ເລກລຳດັບທີ: 1631
ລະດັບການຮວບຮວມຂໍ້ມູນ: ຂໍ້ມູນພື້ນຖານ
ປັບປູງຄັ້ງລ່າສຸດ: 2025-08-18
ດອກໄໝ
Shoe Flower
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.
ພືດ
ໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ
ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
×
ຊື່ທ້ອງຖີ່ນ:
ດອກສະບາ ( Chinese Hibiscus, Hawaiian Hibiscus, Rose-Of-China, China Rose)
ຊື່ພ້ອງ
:
Hibiscus androphoro-petaloides Pancher ex Fosberg, 1997
Hibiscus androphoropetaloides Pancher
Hibiscus arnottii Griff.
Hibiscus arnottii Griff. ex Mast
Hibiscus carminata-perfecta W.Bull
Hibiscus colleri Anon.
Hibiscus denisonii Burb.
Hibiscus festalis Salisb.
Hibiscus festivalis Salisb.
Hibiscus fulgens W.Baxter
Hibiscus fulgidus W.Bull
Hibiscus javanicus Mill.
Hibiscus liliiflorus Griff.
Hibiscus liliiflorus Griff. ex Mast.
Hibiscus metallicus B.S.Williams
Hibiscus miniatus-semiplenus W.Bull
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. albo-pleno J.Harrison
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. albovariegatus Meehan
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. aurantia-pleno J.Harrison
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. carminata-perfecta Meehan
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. colleri Van Houtte
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. flavus G.Lodd.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. miniata-semiplenus Meehan
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. carnea-plenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. carneoplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. flavoplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. flore-pleno Seem.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. floreplena Seem.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. fulgidus W.Bull
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. genuinus Hochr.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. kermesinus W.Bull
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. lucien-lindenii N.E.Br.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. luteoplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. magnificus Van Geert
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. rosa-sinensis
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. rubroplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. variegatus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. vivicans W.Bull
Hibiscus androphoropetaloides Pancher
Hibiscus arnottii Griff.
Hibiscus arnottii Griff. ex Mast
Hibiscus carminata-perfecta W.Bull
Hibiscus colleri Anon.
Hibiscus denisonii Burb.
Hibiscus festalis Salisb.
Hibiscus festivalis Salisb.
Hibiscus fulgens W.Baxter
Hibiscus fulgidus W.Bull
Hibiscus javanicus Mill.
Hibiscus liliiflorus Griff.
Hibiscus liliiflorus Griff. ex Mast.
Hibiscus metallicus B.S.Williams
Hibiscus miniatus-semiplenus W.Bull
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. albo-pleno J.Harrison
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. albovariegatus Meehan
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. aurantia-pleno J.Harrison
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. carminata-perfecta Meehan
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. colleri Van Houtte
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. flavus G.Lodd.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis subsp. miniata-semiplenus Meehan
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. carnea-plenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. carneoplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. flavoplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. flore-pleno Seem.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. floreplena Seem.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. fulgidus W.Bull
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. genuinus Hochr.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. kermesinus W.Bull
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. lucien-lindenii N.E.Br.
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. luteoplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. magnificus Van Geert
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. rosa-sinensis
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. rubroplenus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. variegatus Sweet
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis var. vivicans W.Bull
ຊື່ສະກຸນ:
Malvaceae
ຊະນິດໃກ້ຄຽງ:
ຜັກສົ້ມພໍດີ / Roselle
ຕົ້ນຫາງຫົງ/ Hang hong
ຕົ້ນຫາງຫົງ/ Hang hong
ບັນຍາຍລັກສະນະທາງພືດສາດ:
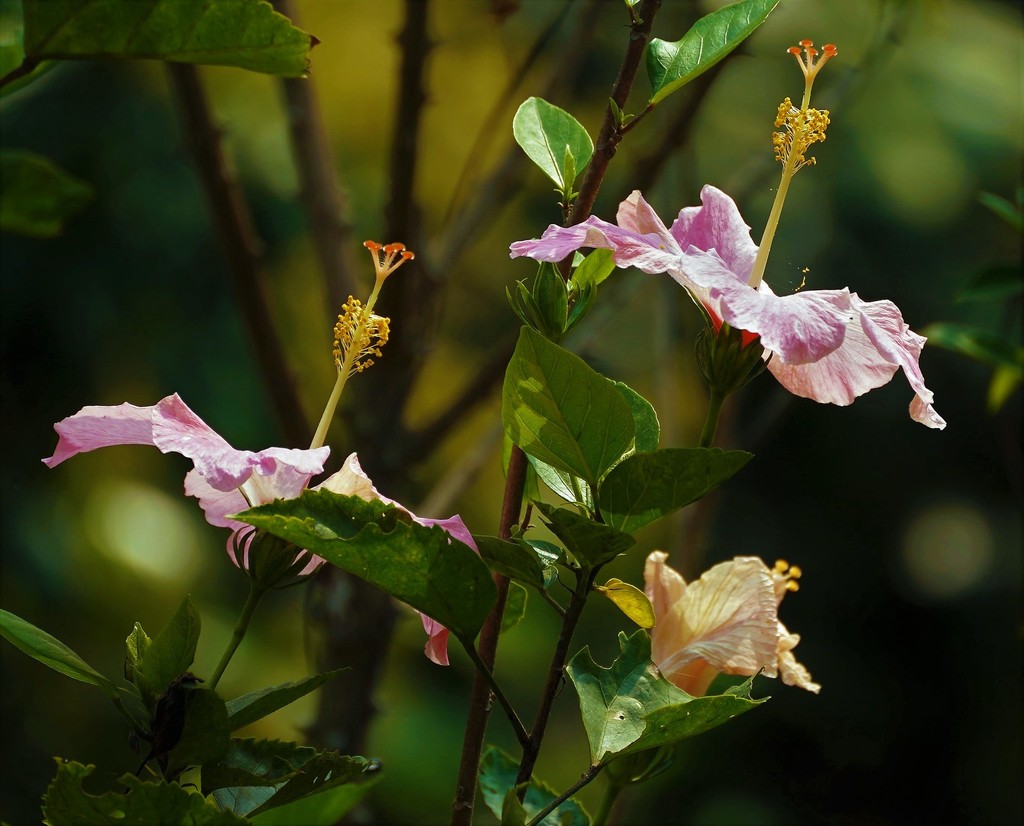
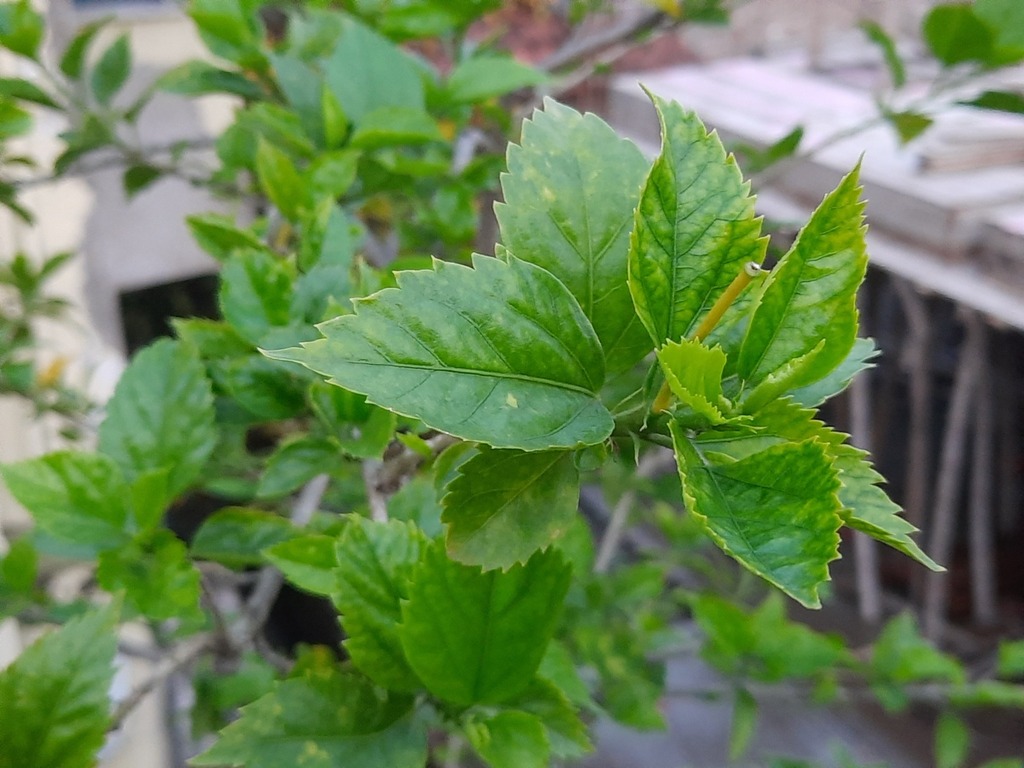
ດອກໄໝ ເປັນໄມ້ພຸ່ມຂຽວຕະຫຼອດປີ ຫຼື ເປັນໄມ້ຂະຫນາດນ້ອຍທີ່ເຕີບໃຫຍ່ລະຫວ່າງ 2.5 ຫາ 5 ແມັດ (8 ຫາ 16 ຟຸດ) ແລະ ກວ້າງ 1.5 ຫາ 3 ແມັດ (5 ຫາ 10 ຟຸດ). ມີຮາກຝອຍງ່າ ແລະ ສີຂຽວ, ຕັ້ງຊື່, ລຳເປັນຮູບທໍ່ກົມ. ໃບລຽບ, ກ້ານໃບ ຈັດລຽງສະລັບກັນ, ມີລັກສະນະເປັນຮູບໄຂ່, ຂອບໃບ ແລະ ພື້ນຜິວເຫຼື້ອມເປັນເງົາ. ລັກສະນະທີ່ໂດດເດັ່ນຂອງມັນມີຮູບແບບທີ່ຄ້າຍຄືຕາຫນ່າງ ແລະ ມີໃບປະດັບຂະຫນາດນ້ອຍຢູ່ດ້ານຂ້າງ.
ດອກໄໝ ເບີກບານໃນຊ່ວງລະຮ້ອນ ແລະ ດູໃບໄມ້ລົ່ນ, ອອກດອກດ່ຽວ, ເຊິ່ງປົກກະຕິແລ້ວມີສີແດງ ມີ 5 ກີບດອກ, ມີເສັ້ນຜ່າກາງປະມານ 10 ຊມ (4 ນິ້ວ). ດອກໄມ້ເຫຼົ່ານີ້ມີເກສອນຜູ້ສີແດງ ຢູ່ປາຍສີສົ້ມທີ່ໂດດເດັ່ນ. ນອກນັ້ນ, ຍັງມີສາຍພັນປະສົມທີ່ມີດອກຢູ່ໃນຫຼາຍສີຂອງພວກມັນ, ລວມທັງສີຂາວ, ສີບົວ, ສີສົ້ມ, ສີເຫຼືອງ, ສີຟ້າ, ແລະ ສີມ່ວງ ແລະ ບາງປະເພດມີກີບດອກຄູ່.
ແຕ່ລະດອກມີກາບດອກສີຂຽວຢູ່ໂຄນ ມີກາບດອກແຫຼມ. ເກສອນແມ່ຈະຍາວ, ມີລັກສະນະເປັນທໍ່ທີ່ມີສ່ວນປະກອບຂອງການສຶບພັນຂອງເກສອນແມ່, ໂດຍມີຍອດເກສອນແມ່ຢູ່ດ້ານເທິງເພື່ອເກັບລະອອງເກສອນ. ລະອອງເກສອນຈະເຄື່ອນທີ່ລົງຕາມເກສອນແມ່ໄປຫາຮວຍໄຂ່ຢູ່ໂຄນຂອງດອກ. ເກສອນເພດຜູ້, ເຊິ່ງເປັນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງຂອງເກສອນ ທີ່ປະກອບດ້ວຍເສັ້ນໄຍລົງຫາເກສອນແມ່ເພື່ອຜະລິດລະອອງເກສອນ. [1]
ດອກໄໝ ເບີກບານໃນຊ່ວງລະຮ້ອນ ແລະ ດູໃບໄມ້ລົ່ນ, ອອກດອກດ່ຽວ, ເຊິ່ງປົກກະຕິແລ້ວມີສີແດງ ມີ 5 ກີບດອກ, ມີເສັ້ນຜ່າກາງປະມານ 10 ຊມ (4 ນິ້ວ). ດອກໄມ້ເຫຼົ່ານີ້ມີເກສອນຜູ້ສີແດງ ຢູ່ປາຍສີສົ້ມທີ່ໂດດເດັ່ນ. ນອກນັ້ນ, ຍັງມີສາຍພັນປະສົມທີ່ມີດອກຢູ່ໃນຫຼາຍສີຂອງພວກມັນ, ລວມທັງສີຂາວ, ສີບົວ, ສີສົ້ມ, ສີເຫຼືອງ, ສີຟ້າ, ແລະ ສີມ່ວງ ແລະ ບາງປະເພດມີກີບດອກຄູ່.
ແຕ່ລະດອກມີກາບດອກສີຂຽວຢູ່ໂຄນ ມີກາບດອກແຫຼມ. ເກສອນແມ່ຈະຍາວ, ມີລັກສະນະເປັນທໍ່ທີ່ມີສ່ວນປະກອບຂອງການສຶບພັນຂອງເກສອນແມ່, ໂດຍມີຍອດເກສອນແມ່ຢູ່ດ້ານເທິງເພື່ອເກັບລະອອງເກສອນ. ລະອອງເກສອນຈະເຄື່ອນທີ່ລົງຕາມເກສອນແມ່ໄປຫາຮວຍໄຂ່ຢູ່ໂຄນຂອງດອກ. ເກສອນເພດຜູ້, ເຊິ່ງເປັນສ່ວນໜຶ່ງຂອງເກສອນ ທີ່ປະກອບດ້ວຍເສັ້ນໄຍລົງຫາເກສອນແມ່ເພື່ອຜະລິດລະອອງເກສອນ. [1]
ນິເວດວິທະຍາ
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນທົ່ວໂລກ:
Introduce to Andaman Is., Ascension, Assam, Azores, Bahamas, Bangladesh, Belize, Benin, Bermuda, Borneo, California, Cambodia, Cameroon, Caroline Is., Cayman Is., China South-Central, China Southeast, Comoros, Cook Is., Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, East Aegean Is., East Himalaya, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Fiji, Florida, Galápagos, Gambia, Gilbert Is., Guatemala, Gulf of Guinea Is., Hainan, Haiti, Hawaii, Honduras, India, Jamaica, Juan Fernández Is., Kenya, Laos, Leeward Is., Lesser Sunda Is., Line Is., Madeira, Marianas, Marquesas, Marshall Is., Mauritius, Mexico Central, Mexico Gulf, Mexico Northeast, Mexico Northwest, Mexico Southeast, Mexico Southwest, Nauru, Nepal, New Caledonia, Nicobar Is., Niue, Pakistan, Pitcairn Is., Puerto Rico, Rodrigues, Réunion, Samoa, Sardegna, Society Is., Solomon Is., Southwest Caribbean, Taiwan, Tanzania, Thailand, Tokelau-Manihiki, Tonga, Trinidad-Tobago, Tuamotu, Tubuai Is., Tunisia, Uganda, Vanuatu, Venezuela, Vietnam, Windward Is., Zaïre. [2]
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນໃນລາວ
:
ລຽບແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງພາກເໜືອ
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງຕອນລຸ່ມ
ເຂດພູສູງພາກເໜືອຂອງລາວ
ທົ່ງພຽງວຽງຈັນ
ເຂດສາຍພູຫຼວງຕອນລຸ່ມ
ເຂດພູສູງພາກເໜືອຂອງລາວ
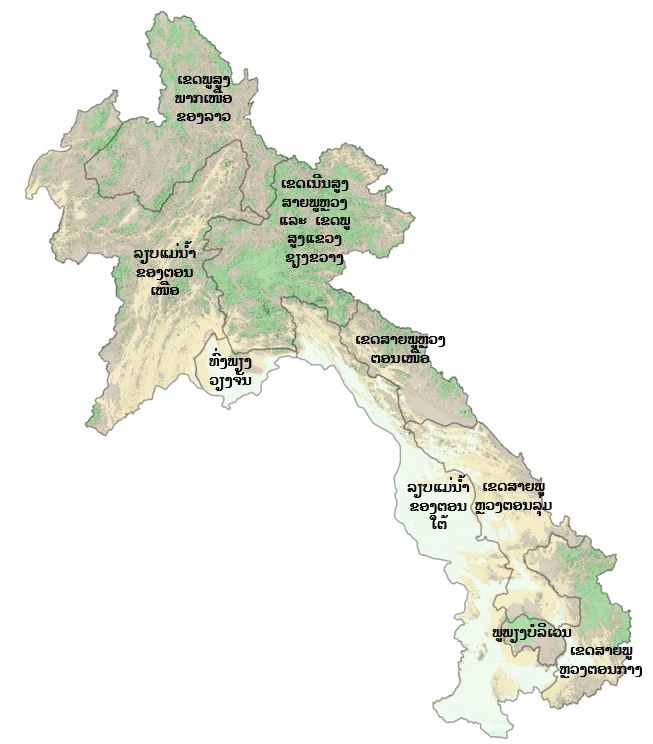
ເຂດກະຈາຍພັນຕາມພູມສັນຖານ
:
ສວນຄົວ
ສວນສາທາລະນະ ແລະ ພື້ນທີ່ສາທາລະນະ
ສວນສາທາລະນະ ແລະ ພື້ນທີ່ສາທາລະນະ

ສະເພາະຖິ່ນໃນລາວ:
ຕ່າງຖິ່ນ
ຮຸກຮານ
:
ບໍ່ຮຸກຮານ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນູຮັກ IUCN
:
ບໍ່ມີຄວາມສ່ຽງ
ສະຖານະພາບການອະນຸຮັກແຫ່ງຊາດລາວ
:
ບໍ່ຖືກລະບຸໃນບັນຊີປະເພດໃດ
ການນຳໃຊ້
ປະເພດການນຳໃຊ້:
ພືດເປັນຢາ
ພືດປະດັບ
ເຄື່ອງດື່ມ
ພືດປະດັບ
ເຄື່ອງດື່ມ
ບັນຍາຍການນຳໃຊ້:
ເຄື່ອງດື່ມ: ດອກໄໝ ທີ່ແຫ້ງມັກຈະຖືກນຳເອົາໄປຕົ້ມເປັນຊາ, ເຊິ່ງມີລົດຊາດສົ້ມ ແລະສີສັນສົດໃສ [1]
ຢາ: ຮາກຂອງດອກໄໝ ເປັນຢາປົວບາດແຜ, ປິ່ນປົວອາການອັກເສບ, ຂັບລົມໃນລຳໄສ້, ຫຼຸດອາການໄຂ້ ແລະ ສົ່ງເສີມການປະຈໍາເດືອນ. [3]. ບົດລາຍງານສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ ມີສັບພະຄຸນທາງການແພດຕ່າງໆຫຼາຍຢ່າງ, ດອກໄມ ມັນມີສານຕ້ານການອັກເສບ, ແກ້ອາການໄຂ້, ແກ້ປວດ, ແລະ ຕ້ານພະຍາດຫອບຫືດ. ການສຶກສາສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າດອກໄມ້ມີຄຸນນະສົມບັດ ສານຕ້ານອະນຸມູນອິດສະລະ, ຕ້ານເຊື້ອລາ ແລະ ຕ້ານເຊື້ອແບັກທີເຣັຍ. ດອກໄໝເປັນພືດມີຄຸນສົມບັດຕ້ານເນື້ອງອກ, ຕ້ານເຊື້ອອະສຸຈິ (ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການຜະລິດເຊື້ອອະສຸຈິ), ຕ້ານແອນໂດຣເຈນ (ຫຼຸດຮໍໂມນເພດຊາຍ), ແລະ ຕ້ານການຊັກ (ປ້ອງກັນການຊັກ). ມີການລາຍງານກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ດອກໄມ້ໃນການປິ່ນປົວສະພາບການຫົວໃຈ. ການສຶກສາໃນເຂດຊົນນະບົດທີ່ເປັນໂລກເບົາຫວານສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ ດອກໄໝ ມີຄຸນສົມບັດຕ້ານພະຍາດເບົາຫວານ (Ah-san MQ, et al., 2021). [4],[5]
ຢາ: ຮາກຂອງດອກໄໝ ເປັນຢາປົວບາດແຜ, ປິ່ນປົວອາການອັກເສບ, ຂັບລົມໃນລຳໄສ້, ຫຼຸດອາການໄຂ້ ແລະ ສົ່ງເສີມການປະຈໍາເດືອນ. [3]. ບົດລາຍງານສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ ມີສັບພະຄຸນທາງການແພດຕ່າງໆຫຼາຍຢ່າງ, ດອກໄມ ມັນມີສານຕ້ານການອັກເສບ, ແກ້ອາການໄຂ້, ແກ້ປວດ, ແລະ ຕ້ານພະຍາດຫອບຫືດ. ການສຶກສາສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າດອກໄມ້ມີຄຸນນະສົມບັດ ສານຕ້ານອະນຸມູນອິດສະລະ, ຕ້ານເຊື້ອລາ ແລະ ຕ້ານເຊື້ອແບັກທີເຣັຍ. ດອກໄໝເປັນພືດມີຄຸນສົມບັດຕ້ານເນື້ອງອກ, ຕ້ານເຊື້ອອະສຸຈິ (ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການຜະລິດເຊື້ອອະສຸຈິ), ຕ້ານແອນໂດຣເຈນ (ຫຼຸດຮໍໂມນເພດຊາຍ), ແລະ ຕ້ານການຊັກ (ປ້ອງກັນການຊັກ). ມີການລາຍງານກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ດອກໄມ້ໃນການປິ່ນປົວສະພາບການຫົວໃຈ. ການສຶກສາໃນເຂດຊົນນະບົດທີ່ເປັນໂລກເບົາຫວານສະແດງໃຫ້ເຫັນວ່າ ດອກໄໝ ມີຄຸນສົມບັດຕ້ານພະຍາດເບົາຫວານ (Ah-san MQ, et al., 2021). [4],[5]
ການປູກ ການລ້ຽງ:
ຊະນິດປູກ
ລະດູການເກັບກູ້:
ພຶກສະພາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ມິຖຸນາ
ກໍລະກົດ
ສິງຫາ
ກັນຍາ
ຕຸລາ
ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຕ່ອງໂສ້ມູນຄ່າ:
N/A
ການຄຸ້ມຄອງຈັດການ
ສະພາບໂດຍລວມ:
ແສງ: ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ, ພືດຊະນິດນີ້ໄດ້ຮັບແສງແດດຫຼາຍເທົ່າໃດຍິ່ງເປັນການດີ. ດອກໄໝ ມັກແສງແດດຫຼາຍແຕ່ກໍທົນທານຕໍ່ຮົ່ມແສງສະຫວ່າງໄດ້. ເມື່ອຕົ້ນໄມ້ໄດ້ຮັບຄວາມຮົ່ມຫຼາຍເທົ່າໃດ, ດອກໄໝກໍຈະຜະລິດໄດ້ໜ້ອຍລົງ. ຖ້າຫາກປູກໃນຊ່ວງລະດູໜາວ, ພະຍາຍາມປູກຕັ້ງໄວ້ຢູ່ໃກ້ກັບປ່ອງຢ້ຽມ ຫັນໜ້າທາງໃຕ້ ຫຼື ຕາເວັນຕົກກໍໄດ້.[7]
ສະພາບອາກາດ: ດອກໄໝ ເຕີບໃຫຍ່ຢູ່ໃນພື້ນທີ່ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ ຍົກເວັ້ນພື້ນທີ່ມີສະພາບອາກາດທີ່ໜາວຫຼາຍເກີນໄປ, ຍ້ອນວ່າພວກມັນບໍ່ທົນຕໍ່ສະພາບອາກາດໜາວ ໃນເຂດໃດທີ່ມີລະດູຮ້ອນຫຼາຍ ແຕ່ລະດູຫນາວເຢັນຫຼາຍ, ຄວນປູກປູກ ດອກໄໝ ໃນຕູ້ຂະຫນາດໃຫຍ່ ຫຼື ຍ້າຍພວກມັນເຂົ້າໄປໃນບ່ອນທີ່ມີແດດບໍ່ແຮງ ແລະ ບໍ່ມີອາກາດໜາວຫຼາຍໃນລະດູໜາວ. [6]
ການກຽມພື້ນທີ່:
ພືດທຸກຊະນິດຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕໄດ້ດີແມ່ນໃນດິນທີ່ອຸດົມສົມບູນ, ລະບາຍນ້ຳໄດ້ດີ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ຄວນເພີ່ມສານອິນຊີ ຫຼື ເພີ່ມຝຸ່ນບົ່ມ ຂອງ Seasol Super ເພື່ອກະກຽມການປູກ.[6]
ການເບິ່ງແຍງ ແລະ ບຳລຸງຮັກສາ:
ການຫົດນໍ້າ: ດອກໄໝ ບໍ່ມັກດິນແຫ້ງ, ມັກດິນທີ່ມີຄວາມຊຸ່ມຊື່ນ. ຫຼັງຈາກປູກແລ້ວ, ສິ່ງສຳຄັນຕ້ອງໄດ້ໃຫ້ນ້ຳເສີມໃນປີທໍາອິດຕາມຄວາມຕ້ອງການຈົນກ່ວາພືດຈະເຕີບໂຕໄດ້ດີ. ເມື່ອໃນເວລາປູກ, ເລືອກຖັງທີ່ມີຂະຫນາດທີ່ເໝາະກັບດອກໄມ້. ຖັງໃຫຍ່ ຫຼື ນ້ອຍເກີນໄປຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ໃນການຫົດນ້ຳຍາກ. ພະຍາຍາມກວດເບິ່ງພືດຂອງຕົນເອງເປັນປະຈໍາວັນ. ເມື່ອເວລາຜ່ານໄປ, ເຈົ້າຈະໄດ້ຮັບຮູ້ວ່າພວກມັນ ແລະ ຄວາມຕ້ອງການນ້ຳໄດ້ປັບປ່ຽນຕາມປະລິມານແສງແດດ ຫຼື ຝົນຄາດວ່າຈະຕົກຫຼາຍເທົ່າໃດ.[7]
ການຕັດອອກ: ດອກໄໝ ຕ້ອງການຕັດກິ່ງງ່າພຽງເລັກນ້ອຍໃນລະຫວ່າງລະດູການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ, ເວັ້ນເສຍແຕ່ວ່າພື້ນທີ່ມີບັນຫາ. ຕັດຕັດກິ່ງອອກປະມານເຄິ່ງໜຶ່ງໃນຕົ້ນລະດູໃບໄມ້ປົ່ງ ເພື່ອຮັກສາຮູບຮ່າງທີ່ສວຍງາມ ແລະສົ່ງເສີມການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕຂອງມັນ. ອາດຈະຈຳເປັນທີ່ຈະຕ້ອງໄດ້ຕັດກິ່ງເລື້ອຍໆໃນຕະຫຼອດປີ ສໍາລັບດອກໄໝທີ່ປູກຢູ່ໃນເຮືອນ, ດອກໄໝຈະອອກດອກຢູ່ໃນດອກໃຫມ່, ສະນັ້ນການຕັດກິ່ງອອກໃນເວລາໃດໜຶ່ງໃນລະຫວ່າງຂອງປີ ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ການອອກດອກບໍ່ສົມບູນ ຫຼື ອາດຈະບໍ່ມີດອກກໍເປັນໄດ້, ແຕ່ມັນຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ພຽງການອອກດອກຊ້າລົງ.[7]
ການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ: ດອກໄໝ ເປັນດອກທີ່ບໍ່ຕ້ອງເບີ່ງແຍງຫຼາຍ, ແຕ່ກໍຕ້ອງໄດ້ໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ ໂດຍສະເພາະຖ້າປູກໃນຖັງບັນຈຸ. ຝຸ່ນທີ່ຍ້ອຍສະລາຍຊ້າແມ່ນວິທີທີ່ງ່າຍທີ່ຈະໃຫ້ໃຫ້ພືດຕະຫຼອດລະດູການມີການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ. ຝຸ່ນທີ່ເປັນຂອງແຫຼວ ຫຼື ນ້ຳ ທີ່ມີຟອດສູງທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນຊ່ວງລະຮ້ອນສາມາດຊ່ວຍໃຫ້ພືດແຂງແຮງ ແລະ ອອກດອກຫຼາຍຂຶ້ນ. ທາດເຫຼັກແມ່ນສານອາຫານຊະນິດໜຶ່ງທີ່ອາດຈະຕ້ອງໄດ້ເສີມເປັນໄລຍະໆ ໂດຍຕ້ອງໃສ່ຝຸ່ນເປັນປົກກະຕິໃນຊ່ວງລະດູໃບໄມ້ປົ່ງຈົນເຖິງລະດູໃບໄມ້ລົນ, ແຕ່ສາມາດໃສ່ຝຸ່ນໃນຊ່ວງລະດູໜາວ. ເຮົາສາມາດຢຸດການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນໄດ້ເມື່ອວິດຍາມລະດູໜາວ, ເວັ້ນເສຍແຕ່ພືດອາດຈະຂາດສານອາຫານໄດ້.[7]
ການປົກປ້ອງ ແລະ ການກຳຈັດສັດຕູພືດ:
ສັດຕູພືດ: ດ້ວຍການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຂອງແມງໄມ້ແລະນົກທີ່ມີປະໂຫຍດ, ພືດທີ່ຢູ່ກາງແຈ້ງທີ່ມີຄວາມແຂງແຮງດີມັນສາມາດຕໍ່ສູ້ກັບສັດຕູພືດຫຼາຍຊະນິດສ່ວນໃຫ່ຍ, ບໍ່ວ່າເປັນຕົວເພີ້ຍ, ເພີ້ຍໄຟ ແລະ ແມງມູມແດງ ທີ່ເປັນຕົວຕົ້ນຕໍທີ່ຈະຊອກຫາທຳລາຍ, ຈະມີມີ່ຂາວ, ແມງໄມ້ ຈະມີປະລິມານທີ່ໜ້ອຍກວ່າສຳລັບໃນເຂດມີຮົ່ມ. ເຮົາຕ້ອງພະຍາຍາມກວດສອບຕະຫຼອດເວລາໃນການກຳຈັດສັດຕູພືດ ແລະ ເຮົາສາມາດໃຊ້ນ້ຳມັນພືດ ຫຼື ສະບູຢາຂ້າແມງໄມ້ເພື່ອກຳຈັດໃນການແຜ່ລະບາດສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ ຫຼື ເຮົາສາມາດແຕ່ຕັດພຽງສ່ວນທີ່ຕິດເຊື້ອອອກກໍ່ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນດີເຊັ່ນກັນ. [7]
ພະຍາດ: ດອກໄໝ ແມ່ນເປັນທີ່ຮູ້ຈັກວ່າມີຄວາມອ່ອນໄຫວຕໍ່ກັບບັນຫາຂອງພະຍາດບາງຊະນິດ ເຊັ່ນ: ໂລກນ້ຳຄ່າງ ຫຼື ໂບຣິທິສ. ເຮົາຈະມັກພົບເຫັນຈຸດດ່າງດຳຕາມໃບມັນ ແລະ ພົບເຫັນຫຼາຍບ່ອນ, ແຕ່ຍາກທີ່ຈະລະບຸໄດ້ຖ້າເຮົາບໍ່ໄດ້ຮັບການທົດສອບຢ່າງເໝາະສົມ. ສໍາລັບການກໍານົດ ແລະ ຄໍາແນະນໍາການປິ່ນປົວທີ່ເຫມາະສົມ, ແມ່ນຕິດຕໍ່ອົງການຂະຫຍາຍພັນພືດໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນຂອງທ່ານ.[7]
ແສງ: ໂດຍທົ່ວໄປ, ພືດຊະນິດນີ້ໄດ້ຮັບແສງແດດຫຼາຍເທົ່າໃດຍິ່ງເປັນການດີ. ດອກໄໝ ມັກແສງແດດຫຼາຍແຕ່ກໍທົນທານຕໍ່ຮົ່ມແສງສະຫວ່າງໄດ້. ເມື່ອຕົ້ນໄມ້ໄດ້ຮັບຄວາມຮົ່ມຫຼາຍເທົ່າໃດ, ດອກໄໝກໍຈະຜະລິດໄດ້ໜ້ອຍລົງ. ຖ້າຫາກປູກໃນຊ່ວງລະດູໜາວ, ພະຍາຍາມປູກຕັ້ງໄວ້ຢູ່ໃກ້ກັບປ່ອງຢ້ຽມ ຫັນໜ້າທາງໃຕ້ ຫຼື ຕາເວັນຕົກກໍໄດ້.[7]
ສະພາບອາກາດ: ດອກໄໝ ເຕີບໃຫຍ່ຢູ່ໃນພື້ນທີ່ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ ຍົກເວັ້ນພື້ນທີ່ມີສະພາບອາກາດທີ່ໜາວຫຼາຍເກີນໄປ, ຍ້ອນວ່າພວກມັນບໍ່ທົນຕໍ່ສະພາບອາກາດໜາວ ໃນເຂດໃດທີ່ມີລະດູຮ້ອນຫຼາຍ ແຕ່ລະດູຫນາວເຢັນຫຼາຍ, ຄວນປູກປູກ ດອກໄໝ ໃນຕູ້ຂະຫນາດໃຫຍ່ ຫຼື ຍ້າຍພວກມັນເຂົ້າໄປໃນບ່ອນທີ່ມີແດດບໍ່ແຮງ ແລະ ບໍ່ມີອາກາດໜາວຫຼາຍໃນລະດູໜາວ. [6]
ການກຽມພື້ນທີ່:
ພືດທຸກຊະນິດຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕໄດ້ດີແມ່ນໃນດິນທີ່ອຸດົມສົມບູນ, ລະບາຍນ້ຳໄດ້ດີ. ດັ່ງນັ້ນ, ຄວນເພີ່ມສານອິນຊີ ຫຼື ເພີ່ມຝຸ່ນບົ່ມ ຂອງ Seasol Super ເພື່ອກະກຽມການປູກ.[6]
ການເບິ່ງແຍງ ແລະ ບຳລຸງຮັກສາ:
ການຫົດນໍ້າ: ດອກໄໝ ບໍ່ມັກດິນແຫ້ງ, ມັກດິນທີ່ມີຄວາມຊຸ່ມຊື່ນ. ຫຼັງຈາກປູກແລ້ວ, ສິ່ງສຳຄັນຕ້ອງໄດ້ໃຫ້ນ້ຳເສີມໃນປີທໍາອິດຕາມຄວາມຕ້ອງການຈົນກ່ວາພືດຈະເຕີບໂຕໄດ້ດີ. ເມື່ອໃນເວລາປູກ, ເລືອກຖັງທີ່ມີຂະຫນາດທີ່ເໝາະກັບດອກໄມ້. ຖັງໃຫຍ່ ຫຼື ນ້ອຍເກີນໄປຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ໃນການຫົດນ້ຳຍາກ. ພະຍາຍາມກວດເບິ່ງພືດຂອງຕົນເອງເປັນປະຈໍາວັນ. ເມື່ອເວລາຜ່ານໄປ, ເຈົ້າຈະໄດ້ຮັບຮູ້ວ່າພວກມັນ ແລະ ຄວາມຕ້ອງການນ້ຳໄດ້ປັບປ່ຽນຕາມປະລິມານແສງແດດ ຫຼື ຝົນຄາດວ່າຈະຕົກຫຼາຍເທົ່າໃດ.[7]
ການຕັດອອກ: ດອກໄໝ ຕ້ອງການຕັດກິ່ງງ່າພຽງເລັກນ້ອຍໃນລະຫວ່າງລະດູການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ, ເວັ້ນເສຍແຕ່ວ່າພື້ນທີ່ມີບັນຫາ. ຕັດຕັດກິ່ງອອກປະມານເຄິ່ງໜຶ່ງໃນຕົ້ນລະດູໃບໄມ້ປົ່ງ ເພື່ອຮັກສາຮູບຮ່າງທີ່ສວຍງາມ ແລະສົ່ງເສີມການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕຂອງມັນ. ອາດຈະຈຳເປັນທີ່ຈະຕ້ອງໄດ້ຕັດກິ່ງເລື້ອຍໆໃນຕະຫຼອດປີ ສໍາລັບດອກໄໝທີ່ປູກຢູ່ໃນເຮືອນ, ດອກໄໝຈະອອກດອກຢູ່ໃນດອກໃຫມ່, ສະນັ້ນການຕັດກິ່ງອອກໃນເວລາໃດໜຶ່ງໃນລະຫວ່າງຂອງປີ ຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ການອອກດອກບໍ່ສົມບູນ ຫຼື ອາດຈະບໍ່ມີດອກກໍເປັນໄດ້, ແຕ່ມັນຈະເຮັດໃຫ້ພຽງການອອກດອກຊ້າລົງ.[7]
ການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ: ດອກໄໝ ເປັນດອກທີ່ບໍ່ຕ້ອງເບີ່ງແຍງຫຼາຍ, ແຕ່ກໍຕ້ອງໄດ້ໃສ່ຝຸ່ນ ໂດຍສະເພາະຖ້າປູກໃນຖັງບັນຈຸ. ຝຸ່ນທີ່ຍ້ອຍສະລາຍຊ້າແມ່ນວິທີທີ່ງ່າຍທີ່ຈະໃຫ້ໃຫ້ພືດຕະຫຼອດລະດູການມີການຈະເລີນເຕີບໂຕ. ຝຸ່ນທີ່ເປັນຂອງແຫຼວ ຫຼື ນ້ຳ ທີ່ມີຟອດສູງທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນຊ່ວງລະຮ້ອນສາມາດຊ່ວຍໃຫ້ພືດແຂງແຮງ ແລະ ອອກດອກຫຼາຍຂຶ້ນ. ທາດເຫຼັກແມ່ນສານອາຫານຊະນິດໜຶ່ງທີ່ອາດຈະຕ້ອງໄດ້ເສີມເປັນໄລຍະໆ ໂດຍຕ້ອງໃສ່ຝຸ່ນເປັນປົກກະຕິໃນຊ່ວງລະດູໃບໄມ້ປົ່ງຈົນເຖິງລະດູໃບໄມ້ລົນ, ແຕ່ສາມາດໃສ່ຝຸ່ນໃນຊ່ວງລະດູໜາວ. ເຮົາສາມາດຢຸດການໃສ່ຝຸ່ນໄດ້ເມື່ອວິດຍາມລະດູໜາວ, ເວັ້ນເສຍແຕ່ພືດອາດຈະຂາດສານອາຫານໄດ້.[7]
ການປົກປ້ອງ ແລະ ການກຳຈັດສັດຕູພືດ:
ສັດຕູພືດ: ດ້ວຍການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຂອງແມງໄມ້ແລະນົກທີ່ມີປະໂຫຍດ, ພືດທີ່ຢູ່ກາງແຈ້ງທີ່ມີຄວາມແຂງແຮງດີມັນສາມາດຕໍ່ສູ້ກັບສັດຕູພືດຫຼາຍຊະນິດສ່ວນໃຫ່ຍ, ບໍ່ວ່າເປັນຕົວເພີ້ຍ, ເພີ້ຍໄຟ ແລະ ແມງມູມແດງ ທີ່ເປັນຕົວຕົ້ນຕໍທີ່ຈະຊອກຫາທຳລາຍ, ຈະມີມີ່ຂາວ, ແມງໄມ້ ຈະມີປະລິມານທີ່ໜ້ອຍກວ່າສຳລັບໃນເຂດມີຮົ່ມ. ເຮົາຕ້ອງພະຍາຍາມກວດສອບຕະຫຼອດເວລາໃນການກຳຈັດສັດຕູພືດ ແລະ ເຮົາສາມາດໃຊ້ນ້ຳມັນພືດ ຫຼື ສະບູຢາຂ້າແມງໄມ້ເພື່ອກຳຈັດໃນການແຜ່ລະບາດສ່ວນໃຫຍ່ ຫຼື ເຮົາສາມາດແຕ່ຕັດພຽງສ່ວນທີ່ຕິດເຊື້ອອອກກໍ່ໄດ້ຮັບຜົນດີເຊັ່ນກັນ. [7]
ພະຍາດ: ດອກໄໝ ແມ່ນເປັນທີ່ຮູ້ຈັກວ່າມີຄວາມອ່ອນໄຫວຕໍ່ກັບບັນຫາຂອງພະຍາດບາງຊະນິດ ເຊັ່ນ: ໂລກນ້ຳຄ່າງ ຫຼື ໂບຣິທິສ. ເຮົາຈະມັກພົບເຫັນຈຸດດ່າງດຳຕາມໃບມັນ ແລະ ພົບເຫັນຫຼາຍບ່ອນ, ແຕ່ຍາກທີ່ຈະລະບຸໄດ້ຖ້າເຮົາບໍ່ໄດ້ຮັບການທົດສອບຢ່າງເໝາະສົມ. ສໍາລັບການກໍານົດ ແລະ ຄໍາແນະນໍາການປິ່ນປົວທີ່ເຫມາະສົມ, ແມ່ນຕິດຕໍ່ອົງການຂະຫຍາຍພັນພືດໃນທ້ອງຖິ່ນຂອງທ່ານ.[7]
ໂພຊະນາການ
ຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
ບັນຍາຍຄຸນຄ່າທາງໂພຊະນາການ:
N/A
| ສານອາຫານ | /100g | ໝາຍເຫດ |
|---|---|---|
| ໂປຣຕີນ | 1.54 | N/A |
| ຄາໂບໄຮເດຣດ | 13.71 | N/A |
| ໄຂມັນ | 0.35 | N/A |
| ວິຕາມິນ | N/A | N/A |
| ແຮ່ທາດ | N/A | N/A |
| ເສັ້ນໄຍ | N/A | N/A |
ອ້າງອິງ
ເຄດິດຮູບພາບ:
[1] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 15 July 2024 by: rexia. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/229501413. [Accessed: 16 October 2024]
[2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 29 July 2024 by: sujata92459. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/232469381. [Accessed: Accessed: 16 October 2024]
[3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 16 October 2024 by: brayanem-manuelcanoespericueta. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/247552869. [Accessed: Accessed: 16 October 2024]
[2] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 29 July 2024 by: sujata92459. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/232469381. [Accessed: Accessed: 16 October 2024]
[3] iNaturalist [Online]. Uploaded on 16 October 2024 by: brayanem-manuelcanoespericueta. Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/observations/247552869. [Accessed: Accessed: 16 October 2024]
ອ້າງອິງ:
[1] iNaturalist [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/62876-Hibiscus-rosa-sinensis. [Accessed: 16 October 2024].
[2] Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/3152559. [Accessed: 16 October 2024].
[3] QSBG. [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: http://www.qsbg.org/Database/plantdb/mdp/medicinal-specimen.asp?id=576. [Accessed: 16 October 2024].
[4] A. A. awfeeq, T. A. awfeeq, I. S. baas & S. H. Salah. (2024, October). “Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activity of HibiscusRosa-SinensisPlant”. Jurnal Ilmu Keperawatan dan Kebidanan [Online]. Vol.2, No.4. Available: https://journal.arikesi.or.id/index.php/Protein/article/view/668/904.
[5] A. Missoum.," An update review on Hibiscus rosa sinensis phyto-chemistry and medicinal uses," Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine Vol 4 (3) Pp: 135-146, October 2018.
[6] Seasol a better way to grow. [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: https://www.seasol.com.au/roses-flowers/hibiscus-2/. [Accessed: 17 October 2024].
[7] Smithsonian Gardens. [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: https://gardens.si.edu/learn/educational-resources/plant-care-sheets/care-of-hibiscus-rosa-sinensis/. [Accessed: 17 October 2024].
[8] A. Bahuguna, K.G. Vijayalaxmi & V.C. Suvarna." Formulation and Evaluation of Fresh Red Hawaiian Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis) Incorporated Valued Added Products," International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences Vol 7(8) Pp: 4282-4290, July 2018.
[2] Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: https://www.gbif.org/species/3152559. [Accessed: 16 October 2024].
[3] QSBG. [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: http://www.qsbg.org/Database/plantdb/mdp/medicinal-specimen.asp?id=576. [Accessed: 16 October 2024].
[4] A. A. awfeeq, T. A. awfeeq, I. S. baas & S. H. Salah. (2024, October). “Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activity of HibiscusRosa-SinensisPlant”. Jurnal Ilmu Keperawatan dan Kebidanan [Online]. Vol.2, No.4. Available: https://journal.arikesi.or.id/index.php/Protein/article/view/668/904.
[5] A. Missoum.," An update review on Hibiscus rosa sinensis phyto-chemistry and medicinal uses," Journal of Ayurvedic and Herbal Medicine Vol 4 (3) Pp: 135-146, October 2018.
[6] Seasol a better way to grow. [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: https://www.seasol.com.au/roses-flowers/hibiscus-2/. [Accessed: 17 October 2024].
[7] Smithsonian Gardens. [Online] “Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.” .Available: https://gardens.si.edu/learn/educational-resources/plant-care-sheets/care-of-hibiscus-rosa-sinensis/. [Accessed: 17 October 2024].
[8] A. Bahuguna, K.G. Vijayalaxmi & V.C. Suvarna." Formulation and Evaluation of Fresh Red Hawaiian Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis) Incorporated Valued Added Products," International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences Vol 7(8) Pp: 4282-4290, July 2018.
ຜູ້ສ້າງ Factsheet:
ຜູ້ກວດສອບ Factsheet:
,


