ເລກລຳດັບທີ: 3580
ລະດັບການຮວບຮວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ຂໍ້ມູນພື້ນຖານ
ປັບປູງຄັ້ງລ່າສຸດ: 2024-10-19
ລີງຜົມແບ່ງ
Assamese Macaque
Macaca assamensis McClelland, 1840
ສັດ
ສັດລ້ຽງລູກດ້ວຍນົມ
×
ຊື່ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ:
ລີງອາຊາມ ( Eastern Assamese Macaque, Assamese Macaque, Western Assamese Macaque, Western Assamese Macaque and pelops)
ຊື່ພ້ອງ
:
Macaca coolidgei Osgood, 1932
Macaca macclellandii (Gray, 1846)
Macaca problematicus (Gray, 1870)
Macaca sikimensis (Hodgson, 1867)
Macacus assamensis (MacClelland, 1839)
Macacus pelops Hodgson, 1840
Macaca macclellandii (Gray, 1846)
Macaca problematicus (Gray, 1870)
Macaca sikimensis (Hodgson, 1867)
Macacus assamensis (MacClelland, 1839)
Macacus pelops Hodgson, 1840
ຊື່ສະກຸນ:
Cercopithecidae
ຊະນິດໃກ້ຄຽງ:
ລີງກັງ/ Pig-tailed Macaque
ລີງເສນ/ Stump-tailed Macaque
ລີງຫາງຍາວ/ Long-tailed Macaque
ລີງວອກ/ Rhesus Macaque
ລີງເສນ/ Stump-tailed Macaque
ລີງຫາງຍາວ/ Long-tailed Macaque
ລີງວອກ/ Rhesus Macaque
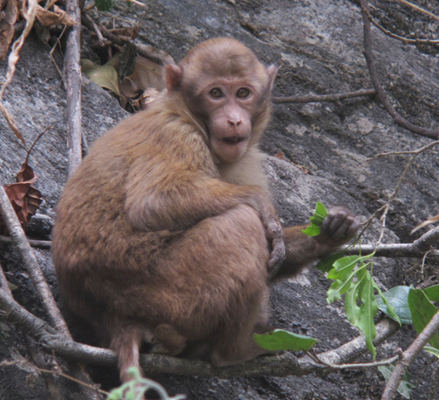
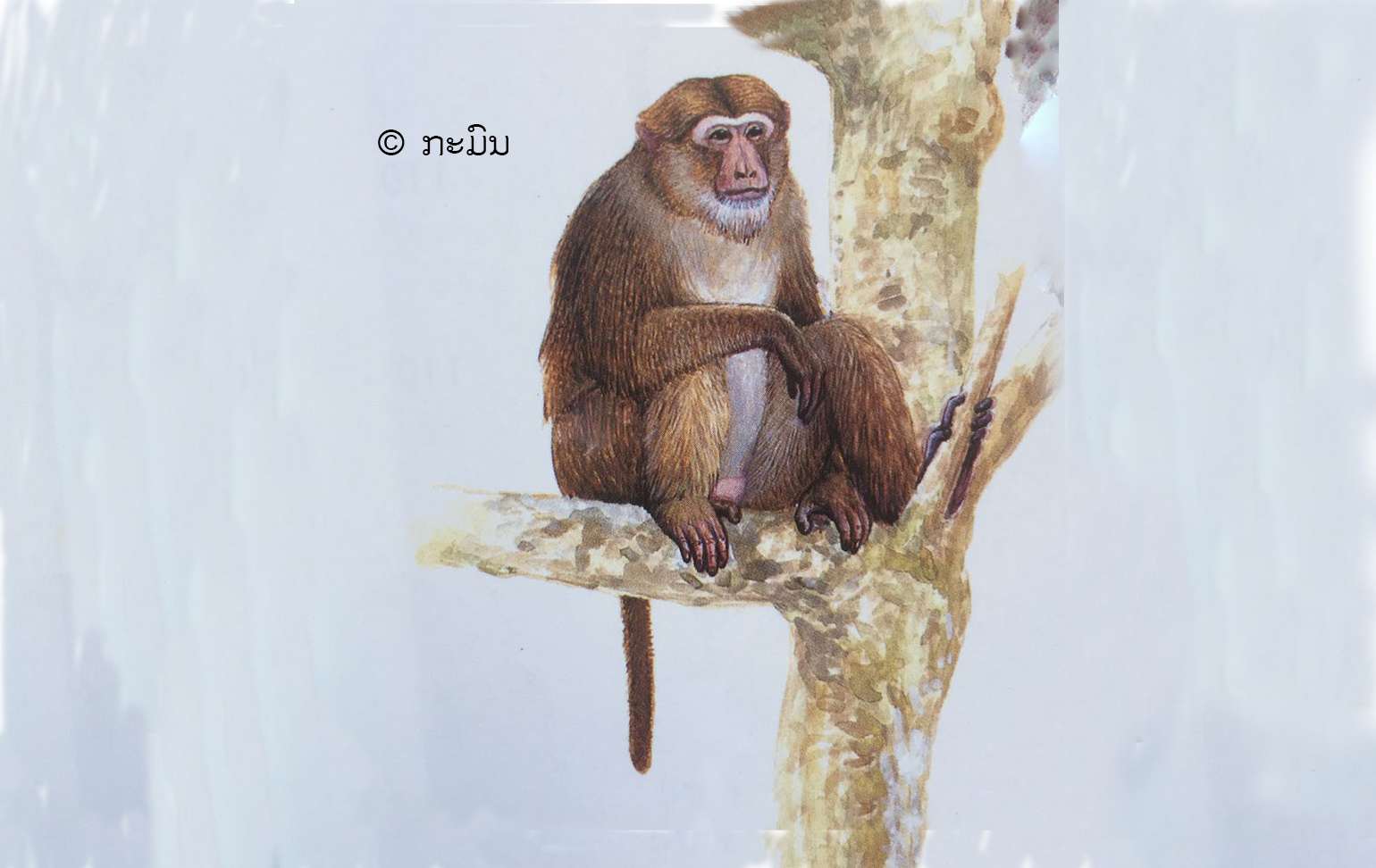
ບັນຍາຍລັກສະນະທາງພືດສາດ:
ຫົວ ແລະ ລາວຍາວ: 51-63 ຊມ. ຫາງຍາວ: 20-38 ຊມ.
ຈຳແນກໄດ້ຈາກລີງອື່ນໆ ບ່ອນທີ່ມັນມີຂົນປົກຄຸມໜາ ແລະ ຫາງຢ່ອນທີ່ຍາວປະມານເຄິ່ງຂອງສ່ວນຫົວ-ລຳໂຕ, ມັນຈະຄ້າຍຄືກັບລີງວອກ, ແຕ່ອາດຈະຈຳແນກໄດ້ຈາກທີ່ມັນມີສີອອກໝົ່ນ ຫຼື ອອກນໍ້າຕານ, ໜຶ່ງສ່ວນສີ່ຂອງລໍາໂຕ, ພາກສ່ວນນີ້ຂອງລີງວອກຈະອອກສີແດງຕັດກັນກັບສີຈາງ ທີ່ຢູ່ທາງພາກສ່ວນໜ້າຢ່າງຈະແຈ້ງ. ລັກສະນະທີ່ຈໍາແນກໄດ້ ຄືມີຂົນສັ້ນເປັນຕອນຢູ່ຂະມ່ອມ, ທາງດ້ານເທິງຂອງລໍາໂຕປ່ຽນເປັນ ຫຼາຍສີຄືສີອອກແດງ, ນໍ້າຕານ ຫຼື ດໍາ.
ອຸປະນິໄສ: ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສຂອງມັນຈະຢູ່ເຮືອນຍອດທີ່ສູງກວ່າລີງກັງ ແລະ ລີງເສນ, ແຕ່ໃນເຂດທີ່ບໍ່ມີສິ່ງ ລົບກວນ, ມັນຈະລົງຫາກິນຢູ່ຕາມແຄມນ້ຳຄືກັນກັບລີງວອກ.
ສຽງຮ້ອງ: ມີສຽງຫຼາຍແບບມີລັກສະນະເປັນສຽງດັງຄືສຽງດົນຕີປີໂອມັກ, ຮ້ອງລື້ມຄືນຫຼາຍເທື່ອ, ການຮ້ອງນີ້ໃຫ້ທຽບໃສ່ກັບໄລຍະປ່ອຍລົມຂອງເບຼກລົດຂົນສົ່ງ, ເຊິ່ງອາດເປັນລັກສະນະທີ່ຈໍາແນກຊະນິດທີ່ມີຢູ່ໃນ ສປປ ລາວ
ຖິ່ນອາໄສ: ປ່າຕາມພູຕໍາທີ່ມີຄວາມສູງລະດັບຕັ້ງແຕ່ 500 ມ ຂຶ້ນໄປ, ປົກກະຕິຈະເປັນລີງທີ່ມີຫຼາຍທີ່ສຸດ ໃນພູ ແລະ ສາຍພູ. ມັນຍັງອາໄສຢູ່ຕາມພູເຂົາຫີນປູນລົງມາເຖິງລະດັບ 300 ມ, ຜ່ານມາໄດ້ບັນທຶກໄວ້ມີຢູ່ທີ່ເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນແຫ່ງຊາດດົງຫົວສາວ.
ຈຳແນກໄດ້ຈາກລີງອື່ນໆ ບ່ອນທີ່ມັນມີຂົນປົກຄຸມໜາ ແລະ ຫາງຢ່ອນທີ່ຍາວປະມານເຄິ່ງຂອງສ່ວນຫົວ-ລຳໂຕ, ມັນຈະຄ້າຍຄືກັບລີງວອກ, ແຕ່ອາດຈະຈຳແນກໄດ້ຈາກທີ່ມັນມີສີອອກໝົ່ນ ຫຼື ອອກນໍ້າຕານ, ໜຶ່ງສ່ວນສີ່ຂອງລໍາໂຕ, ພາກສ່ວນນີ້ຂອງລີງວອກຈະອອກສີແດງຕັດກັນກັບສີຈາງ ທີ່ຢູ່ທາງພາກສ່ວນໜ້າຢ່າງຈະແຈ້ງ. ລັກສະນະທີ່ຈໍາແນກໄດ້ ຄືມີຂົນສັ້ນເປັນຕອນຢູ່ຂະມ່ອມ, ທາງດ້ານເທິງຂອງລໍາໂຕປ່ຽນເປັນ ຫຼາຍສີຄືສີອອກແດງ, ນໍ້າຕານ ຫຼື ດໍາ.
ອຸປະນິໄສ: ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສຂອງມັນຈະຢູ່ເຮືອນຍອດທີ່ສູງກວ່າລີງກັງ ແລະ ລີງເສນ, ແຕ່ໃນເຂດທີ່ບໍ່ມີສິ່ງ ລົບກວນ, ມັນຈະລົງຫາກິນຢູ່ຕາມແຄມນ້ຳຄືກັນກັບລີງວອກ.
ສຽງຮ້ອງ: ມີສຽງຫຼາຍແບບມີລັກສະນະເປັນສຽງດັງຄືສຽງດົນຕີປີໂອມັກ, ຮ້ອງລື້ມຄືນຫຼາຍເທື່ອ, ການຮ້ອງນີ້ໃຫ້ທຽບໃສ່ກັບໄລຍະປ່ອຍລົມຂອງເບຼກລົດຂົນສົ່ງ, ເຊິ່ງອາດເປັນລັກສະນະທີ່ຈໍາແນກຊະນິດທີ່ມີຢູ່ໃນ ສປປ ລາວ
ຖິ່ນອາໄສ: ປ່າຕາມພູຕໍາທີ່ມີຄວາມສູງລະດັບຕັ້ງແຕ່ 500 ມ ຂຶ້ນໄປ, ປົກກະຕິຈະເປັນລີງທີ່ມີຫຼາຍທີ່ສຸດ ໃນພູ ແລະ ສາຍພູ. ມັນຍັງອາໄສຢູ່ຕາມພູເຂົາຫີນປູນລົງມາເຖິງລະດັບ 300 ມ, ຜ່ານມາໄດ້ບັນທຶກໄວ້ມີຢູ່ທີ່ເຂດປ່າສະຫງວນແຫ່ງຊາດດົງຫົວສາວ.
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກ:
Native to Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand, Viet Nam
Global distribution between 2003 to 2024. Source: [7]
Global distribution between 2003 to 2024. Source: [7]
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນໃນລາວ
:
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດພູສູງສາຍພູຫຼວງ ແລະ ເຂດພູພຽງແຂວງຊຽງຂວາງ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກກາງ
ເຂດພູສູງສາຍພູຫຼວງ ແລະ ເຂດພູພຽງແຂວງຊຽງຂວາງ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກເໜືອ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງພາກກາງ
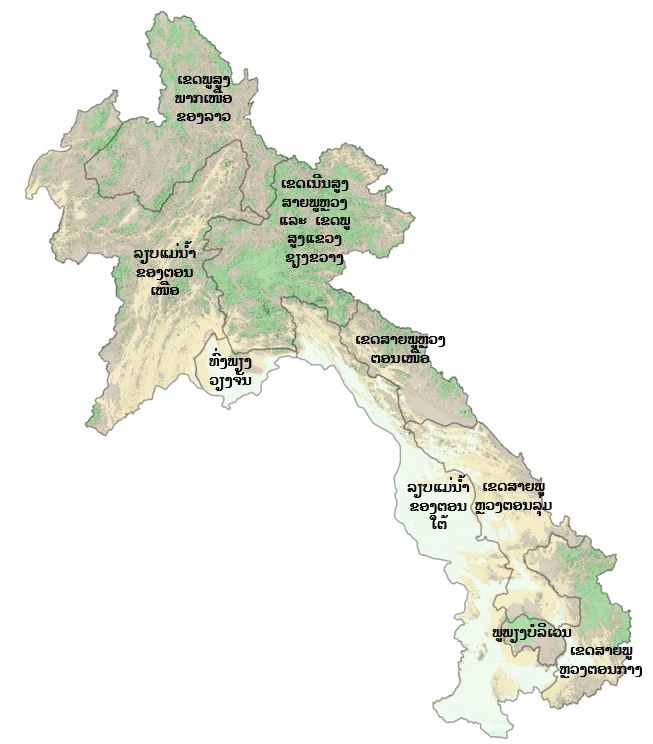
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນຕາມພູມສັນຖານ
:
ປ່າດົງດິບ
ປ່າໂຄກ
ປ່າໄມ້ປ່ອງ
ຜາຫີນ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າແກ່
ປ່າໂຄກ
ປ່າໄມ້ປ່ອງ
ຜາຫີນ
ປ່າເຫຼົ່າແກ່

ສະເພາະຖິ່ນໃນລາວ:
ພື້ນເມືອງ
ຮຸກຮານ
:
ບໍ່ຮຸກຮານ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນູຮັກ IUCN
:
ໃກ້ຖືກຄຸກຄາມ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນຸຮັກແຫ່ງຊາດລາວ
:
ບັນຊີທີ່ I: ຊະນິດພັນປະເພດຫວງຫ້າມ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ປະເພດການນຳໃຊ້:
ຫ້າມນຳໃຊ້
ບັນຍາຍການນຳໃຊ້:
ການປູກ ການລ້ຽງ:
ຊະນິດທຳມະຊາດ
ລະດູການເກັບກູ້:
ມັງກອນ
ກຸມພາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ກຸມພາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຕ່ອງໂສ້ມູນຄ່າ:
N/A
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
N/A
ໂພຊະນາການ
ຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ບັນຍາຍຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
N/A
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | N/A | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
ເຄດິດຮູບພາບ:
Adult Macaca assamensis. [1] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded in April 2023 by: ralf_buerglin. Available: www.inaturalist.org/observations/154054344. [Accessed: 22 August 2024]
Macaca assamensis from the side. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded in November 2020 by: Ayuwat. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/228390081 [Accessed: 22 August 2024]
Younger Macaca assamensis. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded in June 2023 by: paulkingsnorth Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/166243050 [Accessed: 22 August 2024]
Macaca assamensis from the side. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded in November 2020 by: Ayuwat. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/228390081 [Accessed: 22 August 2024]
Younger Macaca assamensis. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded in June 2023 by: paulkingsnorth Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/166243050 [Accessed: 22 August 2024]
ອ້າງອິງ:
1] GBIF [Online]. Uploaded on 28 October 2017 by R. Bürglin. Available: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/4080980225 [22.08.2024]
[2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on November 2020 by Ayuwat. Availa-ble: https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/228390081 [Accessed: 22.08.2024]
[3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on July 2023 by P Kingsnorth. Availa-ble: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/166243050 [Accessed: 22.08.2024]
[4] D. Prathumtong and A. P. Khlaipet, “Mammals of Natural world her-itage Thung Yai Naresuan – Huai Kha Khaeng,” Pahum Thani: National Science Museum Thailand. 2022
[5] O. V. Schülke, D. N. Pesek, J. Brigham, Whitman & J. L. Ostner (2011) Ecology of Assamese Macaques (Macaca assamensis) at Phu Phie-Wildlife sanctuary, Thailand, Journal of Wildlife in Thailand Vol.18 No.1 [online]. Available: https://thaiscience.info/Journals/Article/JWIT/10809073.pdf [Accessed: 22.08.2024]
[2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on November 2020 by Ayuwat. Availa-ble: https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/228390081 [Accessed: 22.08.2024]
[3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on July 2023 by P Kingsnorth. Availa-ble: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/166243050 [Accessed: 22.08.2024]
[4] D. Prathumtong and A. P. Khlaipet, “Mammals of Natural world her-itage Thung Yai Naresuan – Huai Kha Khaeng,” Pahum Thani: National Science Museum Thailand. 2022
[5] O. V. Schülke, D. N. Pesek, J. Brigham, Whitman & J. L. Ostner (2011) Ecology of Assamese Macaques (Macaca assamensis) at Phu Phie-Wildlife sanctuary, Thailand, Journal of Wildlife in Thailand Vol.18 No.1 [online]. Available: https://thaiscience.info/Journals/Article/JWIT/10809073.pdf [Accessed: 22.08.2024]
ຜູ້ສ້າງ Factsheet:
ຜູ້ກວດສອບ Factsheet:
,



