ເລກລຳດັບທີ: 2329
ລະດັບການຮວບຮວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ເກີອບສົມບູນ
ປັບປູງຄັ້ງລ່າສຸດ: 2025-02-11
ກ້ວຍປ່າ
Wild Banana
Musa acuminata Colla
ພືດ
ພືດລົ້ມລຸກ
ຜັກ ແລະ ພືດລົ້ມລຸກ
×
ຊື່ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ:
( Cavendish banana, Chinese banana, Edible Banana and banana)
ຊື່ພ້ອງ
:
Musa acuminata var. burmannicoides DeLanghe
Musa brieyi DeWild.
Musa cavendishii Lamb. ex Paxton
Musa chinensis Lamb.
Musa chinensis Lamb. ex Paxton
Musa corniculata Kurz
Musa sapientum var. rio
Musa simiarum Kurz
Musa sinensis Sagot
Musa sinensis Sagot ex Baker
Musa brieyi DeWild.
Musa cavendishii Lamb. ex Paxton
Musa chinensis Lamb.
Musa chinensis Lamb. ex Paxton
Musa corniculata Kurz
Musa sapientum var. rio
Musa simiarum Kurz
Musa sinensis Sagot
Musa sinensis Sagot ex Baker
ຊື່ສະກຸນ:
Musaceae
ຊະນິດໃກ້ຄຽງ:
ກ້ວຍນ້ຳ / Kluai Nam Wa
ບັນຍາຍລັກສະນະທາງພືດສາດ:
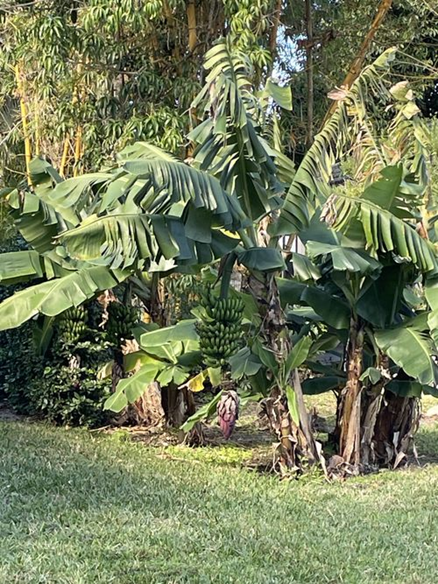
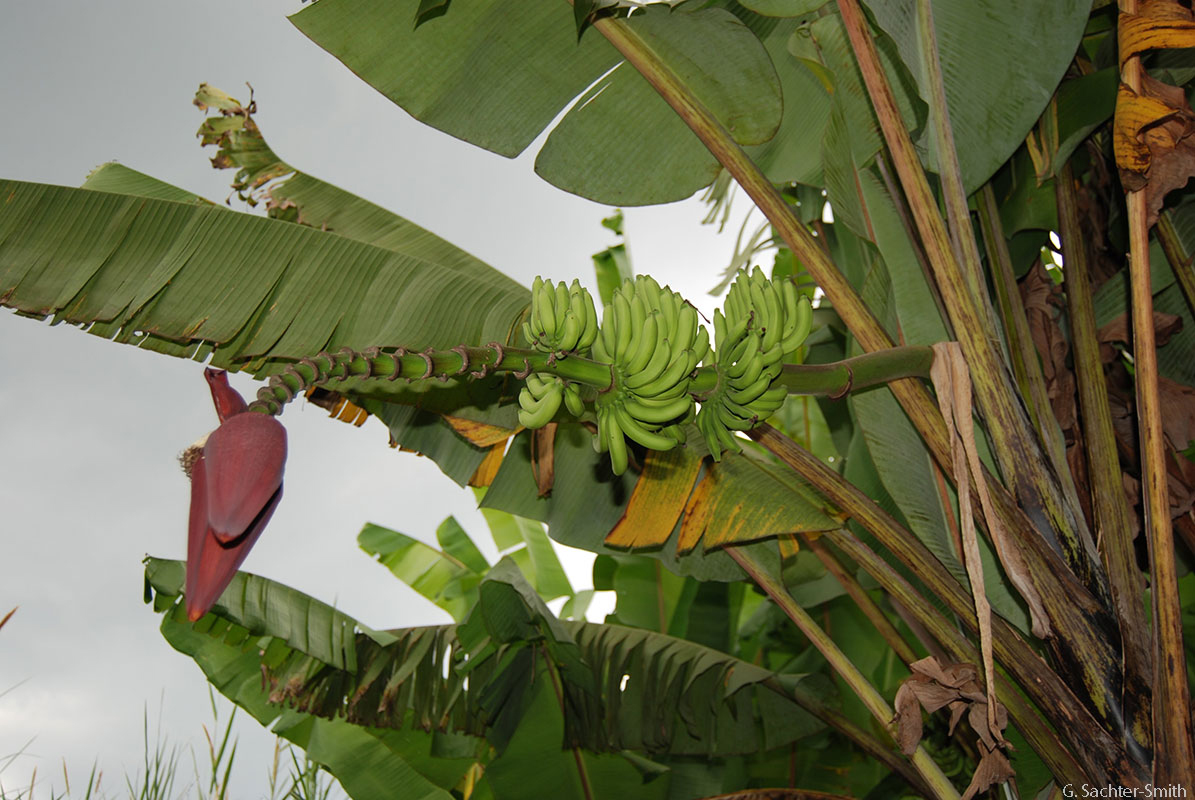
ພືດຊະນິດນີ້ມີລໍາຕົ້ນທຽມສີຂຽວ ທີ່ມີຈຸດສີດຳ, ສູງປະມານ 4,8 ມ., ກາບໃບ ແລະ ກ້ານໃບມີສານເຄີອບຄ້າຍຂີ້ເຜິ້ງເອີ້ນວ່າ ພູອີໂນສ (pruinose), ຍາວປະມານ 80 ຊມ, ຂອບໃບຕັ້ງຊື່ ຫຼື ແຜ່ກວ້າງ, ໂນໃບມີປີກບາງ ແລະ ແຫ້ງ. ແຜ່ນໃບດ້ານເທິງມີສີຂຽວ, ຮູບຂອບຂະໜານ, ຍາວ 1,9 ຫາ 2,3 ມ, ກວ້າງ 50 ຫາ 70 ຊມ, ໂຄນໃບເປັນຮູບຫົວໃຈ ແລະ ບໍ່ລຽບ ໂດຍເສັ້ນກາງໃບດ້ານເທິງເປັນສີຂຽວ ແລະ ດ້ານລຸ່ມເປັນສີຂາວປົນເຫຼືອງ. ຊໍ່ດອກສາມາດໂຄ້ງງໍໄປດ້ານຫຼັງ ໂດຍຮອງຮັບດ້ວຍກ້ານດອກ ເຊິ່ງປົກກະຕິຈະມີຂົນ, ໃບປະດັບ (ໂຄງສ້າງຄ້າຍໃບຊ່ວຍປ້ອງກັນດອກ), ສີແດງສົດ ຫາ ສີມ່ວງເຂັ້ມ ບາງຄັ້ນມີສີເຫຼືອງບໍລິເວນປາຍຊໍ່, ໃບປະດຫບຮູບໄຂ່, ປາຍແຫຼມ. ດອກເພດຜູ້ມີປະມານ 20 ດອກ, ຈັບຮຽງກັນເປັນສອງແຖວ, ກາບດອກມີສີຂາວ ຫຼື ສີຄີມ, ປາຍເປັນສີເຫຼືອອ່ອນ,ຍາວ 3,5 ຫາ 4 ຊມ., ປາຍງໍ ແລະ ມີຂົນ, ກາບດ້ານໃນມີຄວາມຍາວໜ້ອຍກ່ວາກີບນອກເຄິ່ງໜຶ່ງ ແລະ ມີປາຍແສກຕື້ນ. ໝາກມີລັກສະນະເປັນຊໍ່, ຍາວປະມານ 1,2 ມ., ກ້ານຍາວປະມານ 70 ຊມ. ແລະ ກວ້າງ 4 ຊມ., ປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍຂົນສີຂາວ. ໝາກມີລັກສະນະໂຄ້ງງໍ, ສີຂຽວ ຫາສີເຫຼືອງປົນຂຽວ ແລະ ມີ 5 ມຸມເມື່ອໝາກຍັງອ່ອນ, ແຕ່ເມື່ອໝາກສຸກຈະເປັນເປັນຮູບຊົງກະບອກ ແລະ ຍາວປະມານ 9 ຊມ. ກ້ວຍປ່າຈະມີແກ່ນຫຼາຍ, ແຕ່ຖ້ານຳມາປູກຈະບໍ່ມີແກ່ນ, ແກ່ນສີນ້ຳຕານແປ ແລະ ມີເສັ້ນຜ່າສູນກາງ 5 ຫາ 6 ມມ.
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1], [4]
ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [1], [4]
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກ:
Native to Andaman Is., Bangladesh, Borneo, China, India, Jawa, Laos, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Myanmar, Nicobar Is., Philippines, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Thailand, Vietnam. [2]
ຊະນິດພັນພື້ນໃນໝູ່ເກາະອັນດາມັນ, ບັງກາເດດ, ເບີນຽວ, ຈີນ, ອິນເດຍ, ຊາວາ, ລາວ, ເກາະຊຸດານ້ອຍ, ມາລາຍາ, ມຽນມາ, ເກາະນີໂຄບາ, ຟີລິບປິນ, ສີລັງກາ, ສຸລາເວຊີ, ສຸມາຕາ, ໄທ ແລະ ຫວຽດນາມ. [2]
Global distribution between 2004 to 2024. Source: [3]
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກລະຫວ່າງປີ 2004 ຫາ 2024. ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [3]
ຊະນິດພັນພື້ນໃນໝູ່ເກາະອັນດາມັນ, ບັງກາເດດ, ເບີນຽວ, ຈີນ, ອິນເດຍ, ຊາວາ, ລາວ, ເກາະຊຸດານ້ອຍ, ມາລາຍາ, ມຽນມາ, ເກາະນີໂຄບາ, ຟີລິບປິນ, ສີລັງກາ, ສຸລາເວຊີ, ສຸມາຕາ, ໄທ ແລະ ຫວຽດນາມ. [2]
Global distribution between 2004 to 2024. Source: [3]
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກລະຫວ່າງປີ 2004 ຫາ 2024. ແຫຼ່ງທີ່ມາ: [3]
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນໃນລາວ
:
ເຂດພູສູງພາກເໜືອຂອງລາວ
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກໃຕ້
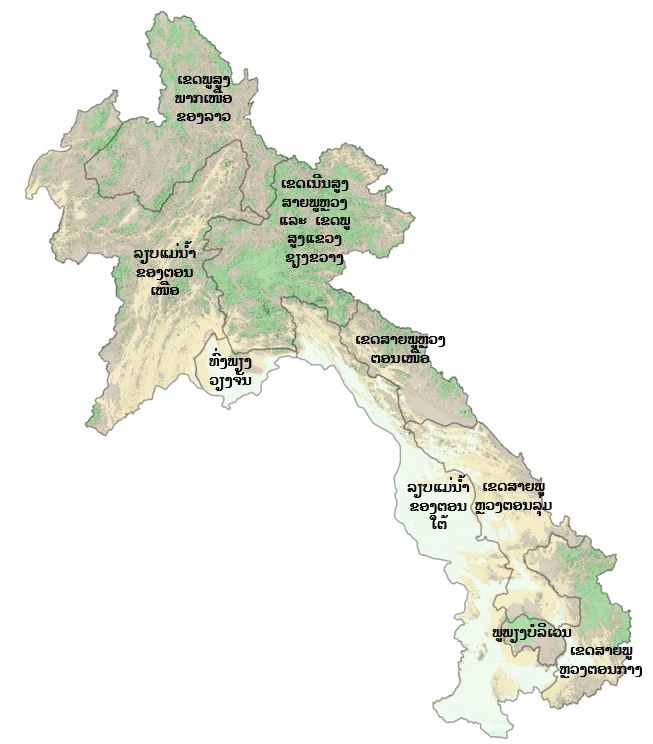
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນຕາມພູມສັນຖານ
:
ປ່າດົງດິບ
ປ່າປູກ
ແຄມຝັ່ງນໍ້າ
ປ່າປູກ
ແຄມຝັ່ງນໍ້າ

ສະເພາະຖິ່ນໃນລາວ:
ພື້ນເມືອງ
ຮຸກຮານ
:
ບໍ່ຮຸກຮານ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນູຮັກ IUCN
:
ມີຄວາມສ່ຽງໜ້ອຍສຸດ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນຸຮັກແຫ່ງຊາດລາວ
:
N/A
ການນຳໃຊ້
ປະເພດການນຳໃຊ້:
ອຸປະກອນ ແລະ ເຄື່ອງມື
ວັດທະນະທຳ ແລະ ຮີດຄອງ
ອາຫານ
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ວັດທະນະທຳ ແລະ ຮີດຄອງ
ອາຫານ
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ບັນຍາຍການນຳໃຊ້:
ອາຫານ: ໝາກສຸກສາມາດກິນໄດ້. [7]
ສະໝຸນໄພ: ໃນຕຳລາຢາພື້ນເມືອງຂອງລາວ ສ່ວນຕ່າງໆຂອງກ້ວຍປ່າ ຖືກນຳໃຊ້ສຳລັບປະໂຫຍດທາງການແພດ ເຊັ່ນ ດອກ (ປີ) ໃຊ້ຮັກສາພະຍາດຫຼອດລົມອັກເສບ, ເບົາຫວານ, ໂຣກບິດ ແລະ ແຜ່ໃນກະເພາະ. ໃບໃຊ້ພອກບໍລິເວນທີ່ຖືກໄຟໄໝ້ ແລະ ພະຍາດທາງຜິວໜັງອື່ນໆ. ຮາກໃຊ້ຮັກສາອາການອາຫານບໍ່ຍ່ອຍ ແລະ ຢາງຂອງຕົ້ນໃຊ້ຮັກສາພະຍາດຕ່າງໆ ເຊັ່ນ ລິດສີດວງທະວານ, ແມງໄມ້ກັດ, ພະຍາດເຮື້ອນ, ພະຍາດຮິວທິເຣຍ, ລົມບ້າໝູ, ໄຂ້ເລືອດອອກ ແລະ ບັນຫາອາຫານບໍ່ຍ່ອຍ. [7]
ວັດທະນະທຳ: ໃບກ້ວຍມີປະໂຫຍດຫຼາຍໃນວັດທະນະຂອງລາວ ໂດຍສະເພາະໃຊ້ໃນພິທີບາສີສູ່ຂວັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ. [7]
ເຄື່ອງມື ແລະ ອຸປະກອນ: ໃບຕອງສາມາດນຳມາໃຊ້ເປັນຈານຮອງ, ຄຸມອາຫານ, ຫໍ່ອາຫານ, ເປັນທີ່ບັງແດດ, ໃຫ້ຮົ່ມ ແລະ ມຸງຫຼັງຄາ. [7]
ຂໍ້ຄວນລະວັງ: ການບໍລິໂພກກ້ວຍປ່າທີ່ມີແກ່ນອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ລຳໄສ້ອຸດຕັນໄດ້ ບາງກໍລະນີໃນລາວ. ຈາການສຶກສາລາຍງານວ່າ ມີຄົນຕ້ອງເຂົ້າຮັກສາທາງການແພດຫຼັງຈາກບໍລິໂພກແກ່ນກ້ວຍປ່າ. [8]
ສະໝຸນໄພ: ໃນຕຳລາຢາພື້ນເມືອງຂອງລາວ ສ່ວນຕ່າງໆຂອງກ້ວຍປ່າ ຖືກນຳໃຊ້ສຳລັບປະໂຫຍດທາງການແພດ ເຊັ່ນ ດອກ (ປີ) ໃຊ້ຮັກສາພະຍາດຫຼອດລົມອັກເສບ, ເບົາຫວານ, ໂຣກບິດ ແລະ ແຜ່ໃນກະເພາະ. ໃບໃຊ້ພອກບໍລິເວນທີ່ຖືກໄຟໄໝ້ ແລະ ພະຍາດທາງຜິວໜັງອື່ນໆ. ຮາກໃຊ້ຮັກສາອາການອາຫານບໍ່ຍ່ອຍ ແລະ ຢາງຂອງຕົ້ນໃຊ້ຮັກສາພະຍາດຕ່າງໆ ເຊັ່ນ ລິດສີດວງທະວານ, ແມງໄມ້ກັດ, ພະຍາດເຮື້ອນ, ພະຍາດຮິວທິເຣຍ, ລົມບ້າໝູ, ໄຂ້ເລືອດອອກ ແລະ ບັນຫາອາຫານບໍ່ຍ່ອຍ. [7]
ວັດທະນະທຳ: ໃບກ້ວຍມີປະໂຫຍດຫຼາຍໃນວັດທະນະຂອງລາວ ໂດຍສະເພາະໃຊ້ໃນພິທີບາສີສູ່ຂວັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ. [7]
ເຄື່ອງມື ແລະ ອຸປະກອນ: ໃບຕອງສາມາດນຳມາໃຊ້ເປັນຈານຮອງ, ຄຸມອາຫານ, ຫໍ່ອາຫານ, ເປັນທີ່ບັງແດດ, ໃຫ້ຮົ່ມ ແລະ ມຸງຫຼັງຄາ. [7]
ຂໍ້ຄວນລະວັງ: ການບໍລິໂພກກ້ວຍປ່າທີ່ມີແກ່ນອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ລຳໄສ້ອຸດຕັນໄດ້ ບາງກໍລະນີໃນລາວ. ຈາການສຶກສາລາຍງານວ່າ ມີຄົນຕ້ອງເຂົ້າຮັກສາທາງການແພດຫຼັງຈາກບໍລິໂພກແກ່ນກ້ວຍປ່າ. [8]
ການປູກ ການລ້ຽງ:
ປູກ ແລະ ທຳມະຊາດ
ລະດູການເກັບກູ້:
ມັງກອນ
ກຸມພາ
ມີນາ
ເມສາ
ພຶກສະພາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ກຸມພາ
ມີນາ
ເມສາ
ພຶກສະພາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ພະຈິກ
ທັນວາ
ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຕ່ອງໂສ້ມູນຄ່າ:
N/A
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ໄພຂົ່ມຂູ່: ການຖ່າງປ່າເຮັດໄຮ່, ການຕັດໄມ້ເພື່ອການປູກຝັງ ເປັນໄພຂົ່ມຂູ່ອັນຮ້າຍແຮງ. ການຫຼຸດລົງຂອງເນື້ອທີ່ປ່າໄມ້ 8% ຈາກປີ 1990-2015 ໃນທົ່ວອາຊີຕາເວັນອອກສຽງໃຕ້
ປະລິມານ: ບໍມີຂໍ້ມູນສຳລັບແນວໂນ້ມຂອງປະລິມານທີ່ມີໃນປະຈຸບັນ. ຢ່າງໃດກໍ່ຕາມ, ເນື່ອງຈາກການສູນເສຍຖິ່ນທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສໃນບາງຂອບເຂດ, ອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ປະລິມານມີແນວໂນ້ມຫຼຸດລົງ, ແນະນໍາໃຫ້ມີການຄົ້ນຄ້ວາເພີ່ມເຕີມ.
ປະລິມານ: ບໍມີຂໍ້ມູນສຳລັບແນວໂນ້ມຂອງປະລິມານທີ່ມີໃນປະຈຸບັນ. ຢ່າງໃດກໍ່ຕາມ, ເນື່ອງຈາກການສູນເສຍຖິ່ນທີ່ຢູ່ອາໄສໃນບາງຂອບເຂດ, ອາດເຮັດໃຫ້ປະລິມານມີແນວໂນ້ມຫຼຸດລົງ, ແນະນໍາໃຫ້ມີການຄົ້ນຄ້ວາເພີ່ມເຕີມ.
ໂພຊະນາການ
ຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ບັນຍາຍຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ກ້ວຍເປັນແຫຼ່ງໂພແທັກຊ້ຽມ, ໄຍອາຫານ ແລະ ວິຕາມິນທີ່ຈຳເປັນ. [7]
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | N/A | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | N/A | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | N/A | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
ເຄດິດຮູບພາບ:
Cavendish banana tree. [1] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 29 January 2024 by: mvanleuken. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/348668636. [Accessed: 26 September 2024]
Flower of the Cavendish Banana plant. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 3 February 2022 by: gkonings. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/106080593. [Accessed: 26 September 2024
Fruit of the Cavendish banana plant. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 22 January 2024 by: pickin. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/408218058. [Accessed: 26 September 2024]
Flower of the Cavendish Banana plant. [2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 3 February 2022 by: gkonings. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/106080593. [Accessed: 26 September 2024
Fruit of the Cavendish banana plant. [3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 22 January 2024 by: pickin. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/photos/408218058. [Accessed: 26 September 2024]
ອ້າງອິງ:
[1] World Flora Online, “Musa acuminata Colla,” [Online]. Available: https://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-0000473834. [Ac-cessed: 10 September 2024].
[2] Appendix 4: Wild Banana, “The Role of Wild Banana (Musa acumina-ta Colla) on Wildlife Diversity in Mixed Deciduous Forest, Kan-chanaburi Province, Western Thailand”, [Online]. Available: file:///C:/Users/duang/Downloads/Appendix4_Wildbanana_KU2010.pdf. [Accessed: 10 September 2024].
[3] Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), “Musa acuminata Col-la.” [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/2762680. [Accessed: 26 September 2024]
[4] A New Species of [Musa acuminata Colla],”Flora of China”, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 440, [Online]. Available: http://flora.huh.harvard.edu/china/novon/novo-17-04-440.pdf. [Accessed: 10 September2024].
[5] IUCN Red List, "Species Information," 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22486320/22486950. [Ac-cessed: Oct. 20, 2024].
[6] "Horticulture :: Fruits :: Banana," TNAU Agritech Portal, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/horticulture/horti_fruits_banana.html. [Ac-cessed: Jan. 6, 2025].
[7] "Taxon Page for Plant ID 975," University of Arizona Campus Arbore-tum, 2012. [Online]. Available: https://apps.cals.arizona.edu/arboretum/taxon.aspx?id=975&utm_source=chatgpt.com. [Accessed: Feb. 11, 2025].
[8] Gunther Slesak, Tropenklinik PaulLechler-Krankenhaus, Paul-Lechler-Strasse, " Bowel obstruction from wild bananas: a neglected health problem in Laos," unpublished. Available: file:///C:/Users/duang/Downloads/TD-10-0293.pdf. [Accessed: Jan. 6, 2025].
[2] Appendix 4: Wild Banana, “The Role of Wild Banana (Musa acumina-ta Colla) on Wildlife Diversity in Mixed Deciduous Forest, Kan-chanaburi Province, Western Thailand”, [Online]. Available: file:///C:/Users/duang/Downloads/Appendix4_Wildbanana_KU2010.pdf. [Accessed: 10 September 2024].
[3] Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF), “Musa acuminata Col-la.” [Online]. Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/2762680. [Accessed: 26 September 2024]
[4] A New Species of [Musa acuminata Colla],”Flora of China”, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 440, [Online]. Available: http://flora.huh.harvard.edu/china/novon/novo-17-04-440.pdf. [Accessed: 10 September2024].
[5] IUCN Red List, "Species Information," 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22486320/22486950. [Ac-cessed: Oct. 20, 2024].
[6] "Horticulture :: Fruits :: Banana," TNAU Agritech Portal, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/horticulture/horti_fruits_banana.html. [Ac-cessed: Jan. 6, 2025].
[7] "Taxon Page for Plant ID 975," University of Arizona Campus Arbore-tum, 2012. [Online]. Available: https://apps.cals.arizona.edu/arboretum/taxon.aspx?id=975&utm_source=chatgpt.com. [Accessed: Feb. 11, 2025].
[8] Gunther Slesak, Tropenklinik PaulLechler-Krankenhaus, Paul-Lechler-Strasse, " Bowel obstruction from wild bananas: a neglected health problem in Laos," unpublished. Available: file:///C:/Users/duang/Downloads/TD-10-0293.pdf. [Accessed: Jan. 6, 2025].
ຜູ້ສ້າງ Factsheet:
ຜູ້ກວດສອບ Factsheet:
Daniela Barcelo, Biologists



