດ: N/A
ໝີຄົນ
Sun Bear
Helarctos malayanus (Raffles, 1821)
ສັດ
ສັດລ້ຽງລູກດ້ວຍນົມ
×
ຊື່ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ:
ເໝືອຍ, ຫມີຫມາ ( Dog Bear, Honey Bear, Malayan Sun Bear)
ຊື່ພ້ອງ
:
Helarctos euryspilus Horsfield, 1826
Ursus malayanus Raffles, 1822
Ursus malayanus Raffles, 1822
ຊື່ສະກຸນ:
Ursidae
ຊະນິດໃກ້ຄຽງ:
ບັນຍາຍລັກສະນະທາງພືດສາດ:
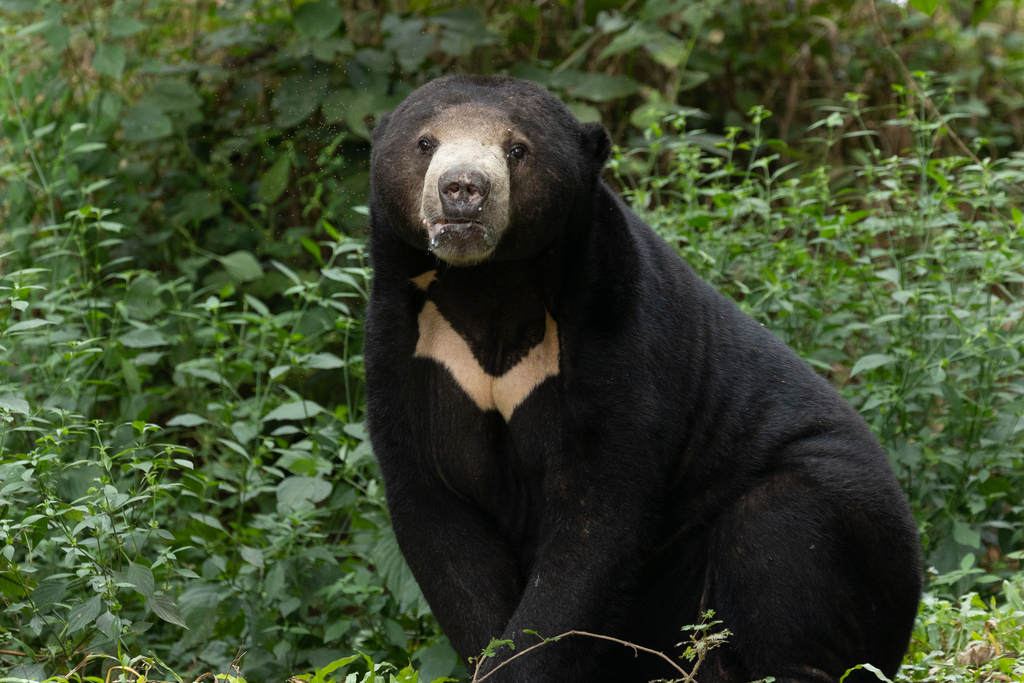
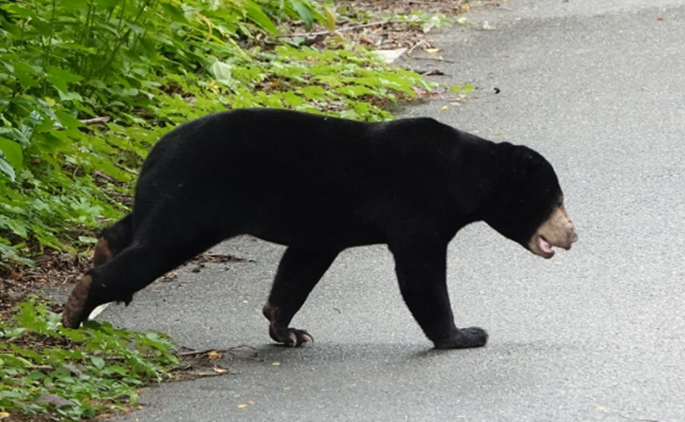
ລຳຕົວທົ່ວໄປມີສີດຳ ຫຼື ສີນ້ຳຕານເຂັ້ມ ໂດຍມີລວດລາຍເປັນຮູບໂຕ U ຫຼື ວົງມົນທີ່ມີສີຂາວ, ສີເຫລືອງ ຫລື ສີສົມທີ່ໂດດເດັ່ນຢູ່ຫນ້າເອິກ. ໂດຍປົກກະຕິແລ້ວ ເພດຜູ້ຈະມີຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່ກ່ວາເພດແມ່, ຕົວເຕັມໄວສາມາດສູງໄດ້ປະມານ 100 ຫາ 150 ຊັງຕີແມັດ ແລະ ມີນ້ຳຫນັກ 30 ຫາ 80 ກິໂລກຼາມ, ຫາງຍາວ 3 ຫາ 7 ຊັງຕີແມັດ.
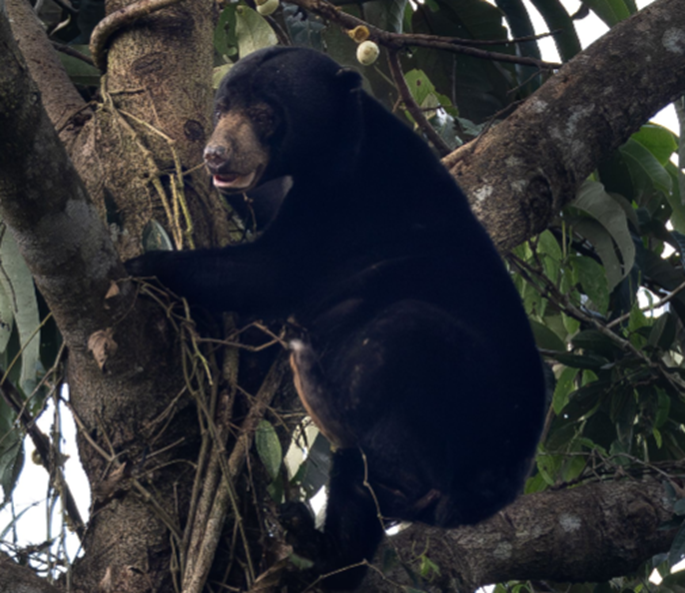
ລັກສະນະເດັ່ນ: ສັດຊະນິດນີ້ມີອຸ້ງຕີນທີ່ໃຫ່ຍ, ຂາຫນ້າໂຄ້ງ ຫັນເຂົ້າດ້ານໃນ, ມີເລັບຍາວເພື່ອໃຊ້ປີນຕົ້ນໄມ້, ປາກສັ້ນ, ຫູູນ້ອຍ ແລະ ຂົນສັ້ນ ເໝາະສຳລັບການດຳລົງຊີວິດຢູ່ເທິງຕົ້ນໄມ້. ລິ້ນຂອງມັນມີຄວາມຍາວ 20 ຫາ 25 ຊັງຕີແມັດ
ສຳລັບເລຍ ແມງໄມ້ ແລະ ນ້ຳເຜິ້ງ.
ອາຫານ: ສັດເຫລົ່ານີ້ມັກຈະກິນໝາກໄມ້ຈາກຕົ້ນໄມ້ເປັນຫລັກ. ມັນມັກກິນໝາກໄມ້ຫຼາກຫຼາຍຊະນິດ ລວມທັງສັດຂະໜາດນ້ອຍທົ່ວໄປ ເຊັ່ນ: ໂຕນົກ, ສັດເລືອຄານ, ສັດລ້ຽງລູກດ້ວຍນ້ຳນົມ...
ການປະສົມພັນ: ສັດເຫຼົ່ານີບໍ່ມີລະດູການປະສົມພັນທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ການຖືພາຈະໃຊ້ເວລາປະມານ 3 ຫາ 3.5 ເດືອນ, ຖ້າຫາກເພດແມ່ສູນເສຍລູກຂອງມັນໄປ ໂດຍປົກກະຕີແລ້ວມັນຈະສາມາດຖືພາໄດ້ອີກຄັ້ງ ພາຍໃນ 2 ຫາ 5 ອາທິດ.
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1], [2],
ລັກສະນະເດັ່ນ: ສັດຊະນິດນີ້ມີອຸ້ງຕີນທີ່ໃຫ່ຍ, ຂາຫນ້າໂຄ້ງ ຫັນເຂົ້າດ້ານໃນ, ມີເລັບຍາວເພື່ອໃຊ້ປີນຕົ້ນໄມ້, ປາກສັ້ນ, ຫູູນ້ອຍ ແລະ ຂົນສັ້ນ ເໝາະສຳລັບການດຳລົງຊີວິດຢູ່ເທິງຕົ້ນໄມ້. ລິ້ນຂອງມັນມີຄວາມຍາວ 20 ຫາ 25 ຊັງຕີແມັດ
ສຳລັບເລຍ ແມງໄມ້ ແລະ ນ້ຳເຜິ້ງ.
ອາຫານ: ສັດເຫລົ່ານີ້ມັກຈະກິນໝາກໄມ້ຈາກຕົ້ນໄມ້ເປັນຫລັກ. ມັນມັກກິນໝາກໄມ້ຫຼາກຫຼາຍຊະນິດ ລວມທັງສັດຂະໜາດນ້ອຍທົ່ວໄປ ເຊັ່ນ: ໂຕນົກ, ສັດເລືອຄານ, ສັດລ້ຽງລູກດ້ວຍນ້ຳນົມ...
ການປະສົມພັນ: ສັດເຫຼົ່ານີບໍ່ມີລະດູການປະສົມພັນທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ການຖືພາຈະໃຊ້ເວລາປະມານ 3 ຫາ 3.5 ເດືອນ, ຖ້າຫາກເພດແມ່ສູນເສຍລູກຂອງມັນໄປ ໂດຍປົກກະຕີແລ້ວມັນຈະສາມາດຖືພາໄດ້ອີກຄັ້ງ ພາຍໃນ 2 ຫາ 5 ອາທິດ.
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1], [2],
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກ:
Bangladesh, Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, Viet Nam, Singapore and China
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນໃນລາວ
:
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ພູພຽງບໍລິເວນ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ພູພຽງບໍລິເວນ
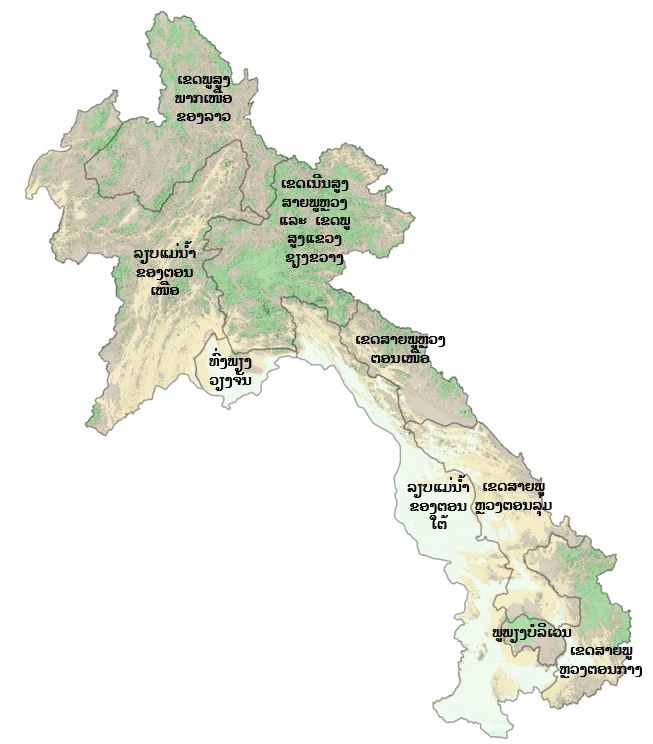
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນຕາມພູມສັນຖານ
:
ປ່າດົງດິບ
ປ່າປະສົມປ່ຽນໃບ
ປ່າໂຄກ
ປ່າປະສົມປ່ຽນໃບ
ປ່າໂຄກ

ສະເພາະຖິ່ນໃນລາວ:
ພື້ນເມືອງ
ຮຸກຮານ
:
ບໍ່ຮຸກຮານ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນູຮັກ IUCN
:
ມີຄວາມສ່ຽງສູນພັນ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນຸຮັກແຫ່ງຊາດລາວ
:
ບັນຊີທີ່ I: ຊະນິດພັນປະເພດຫວງຫ້າມ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ປະເພດການນຳໃຊ້:
ຫ້າມນຳໃຊ້
ບັນຍາຍການນຳໃຊ້:
ພວກເຮົາໃນນາມ PKL ພວກເຮົາບໍ່ສະຫໜັບສະໜູນການລ່າ ສັດຊະນິດນີ້ເນື່ອງຈາກມີຄວາມສ່ຽງສູງທີ່ຈະໃກ້ຈະສູນພັນ, ແລະ ການອານຸລັກຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍທາງຊີວະນາໆພັນຕ່າງໆ ຖືເປັນສິ່ງສຳຄັນຢ່າງຍິ່ງໃນການຮັບຮອງການມີຢູ່ ແລະ ການຢູ່ຮ່ວມກັນກັບພວກເຮົາໃນໄລ່ຍະຍາວ.
ການປູກ ການລ້ຽງ:
ຊະນິດທຳມະຊາດ
ລະດູການເກັບກູ້:
ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຕ່ອງໂສ້ມູນຄ່າ:
N/A
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ການອານຸລັກທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສ: ໝີຖືກຄຸກຄາມໂດຍການຕັດໄມ້ທຳລາຍປ່າ ແລະ ການລ່າເພື່ອການຄ້າເປັນຫຼັກ ເຊິ່ງເກີດຂື້ນໃນລະດັບທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນໄປຕາມແຕ່ລະພື້ນທີ່, ການຂ້າເນື່ອງຈາກຄວາມຂັດແຍ່ງລະຫວ່າງມະນຸດກັບໝີເປັນໄພຄຸກຄາມເພີ່ມເຕີມ, ເຖິ່ງວ່າຜົນກະທົບບໍ່ສາມາດເບິ່ງເຫັນໄດ້ຊັດເຈນກໍ່ຕາມ. ການຄ້າຂາຍໝີ ແລະ ສິ້ນສ່ວນຂອງໝີຖືວ່າເປັນໄພຄຸກຄາມທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງລະດັບທີ່ສອງຕໍ່ກັບປະຊາກອນໝີ. ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານລະດັບພູມີພາກ ມີການລາຍງານວ່າການລັກລອບລ່າໝີເພື່ອການຄ້າເປັນໄພຄຸກຄາມລະດັບປານກາງ ຫາຮຸນແຮງໃນທຸກປະເທດທີ່ມີແຫຼ່ງທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສ. [4]
ການຕິດຕາມປະຊາກອນ: ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານໃນພູມີພາກລາຍງານວ່າ ຈຳນວນປະຊາກອນຂອງໝີຫຼຸດລົງໃນ 8 ຫາ 10 ປະເທດທີ່ມີແຫຼ່ງທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສໃນປັດຈຸບັນ, ມີການປະເມີນຂະໜາດປະຊາກອນຂອງໝີທີ່ເຊື່ອຖືໄດ້ໜ້ອຍຫຼາຍ ແລະ ມີການສຶກສາຈຳນວນໜ້ອຍທີ່ສາມາດວັດແທກແນວໂນ້ມຈຳນວນປະຊາກອນໄດ້ [4]
ການຕິດຕາມປະຊາກອນ: ຜູ້ຊ່ຽວຊານໃນພູມີພາກລາຍງານວ່າ ຈຳນວນປະຊາກອນຂອງໝີຫຼຸດລົງໃນ 8 ຫາ 10 ປະເທດທີ່ມີແຫຼ່ງທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສໃນປັດຈຸບັນ, ມີການປະເມີນຂະໜາດປະຊາກອນຂອງໝີທີ່ເຊື່ອຖືໄດ້ໜ້ອຍຫຼາຍ ແລະ ມີການສຶກສາຈຳນວນໜ້ອຍທີ່ສາມາດວັດແທກແນວໂນ້ມຈຳນວນປະຊາກອນໄດ້ [4]
ໂພຊະນາການ
ຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ບັນຍາຍຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
N/A
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | N/A | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
ເຄດິດຮູບພາບ:
Sun Bear. [1] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 04 December 2022 by M. Baum garten. Available: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/4165789200. [Accessed: 02 October 2024]
Sun bear is climbing the tree. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 01 September 2024 by S. V. D. Meulen. Available: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/4946433183. [Accessed: 01 October 2024]
Sun bear. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded in May 2021 by D. Diller. Available: ttps://www.inaturalist.org/observations/80598589. [Accessed: 01 October 2024]
Sun bear is climbing the tree. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 01 September 2024 by S. V. D. Meulen. Available: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/4946433183. [Accessed: 01 October 2024]
Sun bear. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded in May 2021 by D. Diller. Available: ttps://www.inaturalist.org/observations/80598589. [Accessed: 01 October 2024]
ອ້າງອິງ:
[4] D. Pratumthong and A. m. ph. Khlaipet, “Mammals of Natural World
Heritage Thung Yai Naresuan – Huai Kha Khaeng,” Pathum Thani, Thailand: national Science Museum Thailand, 2022.
[5] Ch. R. M. Francis, “Mammals of Thailand & South – East Asia,”
Bangkok, Thailand: Asia book, 2001.
[6] Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), “Helarctos malayanus
(Raffles, 1822),” [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/2433403. [Accessed: 02 October 2024]
[7] IUCN Red List, “Sun bear,” [Online]. Available:
https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/9760/123798233. [Ac-cessed: 02 October 2024]
[8] ສະພາແຫ່ງຊາດ, “ກົດມາຍວ່າດ້ວຍສັດປ່າ (ສະບັບປັບປຸງ),” 2023.
[online]. Available: https://shorturl.at/MjWv3.
Heritage Thung Yai Naresuan – Huai Kha Khaeng,” Pathum Thani, Thailand: national Science Museum Thailand, 2022.
[5] Ch. R. M. Francis, “Mammals of Thailand & South – East Asia,”
Bangkok, Thailand: Asia book, 2001.
[6] Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), “Helarctos malayanus
(Raffles, 1822),” [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/2433403. [Accessed: 02 October 2024]
[7] IUCN Red List, “Sun bear,” [Online]. Available:
https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/9760/123798233. [Ac-cessed: 02 October 2024]
[8] ສະພາແຫ່ງຊາດ, “ກົດມາຍວ່າດ້ວຍສັດປ່າ (ສະບັບປັບປຸງ),” 2023.
[online]. Available: https://shorturl.at/MjWv3.
ຜູ້ສ້າງ Factsheet:
ຜູ້ກວດສອບ Factsheet:
,



